გაგლეჯილი ანევრიზმის მქონე პაციენტი საჭიროებს ურგენტულ ოპერაციას.
პაციენტებისათვის, რომელთაც აღენიშნებათ სიმპტომური აორტის ანევრიზმა, მკურნალობა ნაჩვენებია მიუხედავად დიამეტრისა.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
პაციენტებში, რომელთაც მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმა დაუდგინდათ შემთხვევით, უსიმპტომოდ, ქირურგიულ ჩარევასთან შედარებით უპირატესია დაკვირვება მანამდე, სანამ გაგლეჯის რისკი არ გადააჭარბებს ოპერაციის შემდგომი სიკვდილობის რისკს. მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის დროს, ძირითადად, ქირურგიული მკურნალობა ნაჩვენებია მაშინ, როდესაც ანევრიზმა დიდი ზომისაა (მაგ.: აშშ-ში მამაკაცებში დიამეტრი > 5.5 სმ, ხოლო ქალებში - >5.0 სმ), ასევე, სხვა ქვეყნებში, მკურნალობის შესახებ გადაწყვეტილება მიიღება ანევრიზმის უფრო დიდი ზომის შემთხვევაში.[1]Dehlin JM, Upchurch GR. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2005 Jun;7(2):119-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15935120?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[105]Lederle FA, Wilson SE, Johnson GR, et al; Aneurysm Detection and Management Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group. Immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002 May 9;346(19):1437-44.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12000813?tool=bestpractice.com
[106]UK Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Mortality results for randomized controlled trial of early elective surgery or ultrasonographic surveillance for small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Lancet. 1998 Nov 21;352(9141):1649-55.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9853436?tool=bestpractice.com
[107]Powell JT, Brady AR, Brown LC, et al; United Kingdom Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Long-term outcomes of immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002 May 9;346(19):1445-52.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa013527
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12000814?tool=bestpractice.com
[108]Powell JT, Brown LC, Forbes JF, et al. Final 12-year follow-up of surgery versus surveillance in the UK Small Aneurysm Trial. Br J Surg. 2007 Jun;94(6):702-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17514693?tool=bestpractice.com
უსიმპტომო, სიმპტომური და გაგლეჯილი ანევრიზმების მკურნალობა შსაძლებელია ენდოვასკულური ან ღია ქირურგიული მიდგომით; ქირურგიული მიდგომის შერჩევისას გასათვალისწინებელია პაციენტის არჩევანი, ასაკი, სქესი, პერიოპერაციული რისკფაქტორები და ანატომიური თავისებურებები. რეკომენდებულია გადაწყვეტილების მიღების საერთო მიდგომა პროცედურების რისკებისა და სარგებლის გათვალისწინებით.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
მუცლის აორტის გამსკდარი ანევრიზმა (AAA)
პაციენტს, რომელსაც აღენიშნება ტრიადა: მუცლის და/ან ზურგის ტკივილი, მოპულსირე წარმონაქმნი მუცელში და ჰიპოტენზია, დაუყოვნებლივ ესაჭიროება რეანიმაცია და ქირურგიული შეფასება, რადგან ქირურგიული ჩარევა წარმოადგენს ერთადერთ პოტენციურ მკურნალობას.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[109]Harkin DW, Dillon M, Blair PH, et al. Endovascular ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (EVRAR): a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007 Dec;34(6):673-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17719809?tool=bestpractice.com
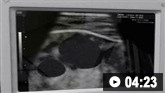
თუმცა, პაციენტთა უმეტესობაგასკდომის შემთხვევაში საოპერაციომდე ცოცხალი ვერ აღწევს.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: გაგლეჯილი მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის კომპიუტერული სკანირებამიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].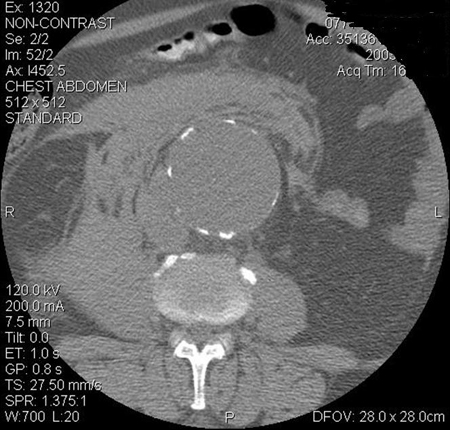
კარდიოლოგიის ამერიკული კოლეჯი/ამერიკული გულის ასოციაცია (ACC/AHA) რეკომენდაციას უწევს კომპიუტერულ ტომოგრაფიას (CT) იმ პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც აღენიშნებათ გაგლეჯილი AAA, რომლებიც არიან ჰემოდინამიკურად სტაბილური, რათა შეაფასონ, ექვემდებარება თუ არა AAA ენდოვასკულარულ შეკეთებას.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
ეს რეკომენდაცია მხარდაჭერილია IMPROVE მრავალცენტრიანი რანდომიზებული კონტროლირებადი კვლევის შედეგებით, რომლებიც ვარაუდობენ, რომ პაციენტების უმეტესობისთვის დამადასტურებელი CT არ აფერხებდა მკურნალობის მიმდინარეობას და ხელს უწყობდა შესაბამის პრეოპერაციულ დაგეგმვას.[110]Powell JT, Hinchcliffe RJ, Thompson MM, et al; IMPROVE Trial Investigators. Observations from the IMPROVE trial concerning the clinical care of patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2014 Feb;101(3):216-24.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.9410
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24469620?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ ანატომია შესაბამისია, ACC/AHA რეკომენდაციას უწევს ენდოვასკულარულ ჩარევას, ღია პლასტიკის ნაცვლად, რათა შემცირდეს ავადობისა და სიკვდილიანობის რისკი.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ პაციენტს დადასტურებული აქვს გაგლეჯილი მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმა, ოპერაიის შემდეგ 3 წელიწადში სიკვდილობა უფრო დაბალია ენდოვასკულარული მიდგომის (EVAR) ჯგუფში, ვიდრე ღია მიდგომის ჯგუფში (48% vs. 56%; საფრთხის თანაფარდობა [HR] 0.57, 95% სარწმუნოობის ინტერვალი 0.36 - 0.90).[111]IMPROVE Trial Investigators. Comparative clinical effectiveness and cost effectiveness of endovascular strategy v open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: three year results of the IMPROVE randomised trial. BMJ. 2017 Nov 14;359:j4859.
https://www.bmj.com/content/359/bmj.j4859.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29138135?tool=bestpractice.com
განსხვავება სამკურნალო ჯგუფებს შორის აღარ იყო გამოხატული 7-წლიანი მეთვალყურეობის შემდეგ (HR 0.92, 95% CI 0.75 - 1.13). ხელახალი ჩარევის საჭიროების სიხშირე მნიშვნელოვნად არ განსხვავდებოდა რანდომიზებულ ჯგუფებს შორის 3 წლის შემდეგ (HR 1.02, 95% CI 0.79 - 1.32).[111]IMPROVE Trial Investigators. Comparative clinical effectiveness and cost effectiveness of endovascular strategy v open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: three year results of the IMPROVE randomised trial. BMJ. 2017 Nov 14;359:j4859.
https://www.bmj.com/content/359/bmj.j4859.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29138135?tool=bestpractice.com
არსებობს გარკვეული მტკიცებულება, რომ გაგლეჯილი მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის ენდოვასკულური სტრატეგიით ოპერირება ამცირებს სიკვდილობას უფრო ეფექტურად ქალებში, ვიდრე მამაკაცებში.[111]IMPROVE Trial Investigators. Comparative clinical effectiveness and cost effectiveness of endovascular strategy v open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: three year results of the IMPROVE randomised trial. BMJ. 2017 Nov 14;359:j4859.
https://www.bmj.com/content/359/bmj.j4859.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29138135?tool=bestpractice.com
[112]Sweeting MJ, Balm R, Desgranges P, et al; Ruptured Aneurysm Trialists. Individual-patient meta-analysis of three randomized trials comparing endovascular versus open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015 Sep;102(10):1229-39.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.9852
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26104471?tool=bestpractice.com
არსებობს გარკვეული მტკიცებულებები, რომლებიც ვარაუდობენ, რომ ანესთეზიის რეჟიმი AAA-ს ოპერაციული ჩარევის დროს გავლენას ახდენს შედეგებზე.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[113]Armstrong RA, Squire YG, Rogers CA, et al. Type of anesthesia for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019 Feb;33(2):462-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30342821?tool=bestpractice.com
IMPROVE(პაციენტებს აორტის გახეთქვის შემთხვევაში დაუყოვნებლივ უნდა ჩაუტარდეთ კორექცია ღია ან ენდოვასკულარული აღდგენის მეთოდით.) 30 დღიანი პერიოდის სიკვდილიანობის მნიშვნელოვნად მცირეა პაციენტებში,რომლებსაც ჩაუტარდათ EVAR ადგილობრივი ანესთეზიით,იმ პაციენტებთან შედარებით,რომლებსაც ჩაუტარდათ ზოგადი ანესთეზიის ქვეშ.(კორექტირებული OR 0,27-დან 0,7 მდე).[110]Powell JT, Hinchcliffe RJ, Thompson MM, et al; IMPROVE Trial Investigators. Observations from the IMPROVE trial concerning the clinical care of patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2014 Feb;101(3):216-24.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.9410
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24469620?tool=bestpractice.com
ცალკეულმა მეტა-ანალიზმა, რომელიც ადარებს ანესთეზიის რეჟიმს გახეთქილი AAA-ს ენდოვასკულარული აღდგენისთვის, გაიმეორა ეს დასკვნები ან გააუმჯობესა შედეგები EVAR-ით ადგილობრივი ანესთეზიის ქვეშ.[114]Harky A, Ahmad MU, Santoro G, et al. Local versus general anesthesia in nonemergency endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020 Apr;34(4):1051-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31473112?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, სხვა სისტემურმა მიმოხილვამ არ აჩვენა რაიმე სარგებელი სიკვდილიანობის შესახებ ადგილობრივი ანესთეზიით, მაგრამ აჩვენა სტაციონარული მკურნალობის უფრო ხანმოკლე პერიოდი.[115]Deng J, Liu J, Rong D, et al. A meta-analysis of locoregional anesthesia versus general anesthesia in endovascular repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2021 Feb;73(2):700-10.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.08.112
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32882348?tool=bestpractice.com
დამხმარე მკურნალობა გამსკდარი მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის დროს
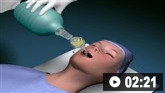
სტანდარტული რეანიმაციული ღონისძიებები იწყება დაუყოვნებლივ. ესენია:
სასუნთქი გზების მართვა (დამატებითი ჟანგბადი ან ენდოტრაქეული ინტუბაცია და ხელოვნური ვენტილაცია თუ პაციენტი უგონოდაა).
ინტრავენური წვდომა (ცენტრალური ვენური კათეტერი)
არტერიული კათეტერი; შარდის ბუშტის კათეტერი.
ჰიპოტენზიის მართვა: სითხის აგრესიულმა ჩანაცვლებითმა თერაპიამ შეიძლება გამოიწვიოს განზავება და ჰიპოთერმული კოაგულოპათია, და მეორადად - თრომბის მოწყვეტა სისხლის ნაკადის ზრდის, პერფუზიის წნევის მომატებისა და სისხლის ვისკოზურობის დაქვეითების გამო, რაც თავის მხრივ იწვევს ხელახალ სისხლდენას.[116]Roberts K, Revell M, Youssef H, et al. Hypotensive resuscitation in patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2006 Apr;31(4):339-44.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16388972?tool=bestpractice.com
[117]Ohki T, Veith FJ. Endovascular grafts and other image-guided catheter-based adjuncts to improve the treatment of ruptured aortoiliac aneurysms. Ann Surg. 2000 Oct;232(4):466-79.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10998645?tool=bestpractice.com
ოპერაციამდე რეკომენდებულია სამიზნე სისტოლური წნევა იყოს 50-79 მმ.ვწყ.სვ.-ს ფარგლებში და სითხეების შეზღუდვა.[116]Roberts K, Revell M, Youssef H, et al. Hypotensive resuscitation in patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2006 Apr;31(4):339-44.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16388972?tool=bestpractice.com
[117]Ohki T, Veith FJ. Endovascular grafts and other image-guided catheter-based adjuncts to improve the treatment of ruptured aortoiliac aneurysms. Ann Surg. 2000 Oct;232(4):466-79.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10998645?tool=bestpractice.com
ACC/AHA გაიდლაინები გვირჩევენ დასაშვებ ჰიპოტენზიას სისხლდენის შესამცირებლად.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა რეკომენდებული მიზნები განსხვავდება და არ არსებობს კონსენსუსი გლობალურ გაიდლაინ ჯგუფებს შორის.
IMPROVE მრავალცენტრიანმა რანდომიზებულმა კონტროლირებადმა კვლევამ აჩვენა, რომ ყველაზე დაბალი SBP მნიშვნელოვნად და დამოუკიდებლად იყო დაკავშირებული 30-დღიან სიკვდილთან პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც აქვთ AAA გახეთქვა და რომ სამიზნე SBP 70 mmHg-ზე დაბლა ხანდაზმულ პაციენტებში შესაძლოა ხელი შეუწყო უარეს შედეგებს.[110]Powell JT, Hinchcliffe RJ, Thompson MM, et al; IMPROVE Trial Investigators. Observations from the IMPROVE trial concerning the clinical care of patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2014 Feb;101(3):216-24.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.9410
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24469620?tool=bestpractice.com
ადამიანებში, რომლებსაც აქვთ გაგლეჯილი AAA, დაფიქსირებული წინასაოპერაციო SBP 70 mmHg-ზე ნაკლები, სიკვდილიანობა 30 დღის განმავლობაში უფრო მაღალი იყო (51.0%), ვიდრე SBP 70 mmHg-ზე მეტის მქონე ადამიანებში. (34.1%).[110]Powell JT, Hinchcliffe RJ, Thompson MM, et al; IMPROVE Trial Investigators. Observations from the IMPROVE trial concerning the clinical care of patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2014 Feb;101(3):216-24.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.9410
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24469620?tool=bestpractice.com
კონტროლირებადი (ნებადართული) ჰიპოტენზიის კოქრეინის ერთმა მიმოხილვამ გახეთქილი AAA-ს მქონე ადამიანებისთვის ნორმატიული რეანიმაციული სტრატეგიის წინააღმდეგ რომელიც მოიცავდა IMPROVE კვლევას, აღნიშნა, რომ გახეთქილი AAA-ს მქონე ადამიანები ჩვეულებრივ ხანდაზმულები არიან და უფრო მეტად აქვთ კორონარული და თირკმლის ათეროსკლეროზული დაავადება. ეს პაციენტები ასევე იმყოფებიან მიოკარდიუმის ინფარქტის და თირკმლის უკმარისობის უფრო დიდი რისკის ქვეშ დაბალი SBP-ის მაჩვენებლის დროს,იმ ახალგაზრდებთან შედარებით,რომლებმაც მიიღეს ტრავმა [118]Moreno DH, Cacione DG, Baptista-Silva JC. Controlled hypotension versus normotensive resuscitation strategy for people with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 13;6(6):CD011664.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011664.pub3
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29897100?tool=bestpractice.com
სისხლის პროდუქტებზე (ერითროციტარული მასა, თრომბოციტები და ახალი გაყინული პლაზმა) ხელმისაწვდომობა და ტრანსფუზია რეანიმაციული ღნისძიებების მიზნით, მძიმე ფორმის ანემია და კოაგულოპათია.
შეტყობინება ეგზავნება ანესთეზიოლოგის, რეანიმატოლოგისა და ქირურგების ჯგუფებს.
სიმპტომური, მაგრამ არაგაგლეჯილი მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმა
პაციენტებისათვის, რომელთაც აღენიშნებათ სიმპტომური აორტის ანევრიზმა, მკურნალობა ნაჩვენებია მიუხედავად აორტის დიამეტრისა.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
[122]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
ახლად აღმოცენებული ტკივილი ან ტკივილის გაუარესება შეიძლება მიანიშნებდეს ანევრიზმის გაფართოებაზე ან მოსალოდნელ გაგლეჯაზე. სიმპტომური, მთლიანი ანევრიზმის მკურნალობა ურგენტულადაა რეკომენდებული.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
ზოგიერთ შემთხვევაში ოპერაციისათვის ოპტიმალური პირობების შესაქმნელად, ჩარევა შეიძლება რამდენიმე საათით გადაიდოს; ასეთ დროს პაციენტების მონიტორინგი რეკომენდებულია ინტენსიურ განყოფილებაში.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR უფრო და უფრო ხშირად გამოიყენება სიმპტომური მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის სამართავად.[123]De Martino RR, Nolan BW, Goodney PP, Chang CK, et al; Vascular Study Group of Northern New England. Outcomes of symptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2010 Jul;52(1):5-12.e1.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(10)00259-4/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20471771?tool=bestpractice.com
[124]Chandra V, Trang K, Virgin-Downey W, et al. Management and outcomes of symptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms during the past 20 years. J Vasc Surg. 2017 Dec;66(6):1679-85.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28619644?tool=bestpractice.com
ობსერვაციული კვლევების თანახმად, მოკლევადიანი, ნებისმიერი მიზეზით განპირობებული სიკვდილობის სიხშირე არ განსხვავდებოდა ენდოვასკულურ და ღია მეთოდებს შორის სიმპტომური ანევრიზმის დროს.[123]De Martino RR, Nolan BW, Goodney PP, Chang CK, et al; Vascular Study Group of Northern New England. Outcomes of symptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2010 Jul;52(1):5-12.e1.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(10)00259-4/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20471771?tool=bestpractice.com
[124]Chandra V, Trang K, Virgin-Downey W, et al. Management and outcomes of symptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms during the past 20 years. J Vasc Surg. 2017 Dec;66(6):1679-85.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28619644?tool=bestpractice.com
[125]Ten Bosch JA, Willigendael EM, Kruidenier LM, et al. Early and mid-term results of a prospective observational study comparing emergency endovascular aneurysm repair with open surgery in both ruptured and unruptured acute abdominal aortic aneurysms. Vascular. 2012 Apr;20(2):72-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22454547?tool=bestpractice.com
ამერიკის ქირურგთა კოლეჯის ხარისხის განვითარების 2011-2013 წლის პროგრამის მონაცემებით, სიმპტომური მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის ოპერაციის შემდეგ 30-დღიანი სიკვდილობის რისკი, შედარებით უსიმპტომო ანევრიზმის ოპერაციის შემდეგ რისკთან, დაახლოებით ორმაგია, განურჩევლად ოპერაციული მიდგომისა (EVAR: სიმპტომური 3.8% vs. უსიმპტომო 1.4%, P=0.001; ღია ჩარევა: სიმპტომური 7.7% vs. უსიმპტომო 4.3%, P=0.08).[126]Soden PA, Zettervall SL, Ultee KH, et al. Outcomes for symptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. J Vasc Surg. 2016 Aug;64(2):297-305.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(16)00320-7/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27146791?tool=bestpractice.com
ღია მეთოდის სტატისტიკურად უმნიშვნელო განსხვავება სავარაუდოდ დაკავშირებულია პაციენტების ნაკლებ რაოდენობასთან.
მცირე ზომის მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის შემთხვევით აღმოჩენა
პაციენტებში, რომელთაც მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმა დაუდგინდათ შემთხვევით, უპირატესია დაკვირვება ქირურგიულ ჩარევასთან შედარებით მანამ, სანამ გასკდომის რისკი არ გადააჭარბებს ოპერაციის შემდგომი სიკვდილობის რისკს.[3]Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2211-8.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2757234
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31821437?tool=bestpractice.com
[122]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
უფრო მცირე ზომის მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმების ადრეული ქირურგიული მკურნალობა არ ამცირებს ნებისმიერი მიზეზით ან ანევრიზმით გამოწვეულ სიკვდილობას.[3]Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2211-8.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2757234
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31821437?tool=bestpractice.com
[127]Ulug P, Powell JT, Martinez MA, et al. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 1;7(7):CD001835.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001835.pub5
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32609382?tool=bestpractice.com
[  ]
How does immediate surgery compare with surveillance in people with asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs)?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.3227/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება ერთ-ერთი სისტემური მიმოხილვის თანახმად (4 კვლევა, 3314 მონაწილე), არსებობს მაღალი ხარისხის მტკიცებულება, რომ მცირე ზომის (4 სმ- 5.5 სმ) მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის ოპერაცია გრძელვადიანი გადარჩენის თვალსაზრისით, დაკვირვებით ტაქტიკასთან შედარებით(კორეგირებული საფრთხის თანაფარდობა 0.88, 95% სარწმუნოობის ინტერვალი 0.75 - 1.02, საშუალოდ 10 წელი შემდგომი დაკვირვებით) არაეფსექტურია.[127]Ulug P, Powell JT, Martinez MA, et al. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 1;7(7):CD001835.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001835.pub5
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32609382?tool=bestpractice.com
დაუყოვნებლივი ქირურგიულ ჩარევის დაბალი სარგებლიანობა ვლინდებოდა ყველა ასაკში, მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმის ნებისმიერ დიამეტრზე და ენდოვასკულური/ღია მეთოდების ჯგუფებშიც.[127]Ulug P, Powell JT, Martinez MA, et al. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 1;7(7):CD001835.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001835.pub5
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32609382?tool=bestpractice.com
]
How does immediate surgery compare with surveillance in people with asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs)?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.3227/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება ერთ-ერთი სისტემური მიმოხილვის თანახმად (4 კვლევა, 3314 მონაწილე), არსებობს მაღალი ხარისხის მტკიცებულება, რომ მცირე ზომის (4 სმ- 5.5 სმ) მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის ოპერაცია გრძელვადიანი გადარჩენის თვალსაზრისით, დაკვირვებით ტაქტიკასთან შედარებით(კორეგირებული საფრთხის თანაფარდობა 0.88, 95% სარწმუნოობის ინტერვალი 0.75 - 1.02, საშუალოდ 10 წელი შემდგომი დაკვირვებით) არაეფსექტურია.[127]Ulug P, Powell JT, Martinez MA, et al. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 1;7(7):CD001835.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001835.pub5
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32609382?tool=bestpractice.com
დაუყოვნებლივი ქირურგიულ ჩარევის დაბალი სარგებლიანობა ვლინდებოდა ყველა ასაკში, მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმის ნებისმიერ დიამეტრზე და ენდოვასკულური/ღია მეთოდების ჯგუფებშიც.[127]Ulug P, Powell JT, Martinez MA, et al. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 1;7(7):CD001835.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001835.pub5
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32609382?tool=bestpractice.com
მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმების დროს ქირურგიული ჩარევა რეკომენდებულია თუ ანევრიზმა სწრაფად იზრდება ან ანევრიზმის ქირურგიული ზღვრული მაჩვენებელი მიღწეულია განმეორებითი ულტრაბგერის კვლევაზე.[3]Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2211-8.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2757234
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31821437?tool=bestpractice.com
უსიმპტომო მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმების შემთხვევაში სამედიცინო მიზნები მოიცავს:
1. დაკვირვება:
კარდიოლოგიის ამერიკული კოლეჯის ფონდი/ამერიკის გულის ასოციაცია რეკომენდაციას უწევს თირკმლის ქვედა ან გვერდითა ანევრიზმების (4.0-4,9 სმ დიამეტრი) გადამოწმებას ულტრაბგერა/CT-ით ყოველ 6-12 თვეში ერთხელ.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
4,5 სმ-ზე მეტი დიამეტრი ქალებში და 5 სმ-ზე დიამეტრი მამაკაცებში, ამ შემთხვევაში გაიდლაინის რეკომენდაციით მეთვალყურეობა უნდა მოხდეს ყოველ 6 თვეში.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმა AAA < 3,9 სმ საჭიროებს ულტრასონოგრაფიას ყოველ 2-3 წელიწადში.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
დიდი ბრიტანეთის ჯანდაცვის ეროვნული სააგენტო რეკომენდაციას უწევს ყოველწლიურ სკრინინგს 3.0-4.4 სმ ანევრიზმების დროს, ხოლო 3-თვიან სკრინინგს 4.5-5.4 სმ შემთხვევაში.[128]Public Health England. NHS public health functions agreement 2019-20. Service specification no.23. NHS Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Screening Programme. July 2019 [internet publication].
https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Service-Specification-No.23-Abdominal_Aortic_Aneurysm.pdf
ერთი სისტემური მიმოხილვისა და პაციენტების მონაცემების მეტა-ანალიზის დასკვნის მიხედვით, 2-წლიანი სკრინინგ-ინტერვალი 3.0-4.4 სმ დიამეტრის, ხოლო 6-თვიანი ინტერვალი 4.5-5.4 სმ დიამეტრის მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმისთვის უსაფრთხო და ხარჯთეფექტურია.[104]Thompson S, Brown L, Sweeting M, et al; RESCAN Collaborators. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the growth and rupture rates of small abdominal aortic aneurysms: implications for surveillance intervals and their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2013 Sep;17(41):1-118.
https://www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/hta/hta17410/#/full-report
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24067626?tool=bestpractice.com
მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის ზრდისა და რუპტურის სიხშირის ანალიზით დადგინდა, რომ რუპტურის რისკის <1% შესანარჩუნებლად, საჭიროა 8.5-წლიანი სკრინინგ-ინტერვალი მამაკაცებში, რომელთაც ბაზისურად ანევრიზმა 3.0 სმ ჰქონდათ.[104]Thompson S, Brown L, Sweeting M, et al; RESCAN Collaborators. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the growth and rupture rates of small abdominal aortic aneurysms: implications for surveillance intervals and their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2013 Sep;17(41):1-118.
https://www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/hta/hta17410/#/full-report
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24067626?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ მამაკაცებში ანევრიზმის თავდაპირველი დიამეტრი არის 5.0 სმ, შემდგომი მეთვალყურეობის ინტერვალი შეადგენს 17 თვეს. ანევრიზმის ზრდის სიჩქარის იდენტურობის მიუხედავად, გაგლეჯვის სიხშირე ქალებში მამაკაცებთან შედარებით 4-ჯერ მეტი იყო.[104]Thompson S, Brown L, Sweeting M, et al; RESCAN Collaborators. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the growth and rupture rates of small abdominal aortic aneurysms: implications for surveillance intervals and their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2013 Sep;17(41):1-118.
https://www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/hta/hta17410/#/full-report
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24067626?tool=bestpractice.com
მეთვალყურეობის პროგრამები და ოპერაციული ჩარევის კრიტერიუმები საჭიროა მოერგოს ქალებსაც, რომლებშიც შემთხვევით გამოვლინდა მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმა.
AAA-ების უმეტესობა აჩვენებს ხაზოვან ზრდას; ამაზე დაფუძნებული მოდელირება ვარაუდობს, რომ მცირე ზომის AAA (<4.25 სმ) შეიძლება განხორციელდეს ყოველ 2 წელიწადში ერთხელ, მინიმალური შანსით რომ გადალახოს ინტერვენციული საზღვრები ამ დროის განმავლობაში.[129]Kim GY, Corriere MA. Balancing watching vs waiting during imaging surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. JAMA Surg. 2021 Apr 1;156(4):370-1.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33595617?tool=bestpractice.com
[130]Olson SL, Wijesinha MA, Panthofer AM, et al. Evaluating growth patterns of abdominal aortic aneurysm diameter with serial computed tomography surveillance. JAMA Surg. 2021 Apr 1;156(4):363-70.
https://www.doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2020.7190
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33595625?tool=bestpractice.com
ანევრიზმული ზრდა ≥0.5 სმ-ით 6 თვეში შეიძლება იყოს აღდგენის ჩვენება, რათა შემცირდეს გახეთქვის რისკი.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
2. გაფართოებისა და გაგლეჯის ცვლადი რისკფაქტორების კონტროლი:
მოწევის შეწყვეტა - ნიკოტინჩანაცვლებითი თერაპია, ნორტრიფტილინი და ბუპროპიონი, ან კონსულტაციებით დახმარება.[1]Dehlin JM, Upchurch GR. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2005 Jun;7(2):119-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15935120?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[13]Zankl AR, Schumacher H, Krumsdorf U, et al. Pathology, natural history and treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Clin Res Cardiol. 2007 Mar;96(3):140-51.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17180573?tool=bestpractice.com
[15]Singh K, Bønaa H, Jacobsen BK, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysms in a population-based study: the Tromsø Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2001 Aug 1;154(3):236-44.
https://academic.oup.com/aje/article/154/3/236/125840
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11479188?tool=bestpractice.com
[23]Lederle FA, Johnson GR, Wilson SE, et al; Aneurysm Detection and Management (ADAM) Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group. Prevalence and associations of abdominal aortic aneurysm detected through screening. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Mar 15;126(6):441-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9072929?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Wilmink TB, Quick CR, Day NE. The association between cigarette smoking and abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 1999 Dec;30(6):1099-105.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10587395?tool=bestpractice.com
[131]Hartmann-Boyce J, Chepkin SC, Ye W, et al. Nicotine replacement therapy versus control for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 31;5:CD000146.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD000146.pub5/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29852054?tool=bestpractice.com
[132]Rigotti NA, Clair C, Munafò MR, et al. Interventions for smoking cessation in hospitalised patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD001837.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD001837.pub3/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22592676?tool=bestpractice.com
[133]Howes S, Hartmann-Boyce J, Livingstone-Banks J, et al. Antidepressants for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 22;(4):CD000031.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD000031.pub5/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32319681?tool=bestpractice.com
[  ]
What are the effects of adding bupropion or fluoxetine to other treatments compared with using other treatments alone for people trying to quit smoking?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.4337/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება
]
What are the effects of adding bupropion or fluoxetine to other treatments compared with using other treatments alone for people trying to quit smoking?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.4337/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება
ხანმოკლე მკურნალობის კურსი ბეტა-ბლოკერებით სავარაუდოდ არ ამცირებს ანევრიზმის გაფართოების სიჩქარეს.[3]Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2211-8.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2757234
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31821437?tool=bestpractice.com
[134]Siordia JA. Beta-clockers and abdominal aortic aneurysm growth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2021;17(4):e230421187502.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33143615?tool=bestpractice.com
იმ კვლევების მიხედვით, რომლებშიც მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმის მქონე პაციენტები ანევრიზმის ზრდის საპრევენციოდ პროპრანოლოლით სამკურნალოდ გადაანაწილეს რანდომიზებულად, აღნიშნული მედიკამენტი ვერ ავლენს მნიშვნელოვან დამცავ ეფექტს.[134]Siordia JA. Beta-clockers and abdominal aortic aneurysm growth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2021;17(4):e230421187502.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33143615?tool=bestpractice.com
[135]Rughani G, Robertson L, Clarke M. Medical treatment for small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD009536.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD009536.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22972146?tool=bestpractice.com
ამ კვლევების თანახმად, პროპრანოლოლი ხასიათდება ცუდი ამტანობით.[135]Rughani G, Robertson L, Clarke M. Medical treatment for small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD009536.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD009536.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22972146?tool=bestpractice.com
3. სხვა გულსისხლძარღვთა დაავადების აგრესიული მართვა:
ცვლადი რისკფაქტორები, როგორიცაა ჰიპერტენზია და ჰიპერლიპიდემია, საჭიროებს მკურნალობას.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
სტატინები უნდა დაინიშნოს ქირურგიულ ჩარევამდე სულ მცირე 1 თვით ადრე, რათა შემცირდეს გულსისხლძარღვთა მიზეზით სიკვდილობა. სტატინები გრძელდება განუსაზღვრელი ვადით.[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
[136]Risum Ø, Sandven I, Sundhagen JO, et al. Editor's choice - effect of statins on total mortality in abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Jan;61(1):114-20.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2020.08.007
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32928667?tool=bestpractice.com
არსებობს შეზღუდული მტკიცებულება, მაგრამ რაიმე უკუჩვენების არარსებობის შემთხვევაში, AAA-ს მქონე პაციენტებმა უნდა მიიღონ ერთჯერადი ანტითრომბოციტული თერაპია (ასპირინი ან კლოპიდოგრელი).[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[137]Aboyans V, Bauersachs R, Mazzolai L, et al. Antithrombotic therapies in aortic and peripheral arterial diseases in 2021: a consensus document from the ESC working group on aorta and peripheral vascular diseases, the ESC working group on thrombosis, and the ESC working group on cardiovascular pharmacotherapy. Eur Heart J. 2021 Oct 14;42(39):4013-24.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab390
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34279602?tool=bestpractice.com
მუცლის აორტის დიდი ზომის ანევრიზმის შემთხვევით აღმოჩენა
მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის დროს, ძირითადად, ქირურგიული მკურნალობა ნაჩვენებია მაშინ, როდესაც ანევრიზმა დიდი ზომისაა (მაგ.: აშშ-ში მამაკაცებში დიამეტრი > 5.5 სმ, ხოლო ქალებში - >5.0 სმ), ასევე, სხვა ქვეყნებში, მკურნალობის შესახებ გადაწყვეტილება მიიღება ანევრიზმის უფრო დიდი ზომის შემთხვევაში.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
≥5.5 სმ ანევრიზმის ოპერირებით გადარჩენადობა უმჯობესდება.[1]Dehlin JM, Upchurch GR. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2005 Jun;7(2):119-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15935120?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[106]UK Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Mortality results for randomized controlled trial of early elective surgery or ultrasonographic surveillance for small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Lancet. 1998 Nov 21;352(9141):1649-55.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9853436?tool=bestpractice.com
[107]Powell JT, Brady AR, Brown LC, et al; United Kingdom Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Long-term outcomes of immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2002 May 9;346(19):1445-52.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa013527
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12000814?tool=bestpractice.com
[108]Powell JT, Brown LC, Forbes JF, et al. Final 12-year follow-up of surgery versus surveillance in the UK Small Aneurysm Trial. Br J Surg. 2007 Jun;94(6):702-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17514693?tool=bestpractice.com
ქირურგიულ ჩარევასთან დაკავშირებული გადაწყვეტილებები ინდივიდუალურად უნდა იქნას მიღებული. გასათვალისწინებელია პაციენტის არჩევანი, ასაკი, სქესი, პერიოპერაციული რისკფაქტორები და ანტომიური რისკფაქტორები. საჭიროა პაციენტის სიცოცხლის ხარისხის შეფასება. გასათვალისწინებელია ქირურგიული ჩარევის რისკები (პაციენტს უნდა აუხსნათ Vascular Quality Initiative-ის პერიოპერაციული სიკვდილობის რისკის ქულის არსი) და სიცოცხლის შემდგომი ხარისხი. რეკომენდებულია გადაწყვეტილების მიღების საერთო მიდგომა პროცედურების რისკებისა და სარგებლის გათვალისწინებით.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR განიხილეთ პაციენტებში, რომლებიც არ ექვემდებარებიან ღია ჩარევას.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[127]Ulug P, Powell JT, Martinez MA, et al. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 1;7(7):CD001835.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001835.pub5
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32609382?tool=bestpractice.com
მონაცემების თანახმად, მუცლის აორტის დიდი ზომის ანევრიზმის(5.0-5.5 სმ) დროს გადარჩენის თვალსაზრისით EVAR-ისა და ღია წესით ჩატარებული მკურნალობის გამოსავლები ერთნაირია, თუმცა განმეორებითი ჩარევის მაჩვენებელი EVAR-ის შემთხვევაში უფრო მაღალია.[138]Greenhalgh RM, Brown LC, Powell JT, et al; United Kingdom EVAR Trial Investigators. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 2010 May 20;362(20):1863-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20382983?tool=bestpractice.com
[139]Amato B, Fugetto F, Compagna R, et al. Endovascular repair versus open repair in the treatment of ruptured aortic aneurysms: a systematic review. Minerva Chir. 2019 Dec;74(6):472-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29806754?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR ასევე მცირდება მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმით გამოწვეულ სიკვდილობაც(მაგრამ არა გადარჩენადობა ხანგრძლივ პერსპექტივაში) იმ პაციენტებში, რომელთაც დიდი ანევრიზმა აქვთ (≥5.5 სმ) და ვერ უტარდებათ ღია წესით ოპერაცია.[140]Greenhalgh RM, Brown LC, Powell JT, et al; United Kingdom EVAR Trial Investigators. Endovascular repair of aortic aneurysm in patients physically ineligible for open repair. N Engl J Med. 2010 May 20;362(20):1872-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20382982?tool=bestpractice.com
ოპერაციის შემდგომ, დიდი ზომის ანევრიზმები დაკავშირებულია უფრო დაბალ გრძელვადიან გადარჩენასთან, ვიდრე მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმები (ჯამური საფრთხის თანაფარდობა 1.14 ყოველ 1-სმ დიამეტრზე, 95% სარწმუნოობის ინტერვალი 1.09 - 1.18; 12.0- 91.2-თვიანი შემდგომი მეთვალყურეობა).[141]Khashram M, Hider PN, Williman JA, et al. Does the diameter of abdominal aortic aneurysm influence late survival following abdominal aortic aneurysm repair? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vascular. 2016 Dec;24(6):658-67.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27189809?tool=bestpractice.com
ეს კავშირი უფრო გამოხატულია EVAR-ის შემთხვევაში ვიდრე ღია წესით შესრულების დროს.
უსიმპტომო პაციენტებში ელექტიური მკურნალობა პრეოპერაციული შეფასების, კარდიოლოგიური რისკების სტრატიფიცირების და სხვა თანმხლები დაავადებების სამედიცინო ოპტიმიზაციის საშუალებას იძლევა. კორონარული არტერიების დაავადება (CAD) წარმოადგენს მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის მკურნალობის შემდეგ ადრეული და მოგვიანებითი სიკვდილობის მთავარ მიზეზს.
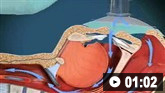
ენდოვასკულური ჩარევა (EVAR)
EVAR-ის დროს დაფარული სტენტის აორტაში მიტანა ხდება ენდოლუმინურად ბარძაყის სისხლძარღვებიდან. სტენტი იცავს ანევრიზმის კედელს სისტემური წნევის ზეგავლენისაგან, ახდენს გაგლეჯის პრევენციას და ამით შესაძლებლობას იძლევა, რომ ზომაში შემცირდეს ანევრიზმის პარკი. ენდოგრაფტი (სტენტი) შეიძლება შეიტანოთ კანქვეშ, ან ქირურგიულად ბარძაყის არტერიების გამოყოფის შემდეგ. კოჰრეინის მიმოხილვის თანახმად, არ არსებობს განსხვავება ამ ორ მიდგომას შორის (6 თვის განმავლობაში), თუმცა კანქვეშა მიდგომა შეიძლება უფრო სწრაფი იყოს.[142]Gimzewska M, Jackson AI, Yeoh SE, et al. Totally percutaneous versus surgical cut-down femoral artery access for elective bifurcated abdominal endovascular aneurysm repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 21;(2):CD010185.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD010185.pub3/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28221665?tool=bestpractice.com
არასაკმარისია მონაცემები ინსტრუმენტების ვარგისიანობის (ხანგრძლივობის) შესახებ.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: სხვადასხვა ენდოვასკულური სტენტის იმპლანტები გამოიყენება ანევრიზმის ენდოვასკულური გზით მკურნალობისათვის (EVAR)მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].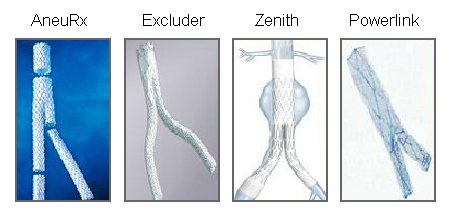 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ენდოვასკულური ჩარევა (EVAR)მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ენდოვასკულური ჩარევა (EVAR)მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].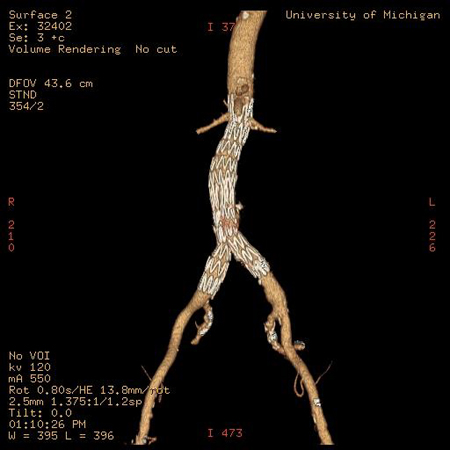
EVAR-ის შესაბამისობა უნდა დადგინდეს 0.5 მმ-ჭრილიანი CT ანგიოგრაფიით.[80]American College of Radiology. ACR Appropriateness Criteria: pulsatile abdominal mass, suspected abdominal aortic aneurysm. 2023 [internet publication].
https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69414/Narrative
ოპერატორმა კარგად უნდა იცოდეს ენდოგრაფტის გამოყენების ინსტრუქციები.
ენდოვასკულური მეთოდის შემდეგ რეკომენდებულია ულტრაბგერით ან კომპიუტერული ტომოგრაფიით ყოველწლიური კვლევა მთელი სიცოცხლის განმავლობაში.[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
ღია ქირურგიული მეთოდი
ღია ქირურგიული მეთოდი შეიძლება იყოს ტრანსპერიტონეული ან რეტროპერიტონეული. აორტის პროქსიმალურ და დისტალურ ნაწილზე კონტროლის დამყარების შემდეგ, იხსნება ანევრიზმა, ხდება სისხლმდენი არტერიების ლიგირება და პროქსიმალური აორტიდან ნორმალურ დისტალურ (მაგ.: თეძოს სეგმენტამდე) აორტამდე იდგმება პროთეზული გრაფტი. მას შემდეგ, რაც თეძოს არტერიებში ბილატერალურად აღდგება ნაკადი, ანევრიზმის პარკი იხურება გრაფტის ზემოთ.[143]Eliason JL, Upchurch GR. Endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysms repair. Circulation. 2008 Apr 1;117(13):1738-44.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.107.747923
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18378627?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტებში, რომელთანაც აღენიშნებათ ანევრიზმული დაავადების გავრცელება იუქსტარენულად და/ან ვისცერული აორტის სეგმენტზე, ან ანთებითი აორტა, ნალისებრი თირკმელი ან პრობლემური მუცელი, საჭიროა რეტროპერიტონეური მიდგომის მიზანშეწონილობის განხილვა.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[144]Sicard GA, Reilly JM, Rubin BG, et al. Transabdominal versus retroperitoneal incision for abdominal aortic surgery: report of a prospective randomized trial. J Vasc Surg. 1995 Feb;21(2):174-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7853592?tool=bestpractice.com
სწორი მილისებრი გრაფტი რეკომენდირებულია იმ შემთხვევაში, თუ არ არის თეძოს არტერიის მნიშვნელოვანი დაავადება.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
პროქსიმალური აორტის ანასტომოზი უნდა დაედოს თირკმლის არტერიასთან შეძლებისდაგვარად ახლოს.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
რეკომენდებულია აორტის გრაფტის ყველა ნაწილის მუცლის ღრუს ნაწლავების შიგთავსთან პირდაპირი კონტაქტის თავიდან აცილება.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
ჯორჯლის ქვედა არტერიის (IMA) რეიმპლანტაცია განიხილება იმ შემთხვევებში, როდესაც გაზრდილია კოლინჯის იშემიის რისკი (ანუ თან ახლავს წვრილი ნაწლავის ან ჯორჯლის ზედა არტერიის ოკლუზია, გაფართოებული დაკლაკნილი არტერია, ანამნეზში - კოლინჯის რეზექცია, ჰიპოგასტრალური პერფუზიის შენარჩუნების შეუძლებლობა, სისხლის მნიშვნელოვანი დანაკარგი ან ინტრაოპერაციული ჰიპოტენზია, ჯორჯლის ქვედა არტერიის (IMA) ტრანსპლანტის (გრაფტი) გახსნის შემდეგ ცუდი უკუდინება, კოლინჯის სისხლძარღვებში ნაკადის დინების შემცირება დოპლეროგრაფიით, ან თუ კოლინჯი ვიზუალურად იშემიურია).[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[145]Senekowitsch C, Assadian A, Assadian O, et al. Replanting the inferior mesentery artery during infrarenal aortic aneurysm repair: influence on postoperative colon ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2006 Apr;43(4):689-94.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16616221?tool=bestpractice.com
ფენესტრირებული EVAR (FEVAR)
FEVAR წარმოადგენს ღია მიდგომის ალტერნატივას იუქსტარენული და სუპრარენული აორტის ანევრიზმაზე ჩარევისათვის, იმ შემთხვევაში, როდესაც მოკლე ან დარღვეული კისერი გამორიცხავს ჩვეულებრივ მიდგომას.[146]Mohamed N, Galyfos G, Anastasiadou C, et al. Fenestrated endovascular repair for pararenal or juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms: a systematic review. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Feb;63:399-408.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31629840?tool=bestpractice.com
FEVAR-ის ენდოტრანსპლანტანტებს გააჩნიათ ხვრელები, რომლებიც შეესაბამება აორტის განშტოების არტერიებს და იძლევა კომპლექსური ანევრიზმების აღდგენის საშუალებას. 7 რეტროსპექტული კვლევის შეჯამებული ანალიზის (მათ შორის, 772 პაციენტი) თანახმად, სიკვდილობის და სამიზნე ვისცერული სისხლძარღვების გამტარობის მაჩვენებლები დამაკმაყოფილებელია (8.0% და 95.4% 1 წლის თავზე, შესაბამისად).[147]Spanos K, Antoniou GΑ, Giannoukas AD, et al. Durability of fenestrated endovascular aortic repair for juxta-renal abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2018 Apr;59(2):213-24.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29327565?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, სხვა მეტა-ანალიზები, რომლებიც განიხილავენ FEVAR-ს კომპლექსური ანევრიზმებისა და იუქსტარენალური მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმებისთვის (მათ შორის, 7061 პაციენტი და 2974 პაციენტი, შესაბამისად)არ მიუთითებს FEVAR-ის შემთხვევაში სიკვდილიანობის სხვაობაში,, მაგრამ მაღალია ხელახალი ინტერვენციის რისკი..[148]Antoniou GA, Juszczak MT, Antoniou SA, et al. Editor's choice - fenestrated or branched endovascular versus open repair for complex aortic aneurysms: meta-analysis of time to event propensity score matched data. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Feb;61(2):228-37.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2020.10.010
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33288434?tool=bestpractice.com
[149]Jones AD, Waduud MA, Walker P, et al. Meta-analysis of fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair versus open surgical repair of juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms over the last 10 years. BJS Open. 2019 Oct;3(5):572-84.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/bjs5.50178
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31592091?tool=bestpractice.com
ეს პროცედურა სრულდება როგორც რუტინულად, ასევე გადაუდებელი სამედიცინო მდგომარეობების დროს.
გეგმიური ჩარევის არჩევანი
აშშ-ში მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის მკურნალობის ქირურგიული მეთოდებიდან EVAR გამოიყენება შემთხვევათა 70%-ში.[150]Beck AW, Sedrakyan A, Mao J, et al; International Consortium of Vascular Registries. Variations in abdominal aortic aneurysm care: a report from the International Consortium of Vascular Registries. Circulation. 2016 Dec 13;134(24):1948-58.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.116.024870
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27784712?tool=bestpractice.com
დიდ ბრიტანეთში გეგმიური ინფრარენული ანევრიზმების ოპერაციის 69%, ხოლო კომპლექსური ანევრიზმების 89% ჩატარდა EVAR-ით 2014-2015 წლებში.[151]Vascular Services Quality Improvement Programme. National Vascular Registry 2021 annual report. November 2021 [internet publication].
https://www.vsqip.org.uk/reports/2021-annual-report
თუმცა, ყველა პაციენტი არ არის EVAR-ის შესაბამისი კანდიდატი. შესაბამისად, გაიდლაინებით რეკომენდებულია, ოპერატორმა ინდივიდუალურად აირჩიოს ქირურგიული მიდგომა.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[152]Kristensen SD, Knuuti J, Saraste A, et al; Authors/Task Force Members. 2014 ESC/ESA guidelines on non-cardiac surgery: cardiovascular assessment and management. Eur Heart J. 2014 Sep 14;35(35):2383-431.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/35/2383/425095
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25086026?tool=bestpractice.com
ამ გადაწყვეტილებაზე გავლენა შემდეგ ფაქტორებს აქვს: ანატომიური მახასიათებლები (მაგ. ანევრიზმის დიამეტრი, კისრის სიგრძე, კისრის დიამეტრი); სიცოცხლის სავარაუდო ხანგრძლივობა, სქესი, თანმხლები დაავადებები და პერიოპერაციული რისკი.[153]Laczynski DJ, Caputo FJ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of endovascular abdominal aortic repair in large diameter infrarenal necks. J Vasc Surg. 2021 Jul;74(1):309-315.e2.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2021.02.043
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33722632?tool=bestpractice.com
[154]Posso M, Quintana MJ, Bellmunt S, et al. GRADE-based recommendations for surgical repair of nonruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiology. 2019 Sep;70(8):701-10.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30961349?tool=bestpractice.com
რეკომენდებულია გადაწყვეტილების მიღების საერთო მიდგომა პროცედურების რისკებისა და სარგებლის გათვალისწინებით.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR უპირატესი შეიძლება იყოს პაციენტებში, რომელთაც:
აქვთ მაღალი პერიოპერაციული რისკი,
აქვთ ანატომიური ფორმა, რომელიც შეესაბამება სტენტ-გრაფტის მწარმოებლის კრიტერიუმებს (ინსტრუქციის შესაბამისად),
შეუძლიათ ქირურგიული ჩარევის შემდეგ საჭირო მეთვალყურეობის გაგრძელება.
პაციენტები,რომლებსაც აქვთ დაბალი პერიოპერაციული რისკი და შესაბამისი ანატომია,შესაძლოა ასევე იყვნენ EVAR-ის კანდიდატები,მაგრამ გასათალისწინებელია პლასტიკის უსაფრთხოება და გამძლეობა(ხელახალი ჩარევის საჭიროება)და ღია წესით პლასტიკა შესაძლოა სასურველი იყოს შედარებით ახალგაზრდა პაციენტებში.[155]Siracuse JJ, Gill HL, Graham AR, et al. Comparative safety of endovascular and open surgical repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms in low-risk male patients. J Vasc Surg. 2014 Nov;60(5):1154-8.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(14)00999-9/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24957410?tool=bestpractice.com
[156]Kontopodis N, Antoniou SA, Georgakarakos E, et al. Endovascular vs open aneurysm repair in the young: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endovasc Ther. 2015 Dec;22(6):897-904.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26403831?tool=bestpractice.com
გეგმიური ჩარევის შედეგები
EVAR-ისა და ღია მიდგომის შედაებითი ეფექტურობისა და უსაფრთხოების მონაცემები განსხვავებულია, ინტერესის სფეროსა და შედეგის მიხედვით. დღესდღეობით არსებული მტკიცებულებებია:
პოსტოპერაციულად მოკლედ დროში ნებისმიერი მიზეზით სიკვდილობა (≤30 დღე) ენდოვასკულური გზით ოპერირების დროს ნაკლებია ღია წესთან შედარებით.
გრძელვადიანი (5-10წელი)გადარჩენა მსგავსია პაციენტებში,რომლებმაც გაიარეს EVAR ღია წესით პლასტიკის დროს.[139]Amato B, Fugetto F, Compagna R, et al. Endovascular repair versus open repair in the treatment of ruptured aortic aneurysms: a systematic review. Minerva Chir. 2019 Dec;74(6):472-80.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29806754?tool=bestpractice.com
[157]Lederle FA, Kyriakides TC, Stroupe KT, et al. Open versus endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 2019 May 30;380(22):2126-35.
https://www.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1715955
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31141634?tool=bestpractice.com
[158]Bulder RMA, Bastiaannet E, Hamming JF, et al. Meta-analysis of long-term survival after elective endovascular or open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2019 Apr;106(5):523-33.
https://academic.oup.com/bjs/article/106/5/523/6092897
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30883709?tool=bestpractice.com
ოპერაციული, პერიოპერაციული და პოსტოპერაციული სიკვდილობა (≤30 დღე) უფრო მეტია ქალებში, ვიდრე მამაკაცებში (როგორც ღია, ასევე EVAR მეთოდით)[159]Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhao J, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of sex differences in outcomes after endovascular aneurysm repair for infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Jan;71(1):283-296.e4.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2019.06.105
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31466739?tool=bestpractice.com
[160]Pouncey AL, David M, Morris RI, et al. Editor's choice - systematic review and meta-analysis of sex specific differences in adverse events after open and endovascular intact abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: consistently worse outcomes for women. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Sep;62(3):367-78.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.05.029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34332836?tool=bestpractice.com
ხელახალი ჩარევის საჭიროების სიხშირე უფრო მაღალია EVAR-ის შემდეგ, ვიდრე ღია მეთოდის შემდეგ.[161]Galanakis N, Kontopodis N, Tavlas E, et al. Does a previous aortic endograft confer any protective effect during abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture? Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Vascular. 2020 Jun;28(3):241-50.
https://www.doi.org/10.1177/1708538119896464
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31937207?tool=bestpractice.com
[162]Wanken ZJ, Barnes JA, Trooboff SW, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of long-term reintervention after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Sep;72(3):1122-31.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.02.030
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32273226?tool=bestpractice.com
[163]Calderón M, Brito V, Alcaraz A, et al. Reparación Endovascular para Aneurisma de Aorta: Revisión Panorámica Sobre su Evidencia en el Mundo y su Aplicación en Latinoamérica. Value Health Reg Issues. 2018 Dec;17:94-101.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.vhri.2018.01.011
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29754017?tool=bestpractice.com
6-თვიანი პოსტოპერაციული სიკვდილობა უფრო დაბალია EVAR-ის შემდეგ, ვიდრე ღია მეთოდის შემდეგ, თუმცა ეს მეტწილად განისაზღვრება დაბალი 30-დღიანი სიკვდილობით.[164]Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, Ulug P, et al; EVAR, DREAM, OVER and ACE Trialists. Meta-analysis of individual-patient data from EVAR-1, DREAM, OVER and ACE trials comparing outcomes of endovascular or open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm over 5 years. Br J Surg. 2017 Feb;104(3):166-78.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.10430
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28160528?tool=bestpractice.com
4 მაღალი ხარისხის რანდომიზებული კვლევის (ჩართული პაციენტების ანევრიზმის დიამეტრი >5 სმ) შედეგების დაჯამება-ანალიზის შედეგად აღმოჩნდა, რომ მოკლევადიანი სიკვდილობა (30 დღე ან ჰოსპიტალიზაციის განმავლობაში) მნიშვნელოვნად დაბალი იყო პაციენტებში, რომლებიც რანდომიზებით EVAR ჯგუფში მოხვდნენ, ღია წესთან შედარებით (1.4% vs. 4.2%, შანსების თანაფარდობა [OR] 0.33, 95% სარწმუნოობის ინტერვალი 0.20 - 0.55; P <0.0001).[165]Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, et al. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 23;(1):CD004178.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24453068?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, EVAR-ის ადრეული სარგებელი იკლებს შემდგომი მეთვალყურეობის დროს.[164]Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, Ulug P, et al; EVAR, DREAM, OVER and ACE Trialists. Meta-analysis of individual-patient data from EVAR-1, DREAM, OVER and ACE trials comparing outcomes of endovascular or open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm over 5 years. Br J Surg. 2017 Feb;104(3):166-78.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.10430
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28160528?tool=bestpractice.com
[165]Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, et al. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 23;(1):CD004178.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24453068?tool=bestpractice.com
[166]Yokoyama Y, Kuno T, Takagi H. Meta-analysis of phase-specific survival after elective endovascular versus surgical repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm from randomized controlled trials and propensity score-matched studies. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Oct;72(4):1464-1472.e6.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.03.041
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32330598?tool=bestpractice.com
დიდი ბრიტანეთის 1 ენდოვასკულარული კვლევის მიხედვით, 8-წლიანი შემდგომი მეთვალყურეობის ფონზე ღია წესით ოპერაცია დაკავშირებული იყო ნაკლებ სიკვდილობასთან (ნებისმიერი მიზეზით), ვიდრე EVAR მეთოდი (46% vs. 53%, P = 0.048).[167]Patel R, Sweeting MJ, Powell JT, et al; EVAR Trial Investigators. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years' follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016 Nov 12;388(10058):2366-74.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(16)31135-7/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27743617?tool=bestpractice.com
[168]Antoniou GA, Antoniou SA, Torella F. Editor's choice - endovascular vs. open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm: systematic review and meta-analysis of updated peri-operative and long term data of randomised controlled trials. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020 Mar;59(3):385-97.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.11.030
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31899100?tool=bestpractice.com
ერთ-ერთი მეტა-ანალიზით გამოვლინდა გადარჩენადობის მრუდის გადაკვეთის წერტილი 1.8 წლის შემდეგ ოპერაციიდან, ხოლო EVAR-ის ჯგუფის პაციენტებში გადარჩენადობა უფრო დაბალი იყო, ვიდრე ღია წესის ჯგუფებში.[169]Takagi H, Ando T, Umemoto T, et al. Worse late-phase survival after elective endovascular than open surgical repair for intact abdominal aortic aneurysm. Int J Cardiol. 2017 Jun 1;236:427-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28096046?tool=bestpractice.com
იგივე ტენდენცია შეინიშნება ანევრიზმასთან დაკავშირებული სიკვდილობის კუთხით. მეტა-ანალიზის მიხედვით, 3 წლის შემდეგ ანევრიზმასთან დაკავშირებული სიკვდილობა ბევრად უფრო მაღალია EVAR ჯგუფში, ვიდრე ღია ჩარევის ჯგუფში (დაჯამებული საფრთხის თანაფარდობა [HR] 5.16, 95% CI 1.49 - 17.89; P = 0.010).[164]Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, Ulug P, et al; EVAR, DREAM, OVER and ACE Trialists. Meta-analysis of individual-patient data from EVAR-1, DREAM, OVER and ACE trials comparing outcomes of endovascular or open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm over 5 years. Br J Surg. 2017 Feb;104(3):166-78.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.10430
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28160528?tool=bestpractice.com
დიდი ბრიტანეთის ენდოვასკულარული კვლევის მიხედვით, 8-წლიანი შემდგომი მეთვალყურეობის ფონზე EVAR მეთოდი დაკავშირებული იყო ანევრიზმული სიკვდილობის უფრო მაღალ მაჩვენებლებთან, ვიდრე ღია წესი (5% vs. 1%, P = 0.0064).[167]Patel R, Sweeting MJ, Powell JT, et al; EVAR Trial Investigators. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years' follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016 Nov 12;388(10058):2366-74.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(16)31135-7/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27743617?tool=bestpractice.com
ანევრიზმის გაგლეჯვა უფრო ხშირი იყო EVAR-ის შემდეგ, ვიდრე ღია წესის დროს (5.4% vs. 1.4%, P <0.001) ფართომასშტაბიან კოჰორტულ კვლევაში, 8-წლიანი შემდგომი მეთვალყურეობით.[170]Schermerhorn ML, Buck DB, O'Malley AJ, et al. Long-term outcomes of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the Medicare population. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jul 23;373(4):328-38.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1405778
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26200979?tool=bestpractice.com
კიდევ ერთი სისტემატური მიმოხილვა, რომელიც მოიცავდა 30000-ზე მეტ პაციენტს 22 დაკვირვებით კვლევაში, არ აღმოაჩინა მნიშვნელოვანი განსხვავება ანევრიზმთან დაკავშირებულ სიკვდილიანობაში EVAR-თან შედარებით ღია რემონტთან შედარებით.[171]Kontopodis N, Galanakis N, Ioannou CV, et al. Time-to-event data meta-analysis of late outcomes of endovascular versus open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2021 Aug;74(2):628-638.e4.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2021.03.019
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33819523?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR-ის ჯგუფის პაციენტებში, ღია წესის ჯგუფთან შედარებით, გვიანი ფაზის მაღალი სიკვდილობის მაჩვენებლის მიზეზად დასახელდა შემამსუბუქებელი გარემოებები. ერთ-ერთი სისტემური მიმოხილვის დასკვნის თანახმად, EVAR-ის პროცედურის შემდეგ ხანგრძლივი გადარჩენადობა უკეთესია 2005 წლის შემდეგ დაბეჭდილ კვლევებში, რის მიზეზადაც სახელდება EVAR-ის ტექნიკების და პერიოპერაციული მოვლის გაუმჯობესება.[172]Tzani A, Doulamis IP, Katsaros I, et al. Mortality after endovascular treatment of infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms - the newer the better? Vasa. 2018 Apr;47(3):187-96.
https://econtent.hogrefe.com/doi/10.1024/0301-1526/a000685
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29334334?tool=bestpractice.com
პერიოპერაციული და მოკლევადიანი სიკვდილობა უფრო მაღალია ქალებში, ვიდრე მამაკაცებში.[159]Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhao J, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of sex differences in outcomes after endovascular aneurysm repair for infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Jan;71(1):283-296.e4.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2019.06.105
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31466739?tool=bestpractice.com
[160]Pouncey AL, David M, Morris RI, et al. Editor's choice - systematic review and meta-analysis of sex specific differences in adverse events after open and endovascular intact abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: consistently worse outcomes for women. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Sep;62(3):367-78.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.05.029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34332836?tool=bestpractice.com
ანევრიზმის გეგმიური ოპერაციის დროს სიკვდილიანობა ქალებში აჭარბებს მამაკაცების მონაცემს როგორც ღია (7.0% vs. 5.2%), ისე ენდოვასკულური მიდგომის შემთხვევაში (2.1% vs. 1.3%).[173]Schermerhorn ML, Bensley RP, Giles KA, et al. Changes in abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture and short-term mortality, 1995-2008: a retrospective observational study. Ann Surg. 2012 Oct;256(4):651-8.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3507435
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22964737?tool=bestpractice.com
დიდ ბრიტანეთში, გეგმიური ოპერაციის დროს ქალებში უფრო მაღალი იყო მოკლევადიანი სიკვდილობა, ვიდრე მამაკაცებში ღია მეთოდის გამოყენებისას (30-დღიანი სიკვდილობა: OR 1.39; 95% CI 1.25 - 1.56) და EVAR-ის შემთხვევაში (30-დღიანი სიკვდილობა: OR 1.57; 95% CI 1.23 - 2.00), მიუხედავად იმისა, რომ ქალებს ნაკლები პრეოპერაციული გულსისხლძარღვთა რისკფაქტორები ჰქონდათ.[174]Desai M, Choke E, Sayers RD, et al. Sex-related trends in mortality after elective abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery between 2002 and 2013 at National Health Service hospitals in England: less benefit for women compared with men. Eur Heart J. 2016 Dec 7;37(46):3452-60.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/37/46/3452/2661739
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27520304?tool=bestpractice.com
მდედრობითი სქესი სიკვდილობის დამოუკიდებელი რისკფაქტორია ქალებში, რომელთაც ღია წესით ჩაუტარდათ ოპერაცია; რისკი გამოხატულია პირველ წელსაც (ჯამური, ნებისმიერი მიზეზით გამოწვეული სიკვდილობა 15.9% vs. 12.1%, P <0.001) და მე-5 წელსაც (22.2% vs. 19.6%, P <0.001).[174]Desai M, Choke E, Sayers RD, et al. Sex-related trends in mortality after elective abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery between 2002 and 2013 at National Health Service hospitals in England: less benefit for women compared with men. Eur Heart J. 2016 Dec 7;37(46):3452-60.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/37/46/3452/2661739
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27520304?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR ჯგუფში გრძელვადიანი გადარჩენადობა მნიშვნელოვნად არ განსხვავდებოდა მამაკაცებსა და ქალებში (P = 0.356). ერთ-ერთი მიმოხილვის დასკვნის თანახმად, ანევრიზმების დიაგნოსტირების და EVAR-ის პროცედურის შეთავაზების დროს მორფოლოგიური კრიტერიუმების ფარგლებში არ იყო გათვალისწინებული აორტის ზომის განსხვავებები სქესის მიხედვით: ქალებს პროცედურა უფრო იშვიათად ესაჭიროებათ, აორტის მცირე ზომის გამო.[175]Ulug P, Sweeting MJ, von Allmen RS, et al. Morphological suitability for endovascular repair, non-intervention rates, and operative mortality in women and men assessed for intact abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: systematic reviews with meta-analysis. Lancet. 2017 Jun 24;389(10088):2482-91.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(17)30639-6/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28455148?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR-ის შემთხვევაში ხელახალი ჩარევის საჭიროება უფრო ხშირად დგებოდა, ვიდრე ღია მეთოდის შემდეგ. თუმცა, კლინიკურ კვლევებში აღნიშნული სიხშირე სხვადასხვაგვარია.[161]Galanakis N, Kontopodis N, Tavlas E, et al. Does a previous aortic endograft confer any protective effect during abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture? Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Vascular. 2020 Jun;28(3):241-50.
https://www.doi.org/10.1177/1708538119896464
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31937207?tool=bestpractice.com
[162]Wanken ZJ, Barnes JA, Trooboff SW, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of long-term reintervention after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Sep;72(3):1122-31.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.02.030
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32273226?tool=bestpractice.com
[164]Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, Ulug P, et al; EVAR, DREAM, OVER and ACE Trialists. Meta-analysis of individual-patient data from EVAR-1, DREAM, OVER and ACE trials comparing outcomes of endovascular or open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm over 5 years. Br J Surg. 2017 Feb;104(3):166-78.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.10430
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28160528?tool=bestpractice.com
[165]Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, et al. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 23;(1):CD004178.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24453068?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტების ინდივიდუალური მონაცემების დაჯამებული ანალიზის თანახმად, ხელახალი ჩარევა საჭირო გახდა EVAR პაციენტების 65.8%-ში I ტიპის ენდოგაჟონვის გამო (79 / 120) ხოლო 22.8%-ში II ტიპის ენდოგაჟონვის გამო (99 / 435) 5 წლის განმავლობაში.[164]Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, Ulug P, et al; EVAR, DREAM, OVER and ACE Trialists. Meta-analysis of individual-patient data from EVAR-1, DREAM, OVER and ACE trials comparing outcomes of endovascular or open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm over 5 years. Br J Surg. 2017 Feb;104(3):166-78.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.10430
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28160528?tool=bestpractice.com
ობსერვაციული კვლევების თანახმად, ანევრიზმის ან მისი გართულებების სამართავი ჩარევები უფრო ხშირად ხდება საჭირო EVAR -ის შემდეგ, ვიდრე ღია წესის შემდეგ (18.8% vs. 3.7%, P <0.001). კვლევა ჩატარდა შემდგომი 8-წლიანი მეთვალყურეობით.[170]Schermerhorn ML, Buck DB, O'Malley AJ, et al. Long-term outcomes of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the Medicare population. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jul 23;373(4):328-38.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1405778
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26200979?tool=bestpractice.com
მეტა-ანალიზის თანახმად, მნიშვნელოვანი განსხვავებები არ გამოვლინდა EVAR და ღია წესს შორის შემდეგი მიმართულებებით: მიოკარდიული სიკვდილი (შანსების თანაფარდობა 1.14, 95% სარწმუნოების ინტერვალი 0.86 - 1.52; P = 0.36), ფატალური ინსულტი (შანსების თანაფარდობა 0.81, 95% სარწმუნოების ინტერვალი 0.42 - 1.55; P = 0.52), არაფატალური ინსულტი (შანსების თანაფარდობა 0.81, 95% სარწმუნოების ინტერვალი 0.50 - 1.31; P = 0.39).[165]Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, et al. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 23;(1):CD004178.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24453068?tool=bestpractice.com
თირკმელების საშუალო სიმძიმის დისფუნქციის ან გულსისხლძარღვთა სისტემისმხრივი დაავადების მქონე პაციენტებში არ გამოვლინდა ადრეული გადარჩენადობის უპირატესობა EVAR-ის შემთხვევაში, ხოლო პერიფერიული არტერიული დაავადებების მქონე პაციენტებში ღია წესი იყო უპირატესი.[164]Powell JT, Sweeting MJ, Ulug P, et al; EVAR, DREAM, OVER and ACE Trialists. Meta-analysis of individual-patient data from EVAR-1, DREAM, OVER and ACE trials comparing outcomes of endovascular or open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm over 5 years. Br J Surg. 2017 Feb;104(3):166-78.
https://bjssjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bjs.10430
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28160528?tool=bestpractice.com
სხვა მეტა-ანალიზის თანახმად, გრძელვადიანი გადარჩენადობა გეგმიური ოპერაციის შემდეგ (EVAR ან ღია) ყველაზე ცუდი იყო თირკმელების ბოლო სტადიის დაავადების მქონე პაციენტებში (HR 3.15, 95% სარწმუნოების ინტერვალი 2.45 - 4.04) და ფილტვის ქრონიკული ობსტრუქციული დაავადების დროს ოქსიგენაციის საჭიროებისას (HR 3.05, 95% სარწმუნოების ინტერვალი 1.93 - 4.80).[176]Khashram M, Williman JA, Hider PN, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of factors influencing survival following abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016 Feb;51(2):203-15.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(15)00682-6/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26602162?tool=bestpractice.com
არსებობს დაბალი ხარისხის მტკიცებულება 4 მცირემასშტაბიანი რანდომიზებული კონტროლირებადი კვლევიდან, რომ გეგმიური ღია ჩარევა რეტროპერიტონეულად ამცირებს სისხლის დანაკარგს და საწოლ-დღეეებს, შედარებით ტრანსპერიტონეულ მიდგომასთან.[177]Mei F, Hu K, Zhao B, et al. Retroperitoneal versus transperitoneal approach for elective open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 21;6(6):CD010373.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010373.pub3
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34152003?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, რეტროპერიტონეულ და ტრანსპერიტონეულ მიდგომებს შორის გეგმიური ოპერაციის დროს განსხვავება არ გამოვლინდა (ძალიან დაბალი ხარისხის მტკიცებულება). მეტიც, რეტროპერიტონეული მიდგომა შეიძლება ზრდიდეს ჰემატომის, ქრონიკული ტკივილის, მუცლის კედლის თიაქრის რისკს (ტრანსპერიტონეულთან შედარებით).[177]Mei F, Hu K, Zhao B, et al. Retroperitoneal versus transperitoneal approach for elective open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 21;6(6):CD010373.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010373.pub3
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34152003?tool=bestpractice.com
გვერდითი მოვლენები
დამატებითი გართულებები შეიძლება იყოს შიდაგაჟონვა, გრაფტის ოკლუზია და გრაფტის მიგრაცია აორტის ყელის გაფართოებით. სისტემური მიმოხილვის თანახმად, აორტის ყელის დილატაცია გამოვლინდა EVAR პროცედურების 24.6%-ში (ჩართული იყო 9439 მამაკაცი), რის გამოც I ტიპის ენდოგაჟონვის, გრაფტის მიგრაციისა და ხელახალი ჩარევის საჭიროების სიხშირე უფრო მაღალი იყო.[178]Kouvelos GN, Oikonomou K, Antoniou GA, et al. A systematic review of proximal neck dilatation after endovascular repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Endovasc Ther. 2017 Feb;24(1):59-67.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27974495?tool=bestpractice.com
ასეთი გართულებები, როგორც წესი, გამოვლენილია ანგიოგრაფიის დასრულების ან პოსტოპერაციული ვიზუალიზაციის დროს, თუმცა კვლევები ვარაუდობენ, რომ ინტრაოპერაციული CT ანგიოგრაფია შეიძლება იყოს უფრო მგრძნობიარე მეთოდი EVAR-ის გართულებების გამოსავლენად.[179]Hansrani V, Halim UA, Goel RR, et al. Intra-operative computed tomography in endovascular aneurysm repair. Vasa. 2020 Apr;49(3):167-74.
https://www.doi.org/10.1024/0301-1526/a000840
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31904305?tool=bestpractice.com
EVAR-თან ერთად თეძოს შიდა არტერიის ორმხრივი ოკლუზია შესაძლოა მისაღები იყოს გარკვეული ანატომიური სიტუაციების შემთხვევაში იმ პაციენტებთან, რომელთაც აქვთ მაღალი რისკი ღია ქირურგიული ჩარევის შემთხვევაში. პროცედურის შემდეგ დუნდოლოების კოჭლობა უვითარდება პაციენტთა 27.9%-ს, თუმცა მათ 48%-ში მდგომარეობა გაივლის საშუალოდ 21.8 თვეში. ცალმხრივი ოკლუზიის შემდეგ ეს მოვლენა უფრო იშვიათია (შანსების თანაფარდობა 0.57, 95% სარწმუნოების ინტერვალი 0.36 - 0.91). თეძოს შიდა არტერიის IIA ოკლუზიის შემდეგ ერექციის დისფუნქცია განუვითარდა მამაკაცების 10%-დან 14%-მდე[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[180]Bosanquet DC, Wilcox C, Whitehurst L, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of internal iliac artery exclusion for patients undergoing EVAR. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2017 Apr;53(4):534-48.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(17)30056-4/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28242154?tool=bestpractice.com
თეძოს შიდა არტერიის IIA რევასკულარიზაციის ტექნიკა რაც თეძოს არტერიის სპეციალურ განმტოტველ ინსტრუმენტებს მოიცავს,საკმაოდ წარმატებულია და დაკავშირებულია დაბალი სიხშირის ავადობასთან(მაგ.კოჭლობის სიხშირე 2,15%-დან 4,1%-მდე)[181]Giosdekos A, Antonopoulos CN, Sfyroeras GS, et al. The use of iliac branch devices for preservation of flow in internal iliac artery during endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Jun;71(6):2133-44.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2019.10.087
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31901362?tool=bestpractice.com
IIA ოკლუზიის ეფექტი IIA რევასკულარიზაციასთან შედარებით კარგად არ არის შესწავლილი.[182]Sousa LHD, Baptista-Silva JC, Vasconcelos V, et al. Internal iliac artery revascularisation versus internal iliac artery occlusion for endovascular treatment of aorto-iliac aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 21;7(7):CD013168.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013168.pub2
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32691854?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ პაციენტს პარალელურად აქვს მუცლის შიდა ავთვისებიანი წარმონაქმნი, EVAR ამცირებს სიკვდილობას და დაყოვნების დროს მეორე ჩარევამდე, მიუხედავად თრომბოზული მოვლენების მნიშვნელოვანი რისკისა.[183]Kumar R, Dattani N, Asaad O, et al. Meta-analysis of outcomes following aneurysm repair in patients with synchronous intra-abdominal malignancy. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016 Dec;52(6):747-56.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27592036?tool=bestpractice.com
[184]Kouvelos GN, Patelis N, Antoniou GA, et al. Management of concomitant abdominal aortic aneurysm and colorectal cancer. J Vasc Surg. 2016 May;63(5):1384-93.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27005754?tool=bestpractice.com
ღია ჩარევით მკურნალობის გართულებები მოიცავს კარდიოლოგიურ და პულმონურ მოვლენებს, მეზენტერული სისხლძარღვების თრომბოზს, თირკმელების უკმარისობას, სისხლდენას, ჭრილობისა და იმპლანტის (გრაფტი) ინფექციას, ზურგის ტვინის იშემიას / პარაპლეგიას, ემბოლიზაციას / კიდურის იშემიას და იმპლანტის (გრაფტის) მხრივ მოგვიანებით გართულებას (ანუ აორტო-ენტერალური ფისტულა და აორტის ფსევდოანევრიზმა).[1]Dehlin JM, Upchurch GR. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2005 Jun;7(2):119-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15935120?tool=bestpractice.com
[185]Johnston KW. Multicenter prospective study of nonruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Part II. Variables predicting morbidity and mortality. J Vasc Surg. 1989 Mar;9(3):437-47.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2646460?tool=bestpractice.com
პერიოპერაციული მართვა
თანმხლები კარდიოლოგიური დაავადებების მკურნალობა:
მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის სკრინინგ-პროგრამებში პრიორიტეტი უნდა მიენიჭოს გულსისხლძარღვთა რისკების პრევენციას.[67]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: diagnosis and management. Mar 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng156
[186]Saratzis A, Sidloff D, Bown MJ. Cardiovascular risk in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Poster abstract. Paper presented at: Spring meeting for clinician scientists in training. 2017. Royal College of Physicians, London. Lancet. 2017 Feb 23;389(S89).
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(17)30485-3/fulltext
არაინვაზიური სტრეს-ტესტირება უნდა განვიხილოთ პაციენტებში, რომელთაც ≥3 კლინიკური რისკფაქტორი აქვთ (მაგ. კორონარული დაავადება, გულის შეგუბებითი უკმარისობა, ინსულტი, დიაბეტი, თირკმლის ქრონიკული უკმარისობა) და ფუნქციური შესაძლებლობები დაბალია ან უცნობია (დავალების მეტაბოლური ექვივალენტი <4).
კორონარული რევასკულარიზაცია ნაჩვენებია იმ პაციენტებისათვის, რომელთაც აღენიშნებათ მიოკარდიუმის მწვავე ინფარქტი ST-სეგმენტის ელევაციით, არასტაბილური სტენოკარდია, ან სტაბილური სტენოკარდია მარცხენა მთავარიკორონარული არტერიის, ან 3-სისხლძარღვის დაავადების შემთხვევაში, ისევე როგორც 2 სისხლძარღვის დაზიანებით მიმდინარე დაავადების დროს, როდესაც ერთ-ერთი მარცხენა უკანა დასწვრივი არტერიაა და ასევე ან არაინვაზიური სტრესტ-ტესტით იშემია ვლინდება ან განდევნის ფრაქცია <0,5-ზე.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
სისხლის გადასხმა:[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
აუტოჰემოტრანსფუზია შეიძლება ეფექტური იყოს იმ პაციენტებში, რომელთაც უტარდებათ ანევრიზმის მკურნალობა ღია წესით.
უჯრედების გამოცალკევება ან სისხლის ულტრაფილტრაცია რეკომენდირებულია იმ შემთხვევაში, თუ დიდი რაოდენობით სისხლის დანაკარგია მოსალოდნელი ან სისხლის ბანკიდან მიღებული სისხლის ტრანსფუზიით ინფიცირების რისკი მაღალია.
სისხლის გადასხმა რეკომენდებულია თუ ინტრაოპერაციულად ჰემოგლობინის დონე <10 გ/დლ-ზე სისხლის მიმდინარე დანაკარგის ფონზე. განიხილეთ ახლადგაყინული პლაზმისა და თრომბოციტების გამოყენება, თანაფარდობა ერითროციტებთან უნდა იყოს 1:1:1.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[187]Phillips AR, Tran L, Foust JE, et al. Systematic review of plasma/packed red blood cell ratio on survival in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2021 Apr;73(4):1438-44.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.10.027
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33189763?tool=bestpractice.com
ფილტვის არტერიის კათეტერის გამოყენება რუტინულად აორტაზე ქირურგიული ჩარევის დროს არ არის რეკომენდებული, თუ არ არის ჰემოდინამიკური არასტაბილობის მაღალი რისკი.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
ანევრიზმის ღია წესით მკურნალობისას ცენტრალური ვენის კათეტერიზაცია რეკომენდებულია ყველა პაციენტისათვის.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
ღრმა ვენების თრომბოზის (DVT) პროფილაქტიკა , რომელიც შედგება წყვეტილი წნევით დაწოლისა და ადრეული გააქტიურებით პროცედურის შემდეგ, რეკომენდებულია ყველა პაციენტისათვის, რომელსაც უტარდება ღია წესით ან EVAR ჩარევა.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[188]Bani-Hani MG, AL Khaffaf H, Titi MA, et al. Interventions for preventing venous thromboembolism following abdominal aortic surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jan 23;(1):CD005509.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD005509.pub2/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18254082?tool=bestpractice.com
ღია ჩარევისა და EVAR-ის დროს ჰიპოთერმიის თავიდან აცილებამ შეიძლება შეამციროს საწოლ-დღეების რაოდენობა, ინტენსიურ განყოფილებაში ჰოსპიტალიზაციის ხანგრძლივობა და ორგანული დისფუნქციის რისკი.[189]Samoila G, Ford RT, Glasbey JC, et al. The significance of hypothermia in abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 Jan;38:323-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27531090?tool=bestpractice.com
პრეოპერაციული კარდიოვასკულური რისკის შემცირება:
ცვლადი გულსისხლძარღვთა რისკფაქტორების კონტროლი პრეოპერაციულად აუმჯობესებს ჩარევის შემდგომ გადარჩენის სიხშირეს.[190]Khashram M, Williman JA, Hider PN, et al. Management of modifiable vascular risk factors improves late survival following abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 Feb;39:301-11.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27666804?tool=bestpractice.com
წინასაოპერაციო ვარჯიშმა ფიზიკური დატვირთვით დააქვეითა პოსტოპერაციული კარდიალური გართულებები მცირე რანდომიზებული კონტროლირებადი კვლევების მიხედვით.პაციენტებში,რომლებმაც გადაიტანეს ღია ან ენდოვასკულარული AAA პლასტიკა, თუმცა კოხრეინის მიმოხილვამ და ოპერაციამდე პრეჰაბილიტაციის (სავარჯიშო ტრენინგის) ცალკეული სისტემატური მიმოხილვამ არ აჩვენა რაიმე შედეგის სარგებელი.[191]Barakat HM, Shahin Y, Khan JA, et al. Preoperative supervised exercise improves outcomes after elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2016 Jul;264(1):47-53.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26756766?tool=bestpractice.com
[192]Fenton C, Tan AR, Abaraogu UO, et al. Prehabilitation exercise therapy before elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 8;7(7):CD013662.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013662.pub2
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34236703?tool=bestpractice.com
[193]Bonner RJ, Wallace T, Jones AD, et al. The content of pre-habilitative interventions for patients undergoing repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms and their effect on post-operative outcomes: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 May;61(5):756-65.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.01.043
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33678532?tool=bestpractice.com
მიუხედავად იმისა, რომ წინასაოპერაციო ვარჯიში შეიძლება სასარგებლო იყოს პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებიც გადიან AAA-ს აღდგენას, საჭიროა შემდგომი გამოკვლევა RCT-ებით, სანამ ის უფრო ფართოდ იქნება რეკომენდებული.[194]Wee IJY, Choong AMTL. A systematic review of the impact of preoperative exercise for patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Jun;71(6):2123-31.e1.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2018.09.039
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30606665?tool=bestpractice.com
პერიოპერაციული სტატინების გამოყენება ანელებს ანევრიზმის ზრდას, ამცირებს რღვევის რისკს და ამცირებს სიკვდილიანობას AAA-ს პლასტიკის ან გახეთქილი AAA-სგან.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
სტატინები უნდა დაინიშნოს ქირურგიულ ჩარევამდე სულ მცირე 1 თვით ადრე, რათა შემცირდეს გულსისხლძარღვთა მიზეზით სიკვდილობა. სტატინები გრძელდება განუსაზღვრელი ვადით.[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
[136]Risum Ø, Sandven I, Sundhagen JO, et al. Editor's choice - effect of statins on total mortality in abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Jan;61(1):114-20.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2020.08.007
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32928667?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტებს AAA-ით აქვთ მაღალი რისკი გულ-სისხლძარღვთა დაავადებების სერიოზული გართულებების მხრივ. არსებობს შეზღუდული მტკიცებულება, მაგრამ რაიმე უკუჩვენების არარსებობის შემთხვევაში, AAA-ს მქონე პაციენტებმა უნდა მიიღონ ერთჯერადი ანტითრომბოციტული თერაპია (ასპირინი ან კლოპიდოგრელი).[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[137]Aboyans V, Bauersachs R, Mazzolai L, et al. Antithrombotic therapies in aortic and peripheral arterial diseases in 2021: a consensus document from the ESC working group on aorta and peripheral vascular diseases, the ESC working group on thrombosis, and the ESC working group on cardiovascular pharmacotherapy. Eur Heart J. 2021 Oct 14;42(39):4013-24.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab390
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34279602?tool=bestpractice.com
დააკვირდეთ პაციენტებს პერიოპერაციულ პერიოდში[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
ჰიპერტენზია უნდა გაკონტროლდეს გულსისხლძარღვთა ავადობის შესამცირებლად.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
პრეოპერაციული კურსი ბეტა-ბლოკერებით შეიძლება გამართლებული იყოს პაციენტებში, რომელთაც მიოკარდიუმის იშემიის მაღალი რისკი აქვთ (გულის იშემიური დაავადება ან მიუკარდიუმის იშემია სტრეს-ტესტზე). თერაპია ქირურგიულ ჩარევამდე 1 თვით ადრე უნდა ჩატარდეს.[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
[195]Chen RJ, Chu H, Tsai LW. Impact of beta-blocker initiation timing on mortality risk in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing noncardiac surgery: a nationwide population-based cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Jan 10;6(1):e004392.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/jaha.116.004392
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28073770?tool=bestpractice.com
ფართომასშტაბიან კვლევებში, რომლებშიც ბეტა ბლოკერი ქირურგიულ ჩარევამდე რამდენიმე დღით ადრე დაიწყოს, პერიოპერაციულად ბეტა ბლოკერის სარგებელი ან ზიანი არ გამოვლინდა.[196]Brady AR, Gibbs JS, Greenhalgh RM, et al; POBBLE Trial Investigators. Perioperative beta-blockade (Pobble) for patients undergoing infrarenal vascular surgery: results of a randomized double-blind controlled trial. J Vasc Surg. 2005 Apr;41(4):602-9.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(05)00189-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15874923?tool=bestpractice.com
[197]Devereaux PJ, Yang H, Yusuf S, et al; POISE Study Group. Effects of extended-release metoprolol succinate in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery (POISE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008 May 31;371(9627):1839-47.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(08)60601-7/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18479744?tool=bestpractice.com
[198]Yang H, Raymer K, Butler R, et al. The effects of perioperative beta-blockade: results of the Metoprolol after Vascular Surgery (MaVS) study, a randomized controlled trial. Am Heart J. 2006 Nov;152(5):983-90.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17070177?tool=bestpractice.com
ანტიბიოტიკების გამოყენება:
გრამ-დადებითი და გრამ-უარყოფითი ფლორის გადასაფარად (მაგ. Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, ნაწლავის გრამუარყოფითი ბაცილები) და ტრანსპლანტანტის დაინფიცირების პრევენციის მიზნით, ნაჩვენებია ანტიბიოტიკოთერაპია იმ პაციენტებისათვის, რომელთაც უტარდებათ გეგმიური და გადაუდებელი ქირურგიული ჩარევა გაგლეჯილი მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის გამო.
ინფექციურ-ანთებითი პროცესების მკურნალობა.
როგორც კი პაციენტის მდგომარეობა სტაბილიზდება და იქნება პრიორიტეტული დაუყოვნებელი ოპერაციული ჩარევა აუცილებელია ინფექციური ან ანთებითი პათოლოგიის გამორიცხვა.
ინფექციური AAA
თუ პაციენტს აქვს საეჭვო ინფექციური ანევრიზმა, ადრეული დიაგნოსტიკა, დროული მკურნალობა ანტიბიოტიკებით და სასწრაფო ქირურგიული ჩარევა აუცილებელია შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად.[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
ღია ქირურგიული პლასტიკა ტრადიციულად განიხილება ოქროს სტანდარტად ინფექციური ანევრიზმებისთვის, თუმცა უახლესი მონაცემები ვარაუდობენ, რომ EVAR შეიძლება დაკავშირებული იყოს თანაბარ ან მაღალ შედეგებთან.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
[199]Sörelius K, Budtz-Lilly J, Mani K, et al. Systematic review of the management of mycotic aortic aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Sep;58(3):426-35.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.05.004
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31320247?tool=bestpractice.com
ხშირად საჭიროა გაფართოებული სანაცია არსებობს მეორადი ინფექციური გართულებების მაღალი რისკი და შეიძლება საჭირო გახდეს შემდგომი ოპერაცია ახალი ინფექციური დაზიანებისთვის.
ინტრაოპერაციული კულტურები უნდა იქნას მიღებული შემდგომი ანტიბიოტიკოთერაპიის სწორად წარმართვისთვის; თუმცა, ემპირიული ანტიბიოტიკები ხშირად ინიშნება, რადგან პერიფერიული სისხლის კულტურები და ქირურგიული ნიმუშების კულტურები ნეგატიურია პაციენტთა დიდ ნაწილში.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
შესაძლოა ნაჩვენები იყოს ხანგრძლივი ანტიბიოტიკოთერაპია (4-6 კვირიდან სიცოცხლის ხანგრძლივ პერიოდში) სპეციფიკური პათოგენის, ოპერაციული პლასტიკის ტიპისა და პაციენტის იმუნოლოგიური მდგომარეობის მიხედვით.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[9]Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Jan;57(1):8-93.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30698-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528142?tool=bestpractice.com
ანთებითი AAA
ანთებითი აორტიტის დროს (გამოწვეული, მაგალითად, ტაკაიასუს არტერიტით ან გიგანტურუჯრედოვანი არტერიტით) მკურნალობა ხდება კორტიკოსტეროიდების მაღალი დოზით და ქირურგიული ჩარევით.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
[200]Ben Jmaà H, Karray R, Jmal H, et al. Surgical and endoluminal management of the inflammatory aortitis: a Tunisian center experience [in French]. J Med Vasc. 2017 Jul;42(4):213-20.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28705339?tool=bestpractice.com
ენდოვასკულური ჩარევა (EVAR) - გაჟონვა
შინაგანი გაჟონვა (endoleak) არის, როდესაც სისხლის ნაკადი მუდმივად გადის გრაფტის გარეთ, ანევრიზმის პარკში.[201]Schurink GW, Aarts NJ, vanBockel JH. Endoleak after stent-graft treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Br J Surg. 1999 May;86(5):581-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10361173?tool=bestpractice.com
[202]Veith FJ, Baum RA, Ohki T, et al. Nature and significance of endoleaks and endotension: summary of opinions expressed at an international conference. J Vasc Surg. 2002 May;35(5):1029-35.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12021724?tool=bestpractice.com
ეს არ არის გართულება ღია პლასტიკის შემდეგ; ის სპეციფიკურია ენდოვასკულარული ანევრიზმის პლასიკისთვის (EVAR).
პოსტოპერაციული მეთვალყურეობით შესაძლებელია გამოხატული გაჟონვების და ანევრიზმის პარკის გადიდების დაფიქსირება.
EVAR -ის შემდგომი ენდოგაჟონვის სიხშირე არის 24%.[201]Schurink GW, Aarts NJ, vanBockel JH. Endoleak after stent-graft treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Br J Surg. 1999 May;86(5):581-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10361173?tool=bestpractice.com
არსებობს 5 ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვა[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J 3rd, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 Dec 13;146(24):e334-e482.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36322642?tool=bestpractice.com
I ტიპი:
მიმაგრების ადგილებიდან (ტიპი Iა ენდო-გრაფტის ან თეძოს ოკლუდერის პროქსიმულ ბოლოში; ტიპი Iბ დისტალურ ბოლოში) გაჟონვა, ჩვეულებრივ, დაუყოვნებლივ ხდება, მაგრამ შესაძლებელია იყოს მოგვიანებითაც.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: I ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვა მარცხენა ბარძაყის ანასტომოზის დისტალურად (შინაგანი გაჟონვა შემოფარგლულია)მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].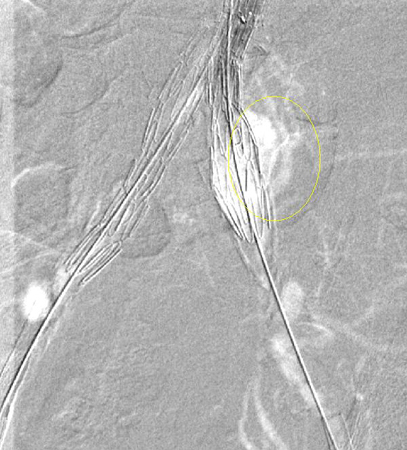
პროცედურის დამთავრების წინ უნდა ვეცადოთ ავიცილოთ თავიდან I ტიპის ენდოგაჟონვა, (მაგალითად,პროქსიმალური ზონის ბალონირება, პროქსიმალური მანჟეტის დადება, ენდოსტეპლერი).[203]van Schaik TG, Meekel JP, Hoksbergen AWJ, et al. Systematic review of embolization of type I endoleaks using liquid embolic agents. J Vasc Surg. 2021 Sep;74(3):1024-32.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2021.03.061
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33940072?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ IA ტიპის გაჟონვა პერსისტირებს, შეიძლება საჭირო გახდეს ღია მეთოდზე გადასვლა.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[204]Perini P, Bianchini Massoni C, Mariani E, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the outcome of different treatments for type 1a endoleak after EVAR. Ann Vasc Surg. 2019 Oct;60:435-46.e1.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31200054?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: გასაფართოვებელი სტენტის იმპლანტის ჩაყენება ხდება იგივე I ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვის (შემოფარგლული) გამო.მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].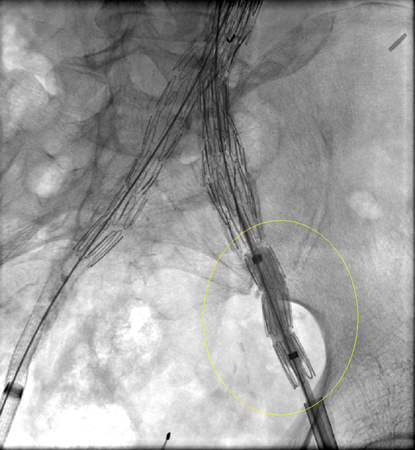 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: I ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვის პრობლემის გადაჭრა ხდება დამატებითი იმპლანტის (გაგრძელების) დამატებით.მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: I ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვის პრობლემის გადაჭრა ხდება დამატებითი იმპლანტის (გაგრძელების) დამატებით.მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].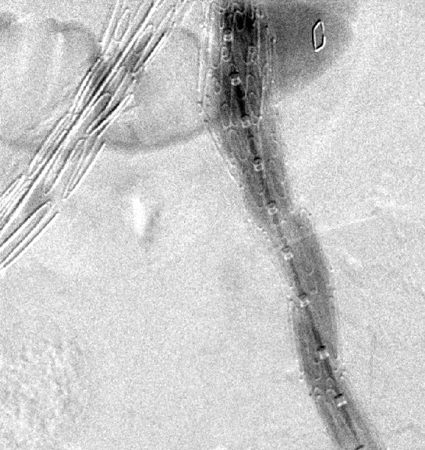
II ტიპი
დასაშვები გაჟონვა.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: II ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვის (შემოფარგლული) აღმოჩენა ხდება ოპერაციის შემდგმი საკონტროლო კომპიუტერული ტომოგრაფიითმიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].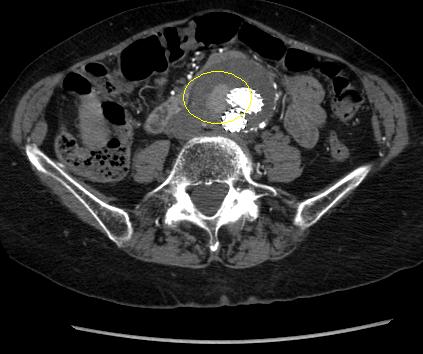
შესაძლებელი შეჩერდეს სპონტანურად, თუმცა ხანგრძლივა ჟონვამ შეიძლება გამოიწვიოს ანევრიზმის პარკის ზრდა.[205]Higashiura W, Greenberg RK, Katz E, et al. Predictive factors, morphologic effects, and proposed treatment paradigm for type II endoleaks after repair of infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007 Aug;18(8):975-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17675614?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ EVAR-ის შემდეგ 1 თვეში, კონტრასტული კტ კვლევით, II ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვა ან სხვა პრობლემა აღინიშნება, რეკომენდებულია ოპერაციიდან 6 თვეში კვლევის განმეორებით ჩატარება.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
IIტიპის ენდოგაჟონვის დაახლოებით 50% დიაგნოზირებულია 30-დღიან დაკვირვებამდე; 40% 30 დღის შემდეგ და 8% დიაგნოზირებულია მეთვალყურეობის 12 თვის შემდეგ.[206]Charisis N, Bouris V, Conway AM, et al. A systematic review and pooled meta-analysis on the incidence and temporal occurrence of type II endoleak following an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021 Aug;75:406-19.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33549794?tool=bestpractice.com
მკურნალობა რჩება საკამათო და მოწოდებულია 6-12 თვის განმავლობაში უცვლელი ზომის შემთხვევაში, ან თუ ანევრიზმის პარკის ზომა იმატებს ისე, რომ პროქსიმალური და/ან დისტალური ზონები შეიძლება დაირღვეს.[207]Mansueto G, Cenzi D, Scuro A, et al. Treatment of type II endoleak with a transcatheter transcaval approach: results at 1-year follow-up. J Vasc Surg. 2007 Jun;45(6):1120-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17543674?tool=bestpractice.com
[208]Baum RA, Stavropoulos SW, Fairman RM, et al. Endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003 Sep;14(9 Pt 1):1111-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14514802?tool=bestpractice.com
[209]Van Marrewijk CJ, Fransen G, Laheij RJ, et al. Is a type II endoleak after EVAR a harbinger of risk? Causes and outcome of open conversion and aneurysm rupture during follow-up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004 Feb;27(2):128-37.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14718893?tool=bestpractice.com
[210]Harris PL, Vallabhaneni SR, Desgranges P, et al. Incidence and risk factors of late rupture, conversion, and death after endovascular repair of infrarenal aortic aneurysms: the EUROSTAR experience. J Vasc Surg. 2000 Oct;32(4):739-49.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11013038?tool=bestpractice.com
[211]Ultee KHJ, Büttner S, Huurman R, et al. Editor's choice - systematic review and meta-analysis of the outcome of treatment for type II endoleak following endovascular aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018 Dec;56(6):794-807.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.06.009
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30104089?tool=bestpractice.com
[212]Smith T, Quencer KB. Best practice guidelines: imaging surveillance after endovascular aneurysm repair. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 May;214(5):1165-74.
https://www.doi.org/10.2214/AJR.19.22197
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32130043?tool=bestpractice.com
მკურნალობის უპირატესი მეთოდია ტრანსარტერიულად სპირალით ემბოლიზაცია, თუმცა ასევე აღრიცხულია კოლატერალური სისხლძარღვების ლაპარასკოპიული ლიგირების, ანევრიზმის პარკის პირდაპირი პერკუტანეული ტრანსლუმბალური პუნქციის, ტრანსლუმბალური ემბოლიზაციის და ტრანსკათეტერული ტრანსკავალური ემბოლიზაციის მეთოდებიც.[202]Veith FJ, Baum RA, Ohki T, et al. Nature and significance of endoleaks and endotension: summary of opinions expressed at an international conference. J Vasc Surg. 2002 May;35(5):1029-35.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12021724?tool=bestpractice.com
[207]Mansueto G, Cenzi D, Scuro A, et al. Treatment of type II endoleak with a transcatheter transcaval approach: results at 1-year follow-up. J Vasc Surg. 2007 Jun;45(6):1120-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17543674?tool=bestpractice.com
[208]Baum RA, Stavropoulos SW, Fairman RM, et al. Endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003 Sep;14(9 Pt 1):1111-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14514802?tool=bestpractice.com
[209]Van Marrewijk CJ, Fransen G, Laheij RJ, et al. Is a type II endoleak after EVAR a harbinger of risk? Causes and outcome of open conversion and aneurysm rupture during follow-up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004 Feb;27(2):128-37.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14718893?tool=bestpractice.com
[213]Steinmetz E, Rubin BG, Sanchez LA, et al. Type II endoleak after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a conservative approach with selective intervention is safe and cost-effective. J Vasc Surg. 2004 Feb;39(2):306-13.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14743129?tool=bestpractice.com
[214]Baum RA, Cope C, Fairman, et al. Translumbar embolization of type 2 endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001 Jan;12(1):111-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11200344?tool=bestpractice.com
[215]Baum RA, Carpenter JP, Golden MA, et al. Treatment of type 2 endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: comparison of transarterial and translumbar techniques. J Vasc Surg. 2002 Jan;35(1):23-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11802129?tool=bestpractice.com
[216]Schmid R, Gurke L, Aschwanden M, et al. CT-guided percutaneous embolization of a lumbar artery maintaining a type II endoleak. J Endovasc Ther. 2002 Apr;9(2):198-202.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12010100?tool=bestpractice.com
[217]Chin KM, Lee SQW, Lee HJ, et al. Preservation of stent graft after iatrogenic type III endoleak during open transperitoneal surgical intervention for complicated type II endoleak. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Jan;62:496.e1-496.e7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31394250?tool=bestpractice.com
[218]Li Q, Hou P. Sac embolization and side branch embolization for preventing type II endoleaks after endovascular aneurysm repair: a meta-analysis. J Endovasc Ther. 2020 Feb;27(1):109-16.
https://www.doi.org/10.1177/1526602819878411
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31566053?tool=bestpractice.com
[219]Akmal MM, Pabittei DR, Prapassaro T, et al. A systematic review of the current status of interventions for type II endoleak after EVAR for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Int J Surg. 2021 Nov;95:106138.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.106138
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34637951?tool=bestpractice.com
[220]Yu HYH, Lindström D, Wanhainen A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prophylactic aortic side branch embolization to prevent type II endoleaks. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Nov;72(5):1783-1792.e1.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.05.020
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32442608?tool=bestpractice.com
[221]Zhang X, Ji L, Chen MY, et al. Transarterial embolization versus translumber embolization for type Ⅱ endoleak after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a meta-analysis. Chin Med Sci J. 2020 Jun 30;35(2):135-41.
https://www.doi.org/10.24920/003618
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32684233?tool=bestpractice.com
III ტიპი:
გრაფტის დეფექტი ქსოვილებში გაჟონვით, გრაფტის მოცილება, ან ქსოვილების დაშლა.[201]Schurink GW, Aarts NJ, vanBockel JH. Endoleak after stent-graft treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Br J Surg. 1999 May;86(5):581-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10361173?tool=bestpractice.com
[202]Veith FJ, Baum RA, Ohki T, et al. Nature and significance of endoleaks and endotension: summary of opinions expressed at an international conference. J Vasc Surg. 2002 May;35(5):1029-35.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12021724?tool=bestpractice.com
[222]Kwon J, Dimuzio P, Salvatore D, et al. Incidence of stent graft failure from type IIIB endoleak in contemporary endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Feb;71(2):645-53.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2019.06.183
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31466740?tool=bestpractice.com
ჩარევა ნაჩვენებია აღმოჩენისთანავე ენდოვასკულური გაფართოება სტენტის იმპლანტით).[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[208]Baum RA, Stavropoulos SW, Fairman RM, et al. Endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003 Sep;14(9 Pt 1):1111-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14514802?tool=bestpractice.com
[212]Smith T, Quencer KB. Best practice guidelines: imaging surveillance after endovascular aneurysm repair. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 May;214(5):1165-74.
https://www.doi.org/10.2214/AJR.19.22197
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32130043?tool=bestpractice.com
[223]Lowe C, Hansrani V, Madan M, et al. Type IIIb endoleak after elective endovascular aneurysm repair: a systematic review. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2020 Jun;61(3):308-16.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29616524?tool=bestpractice.com
IV ტიპი:
გრაფტის ფოროვანი კედლებიდან გაჟონვა.[201]Schurink GW, Aarts NJ, vanBockel JH. Endoleak after stent-graft treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Br J Surg. 1999 May;86(5):581-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10361173?tool=bestpractice.com
[202]Veith FJ, Baum RA, Ohki T, et al. Nature and significance of endoleaks and endotension: summary of opinions expressed at an international conference. J Vasc Surg. 2002 May;35(5):1029-35.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12021724?tool=bestpractice.com
ეს გაჟონვა იშვიათია ახალი სტენტების იმპლანტირებისას და თვითგანკურნებადია.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[208]Baum RA, Stavropoulos SW, Fairman RM, et al. Endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003 Sep;14(9 Pt 1):1111-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14514802?tool=bestpractice.com
V ტიპი (ენდოდაჭიმვა):
მოგვიანებით კონტრასტულ კტ-ზე EVAR-ის შემდეგ შინაგანი წნევა მომატებულია პარკის წნევის ხარჯზე, შინაგანი გაჟონვის ვიზუალიზაციის გარეშე.
ენდოდაჭიმვის ფენომენი შედარებით იშვიათია ახალი თაობის გრაფტების გამოყენებისას.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
არ არსებობს შინაგანი წნევის გაზომვის სტანდარტიზებული მეთოდი და რეკომენდებული მკურნალობის შესახებ კონსენსუსი თუ არ აღინიშნება ანევრიზმის გაფართოება; თუმცა, შინაგანი წნევის შესამცირებლად მკურნალობა ანევრიზმის გასკდომის თავიდან აცილების მიზნით რეკომენდებულია პაციენტების გარკვეული ჯგუფისათვის, რომელთაც აღენიშნებათ ანევრიზმის დროში გახანგრძლივებული გაფართოება.[78]Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-77.e2.
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32369-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268916?tool=bestpractice.com
[202]Veith FJ, Baum RA, Ohki T, et al. Nature and significance of endoleaks and endotension: summary of opinions expressed at an international conference. J Vasc Surg. 2002 May;35(5):1029-35.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12021724?tool=bestpractice.com
[212]Smith T, Quencer KB. Best practice guidelines: imaging surveillance after endovascular aneurysm repair. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 May;214(5):1165-74.
https://www.doi.org/10.2214/AJR.19.22197
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32130043?tool=bestpractice.com

 ]
ერთ-ერთი სისტემური მიმოხილვის თანახმად (4 კვლევა, 3314 მონაწილე), არსებობს მაღალი ხარისხის მტკიცებულება, რომ მცირე ზომის (4 სმ- 5.5 სმ) მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის ოპერაცია გრძელვადიანი გადარჩენის თვალსაზრისით, დაკვირვებით ტაქტიკასთან შედარებით(კორეგირებული საფრთხის თანაფარდობა 0.88, 95% სარწმუნოობის ინტერვალი 0.75 - 1.02, საშუალოდ 10 წელი შემდგომი დაკვირვებით) არაეფსექტურია.[127]დაუყოვნებლივი ქირურგიულ ჩარევის დაბალი სარგებლიანობა ვლინდებოდა ყველა ასაკში, მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმის ნებისმიერ დიამეტრზე და ენდოვასკულური/ღია მეთოდების ჯგუფებშიც.[127]
]
ერთ-ერთი სისტემური მიმოხილვის თანახმად (4 კვლევა, 3314 მონაწილე), არსებობს მაღალი ხარისხის მტკიცებულება, რომ მცირე ზომის (4 სმ- 5.5 სმ) მუცლის აორტის ანევრიზმის ოპერაცია გრძელვადიანი გადარჩენის თვალსაზრისით, დაკვირვებით ტაქტიკასთან შედარებით(კორეგირებული საფრთხის თანაფარდობა 0.88, 95% სარწმუნოობის ინტერვალი 0.75 - 1.02, საშუალოდ 10 წელი შემდგომი დაკვირვებით) არაეფსექტურია.[127]დაუყოვნებლივი ქირურგიულ ჩარევის დაბალი სარგებლიანობა ვლინდებოდა ყველა ასაკში, მცირე ზომის ანევრიზმის ნებისმიერ დიამეტრზე და ენდოვასკულური/ღია მეთოდების ჯგუფებშიც.[127] ]
]
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ენდოვასკულური ჩარევა (EVAR)მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ენდოვასკულური ჩარევა (EVAR)მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].

 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: I ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვის პრობლემის გადაჭრა ხდება დამატებითი იმპლანტის (გაგრძელების) დამატებით.მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: I ტიპის შინაგანი გაჟონვის პრობლემის გადაჭრა ხდება დამატებითი იმპლანტის (გაგრძელების) დამატებით.მიჩიგანის უნივერსიტეტი, კერძოდ სისხლძარღვთა ქირურგიისა და რადიოლოგიის განყოფილების ექ. აპჩერჩის შემთხვევები [Citation ends].