A doença de Wilson é incomum e o diagnóstico muitas vezes passa despercebido. Isso se deve ao seu envolvimento sistêmico e quadros clínicos variados com características sobrepostas. O atraso médio desde o início dos sintomas até o diagnóstico é de 2 anos.[20]Shribman S, Warner TT, Dooley JS. Clinical presentations of Wilson disease. Ann Transl Med. 2019 Apr;7(suppl 2):S60.
https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/25358/23684
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31179297?tool=bestpractice.com
A doença de Wilson pode se manifestar como doença hepática (com icterícia e possivelmente ascite e edema) ou como um distúrbio neurológico do movimento (com tremor, distonia, rigidez), ou pode ser diagnosticada no estágio assintomático.[21]Brewer GJ. Recognition, diagnosis, and management of Wilson's disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 2000 Jan;223(1):39-46.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10632959?tool=bestpractice.com
[22]Starosta-Rubinstein S, Young AB, Kluin K, et al. Clinical assessment of 31 patients with Wilson's disease: correlations with structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol. 1987 Apr;44(4):365-70.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3827691?tool=bestpractice.com
[23]Brewer GJ. Novel therapeutic approaches to the treatment of Wilson's disease. Exp Opin Pharmacother. 2006 Feb;7(3):317-24.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16448326?tool=bestpractice.com
O diagnóstico precoce é importante porque a terapia é eficaz para alcançar o equilíbrio do cobre. Os sintomas da doença podem ser prevenidos ou revertidos se tratados precocemente e, portanto, os familiares dos pacientes diagnosticados devem ser rastreados.
Manifestações hepáticas
Um paciente com doença hepática secundária à doença de Wilson pode ter história de hepatite inexplicada ou elevações de aminotransferase, trombocitopenia, pancitopenia, hiperbilirrubinemia indireta ou hemólise intravascular com teste de Coombs negativo.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[20]Shribman S, Warner TT, Dooley JS. Clinical presentations of Wilson disease. Ann Transl Med. 2019 Apr;7(suppl 2):S60.
https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/25358/23684
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31179297?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
As apresentações alternativas em adultos e crianças incluem hepatite aguda, fígado gorduroso, insuficiência hepática aguda ou cirrose (compensada ou descompensada).[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
Até 20% das pessoas com doença de Wilson apresentam insuficiência hepática aguda, com sintomas de icterícia, encefalopatia hepática, coagulopatia, ascite e insuficiência renal.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
As crianças geralmente apresentam após os 5 anos de idade e podem ser assintomáticas, com hepatomegalia ou transaminases séricas anormais detectadas incidentalmente.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
Os pacientes podem inicialmente receber um diagnóstico de hepatite viral aguda, doença hepática gordurosa associada à disfunção metabólica (anteriormente conhecida como doença hepática gordurosa não alcoólica) ou hepatite autoimune.[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
O exame físico pode revelar hepatomegalia ou esplenomegalia. Pode haver sinais de doença hepática crônica, como aranhas vasculares, ginecomastia, ascite, edema periférico, hematomas fáceis, icterícia ou encefalopatia. O paciente pode ter anéis de Kayser-Fleischer (KF) ou catarata em girassol (depósitos de cobre no cristalino).[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Todos os pacientes com anormalidades hepáticas de causa incerta devem ser examinados para doença de Wilson.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Manifestações neurológicas
Um paciente com doença neurológica pode ter uma história de sintomas de distúrbio do movimento, incluindo tremor, falta de coordenação, caligrafia ruim, disartria, rigidez muscular, rigidez, anormalidade postural, anormalidade da marcha, coreia/atetose, convulsão ou sialorreia.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
[26]Taly AB, Meenakshi-Sundaram S, Sinha S, et al. Wilson disease: description of 282 patients evaluated over 3 decades. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007 Mar;86(2):112-21.
https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/Fulltext/2007/03000/Wilson_Disease__Description_of_282_Patients.6.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17435591?tool=bestpractice.com
Os sintomas neuropsiquiátricos geralmente se desenvolvem na segunda ou terceira décadas de vida, mas foram relatados em crianças menores de 10 anos.[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
Podem estar presentes um ou mais transtornos psiquiátricos por vez.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Os pacientes geralmente apresentam comportamento anormal, alteração de personalidade, depressão, psicose, transtorno bipolar e comprometimento cognitivo.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[27]Dening TR, Berrios GE. Wilson's disease. Psychiatric symptoms in 195 cases. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989 Dec;46(12):1126-34.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2589927?tool=bestpractice.com
[28]Akil M, Brewer GJ. Psychiatric and behavioral abnormalities in Wilson's disease. Adv Neurol. 1995;65:171-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7872138?tool=bestpractice.com
As outras anormalidades comportamentais que podem estar presentes são acessos de raiva, ansiedade, perda de memória, incapacidade de se concentrar em tarefas, impulsividade e desinibição.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
[28]Akil M, Brewer GJ. Psychiatric and behavioral abnormalities in Wilson's disease. Adv Neurol. 1995;65:171-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7872138?tool=bestpractice.com
Os pacientes podem receber o diagnóstico incorreto de doença de Parkinson ou esclerose múltipla (embora não haja nenhum deficit sensorial).
No exame físico do paciente que apresenta a doença neurológica, pode-se observar o seguinte.
Tremor (de qualquer tipo).
Distonia e rigidez de qualquer parte do corpo, porém com maior frequência nas mãos. Isso pode causar anormalidades posturais e de marcha. Um sorriso distônico pode ser observado.
Disdiadococinesia e demonstrações de desajeitamento ou de falta de coordenação.
A caligrafia costuma ser ruim, mas pode ser pequena (micrografia).
A fala pode ser anormal, mas as anormalidades não são específicas para a doença de Wilson. As palavras podem ser indistintas e o volume pode ser baixo (hipofonia). A fala pode ser quase do tipo gaguejante (ecolalia).
A disfagia pode causar uma sialorreia e o paciente pode ter dificuldade com os músculos dos lábios e do rosto.
Movimentos extraoculares são ocasionalmente anormais.
A sensação é normal.
Os anéis de KF podem ser aparentes (mas devem sempre ser confirmados pelo exame com lâmpada de fenda). Cataratas em girassol também podem ser observadas.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Olho com anel de Kayser-FleischerAdaptado de BMJ (2009); utilizado com permissão [Citation ends].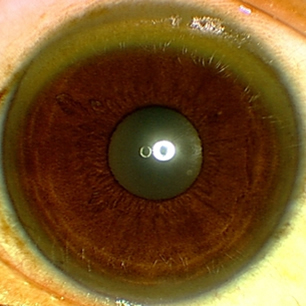
Investigações
Uma história pessoal e familiar detalhada deve ser obtida dos pacientes com suspeita de doença de Wilson.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Todos os pacientes devem ser investigados com testes da função hepática, exame de lâmpada de fenda para anéis de KF, ceruloplasmina sérica e medição de cobre urinário de 24 horas.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Investigações adicionais podem ser indicadas dependendo do quadro clínico e dos resultados dos exames iniciais. Nenhum exame é capaz de diagnosticar a doença de Wilson isoladamente.[29]Ryan A, Nevitt SJ, Tuohy O, et al. Biomarkers for diagnosis of Wilson's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 19;(11):CD012267.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD012267.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31743430?tool=bestpractice.com
O escore de Leipzig compila características clínicas e resultados de investigação e calcula um escore. Um escore de 4 ou mais é diagnóstico para a doença de Wilson.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[6]Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003 Jun;23(3):139-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12955875?tool=bestpractice.com
Consulte Critérios de diagnóstico.
Testes da função hepática, incluindo tempo de protrombina
Os testes da função hepática (TFHs) estão quase sempre anormais em pacientes com uma manifestação hepática.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Aspartato aminotransferase (AST) e alanina aminotransferase (ALT) elevadas estão presentes em 40% a 60% dos pacientes na apresentação.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
Aproximadamente 12% dos pacientes apresentam bilirrubina elevada, devido a lesão hepática, hemólise com teste de Coombs negativo ou ambas.[6]Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003 Jun;23(3):139-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12955875?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
Aqueles com insuficiência hepática aguda podem apresentar albumina baixa e razão normalizada internacional (INR) prolongada. Aqueles com cirrose descompensada podem apresentar INR prolongada, trombocitopenia, padrão misto nos TFHs e albumina baixa.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
Nos pacientes com apresentação neurológica, a ALT e a AST também podem estar anormais, pois podem se sobrepor ao comprometimento hepático.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
Medição de cobre na urina de 24 horas
A amostra deve ser coletada em um recipiente sem oligoelementos. Níveis de cobre na urina de 24 horas >100 microgramas são consistentes com a doença de Wilson.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Níveis de cobre na urina de 24 horas >40 microgramas podem sugerir doença de Wilson e necessitam de investigação adicional.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
A excreção urinária de cobre também pode ser alta em condições colestáticas e autoimunes ou enteropatia perdedora de proteínas, portanto, o diagnóstico da doença não deve ser realizado apenas com os valores de cobre na urina.
Exame com lâmpada de fenda para anéis de KF
Os anéis de KF são formados por um pigmento marrom dourado que representa o depósito de cobre na membrana de Descemet da córnea. Geralmente, aparecem nas porções superior e inferior da córnea e tornam-se circunferenciais à medida que a deposição de cobre evolui.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
Os anéis de KF estão presentes em 95% dos pacientes com apresentações neurológicas e em 44% a 62% dos pacientes com apresentações hepáticas.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Eles podem desaparecer com o tratamento adequado para a doença de Wilson.
Ceruloplasmina sérica e concentração de cobre não ligada à ceruloplasmina (NCC)
A ceruloplasmina, sintetizada no fígado, é a principal proteína transportadora de cobre no sangue. O nível normal de ceruloplasmina sérica é 200-350 mg/L (20-35 mg/dL). Um nível de ceruloplasmina sérica de <50 mg/L (<5 mg/dL) sugere fortemente doença de Wilson.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Exames adicionais são necessários para se fazer o diagnóstico.
A ceruloplasmina sérica nem sempre é diagnóstica porque aproximadamente 20% dos pacientes com doença de Wilson apresentam resultados dentro da faixa normal.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
Cerca de 1% da população é heterozigota para uma mutação em ATP7B e apresenta um nível intermediário baixo de ceruloplasmina. Portanto, uma ceruloplasmina sérica normal não descarta o diagnóstico de doença de Wilson.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
A ceruloplasmina sérica <200 mg/L (<20 mg/dL) apresenta uma sensibilidade de 77.1% a 99% e especificidade de 55.9% a 82.8% para o diagnóstico da doença de Wilson. A ceruloplasmina sérica <100 mg/L (<10 mg/dL) apresenta uma sensibilidade de 65.7% a 94.4% e especificidade de 96.6% a 100%, para o diagnóstico da doença de Wilson.[29]Ryan A, Nevitt SJ, Tuohy O, et al. Biomarkers for diagnosis of Wilson's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 19;(11):CD012267.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD012267.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31743430?tool=bestpractice.com
O ensaio pelo método enzimático parece ser o mais preciso, mas o ensaio mediado por anticorpos pode ser usado como alternativa. A ceruloplasmina pode estar aumentada em casos de inflamação, pois é um reagente de fase aguda.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Também pode estar aumentada na gravidez e na ingestão de estrogênio. Geralmente, é baixa na primeira infância e geralmente não é medida até que a criança tenha >6 meses.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
A ceruloplasmina também pode estar baixa nos casos de enteropatia perdedora de proteínas, perda de proteína renal não seletiva, doença hepática em estágio terminal, síndrome nefrótica, distúrbios neurológicos (distonia cervical), deficiência de cobre absoluta (formulação inadequada de nutrição parenteral total com omissão de cobre, após cirurgia bariátrica ou gástrica, ou ingestão crônica de zinco em excesso), doença de Menkes, aceruloplasminemia, síndrome de MEDNIK, disfunção de AP1B1, distúrbio congênito da glicosilação (PGM1‐CDG, CCDC115‐CGD ou TMEM119‐CDG) ou doença de Niemann-Pick tipo C.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
[30]Merle U, Eisenbach C, Weiss KH, et al. Serum ceruloplasmin oxidase activity is a sensitive and highly specific diagnostic marker for Wilson's disease. J Hepatol. 2009 Nov;51(5):925-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19720421?tool=bestpractice.com
Há sugestões de que o ensaio direto de cobre livre ajuda no diagnóstico.[31]McMillin GA, Travis JJ, Hunt JW. Direct measurement of free copper in serum or plasma ultrafiltrate. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009 Feb;131(2):160-5.
https://academic.oup.com/ajcp/article/131/2/160/1765310
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19141375?tool=bestpractice.com
O cobre sérico está geralmente baixo na doença de Wilson devido à diminuição da ceruloplasmina circulante. A concentração de cobre não ligado à ceruloplasmina (NCC) pode ser calculada usando a seguinte equação:[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
NCC = concentração de cobre sérico (microgramas/dL) - (3.15 x concentração de ceruloplasmina sérica (mg/dL)).
Um nível superior a 25 microgramas/dL é frequentemente observado em pacientes não tratados.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Níveis elevados de NCC podem ser observados na coléstase ou ingestão excessiva de cobre. Embora muitas vezes útil, a NCC não pode ser interpretada se a ceruloplasmina sérica foi superestimada, porque pode ser um número negativo.[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
Biópsia hepática
Se o diagnóstico for incerto, o exame diagnóstico definitivo será uma biópsia hepática com ensaio quantitativo do cobre (o normal é 20 a 50 microgramas/g de peso seco do tecido; na doença de Wilson, o nível é >250 microgramas/g).[5]Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of Wilson disease: executive summary of the 2022 practice guidance on Wilson disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1428-55.
https://journals.lww.com/hep/fulltext/2023/04000/a_multidisciplinary_approach_to_the_diagnosis_and.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36152019?tool=bestpractice.com
A ausência de coloração de cobre no tecido hepático não descarta a doença de Wilson devido à deposição esporádica de cobre nos hepatócitos.[32]Stromeyer FW, Ishak KG. Histology of the liver in Wilson's disease: a study of 34 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jan;73(1):12-24.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7352414?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Johncilla M, Mitchell KA. Pathology of the liver in copper overload. Semin Liver Dis. 2011 Aug;31(3):239-44.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21901654?tool=bestpractice.com
Exames por imagem
A ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) cranioencefálica é útil na manifestação neurológica. Os achados mais comuns são:[16]Dusek P, Litwin T, Członkowska A. Neurologic impairment in Wilson disease. Ann Transl Med. 2019 Apr;7(suppl 2):S64.
https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/24752/23688
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31179301?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]van Wassenaer-van Hall HN. Neuroimaging in Wilson disease. Metab Brain Dis. 1997 Mar;12(1):1-19.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9101534?tool=bestpractice.com
Hiperintensidade em imagens ponderadas em T2 dos gânglios da base
Atrofia da cabeça do núcleo caudado, tronco encefálico e hemisférios cerebrais e cerebelares.
O sinal de "face do panda gigante" é observado nas imagens ponderadas em T2 da parte central do cérebro. É incomum, mas, se presente, é característico da doença de Wilson.[35]Gupta A, Chakravarthi S, Goyal MK. 'Face of giant panda': a rare imaging sign in Wilson's disease. QJM. 2014 Jul;107(7):579.
https://academic.oup.com/qjmed/article/107/7/579/1555920
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24170891?tool=bestpractice.com
Esses achados são sensíveis para a doença de Wilson somente nos casos de manifestação neurológica. Eles não são específicos para a doença de Wilson. Os achados da RNM podem ser semelhantes em outros distúrbios neurológicos.
Teste de DNA para mutações do gene ATP7B
Embora existam mais de 700 mutações patogênicas no gene ATP7B, o sequenciamento de nova geração pode identificar duas mutações patogênicas na maioria das pessoas com doença de Wilson.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
A ausência de duas mutações patogênicas não descarta a doença de Wilson; é necessária a comprovação clínica.[24]Shribman S, Marjot T, Sharif A, et al; British Association for the Study of the Liver Rare Diseases Special Interest Group. Investigation and management of Wilson's disease: a practical guide from the British Association for the Study of the Liver. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun;7(6):560-75.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35429442?tool=bestpractice.com
O teste molecular é preferível antes da biópsia hepática em crianças com suspeita de doença de Wilson.[25]Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Feb;66(2):334-44.
https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/02000/Wilson_s_Disease_in_Children__A_Position_Paper_by.32.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341979?tool=bestpractice.com
A análise do DNA pode ser usada para verificar o genótipo de irmãos de um paciente diagnosticado com doença de Wilson. Não é necessário conhecer a mutação ou mutações específicas do ATP7B no paciente. São caracterizados marcadores de DNA em ambos os lados de ambas as cópias do gene ATP7B no paciente. Se um irmão for compatível com os dois grupos de marcadores, ele é afetado, se ele for compatível com um grupo, ele é portador e se ele não for compatível com nenhum deles, é improvável que tenha a doença.[19]Ala A, Borjigin J, Rochwarger A, et al. Wilson disease in septuagenarian siblings: raising the bar for diagnosis. Hepatology. 2005 Mar;41(3):668-70.
https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.20601
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15723329?tool=bestpractice.com
