Última revisão: 16 Mar 2025
Última atualização: 14 Jul 2023
Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- convulsões
- rigidez da nuca
- nível de consciência reduzido
- deficit neurológico focal
Fatores de risco
- tabagismo
- consumo moderado a elevado de bebidas alcoólicas
- história familiar de hemorragia subaracnoidea
- hemorragia subaracnoide prévia
- doença hereditária do tecido conjuntivo
- hipertensão
- trauma cranioencefálico
- infecção intracraniana
- tumor
- malformações ou fístulas arteriovenosas
- abuso de medicamentos
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
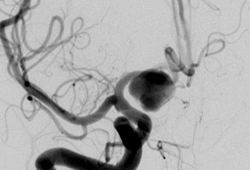
- tomografia computadorizada (TC) de crânio
- angiograma por cateter convencional
- Angiotomografia
- angiografia por ressonância magnética (ARM)
Algoritmo de tratamento
Colaboradores
Autores
Brendan Eby, MD
Assistant Professor
Departments of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis
MO
Declarações
BE has been a paid speaker at a national neurointervention fellows course sponsored by Penumbra Inc; the talk was unrelated to the sponsor's products or services.
Agradecimentos
Dr Eby would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Grasso and Dr Michael Chen, the previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
MC is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Revisores
David Altschul, MD
Chief of Neurovascular Surgery
Montefiore Medical Center
New York
NY
Declarações
DA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peter Martin, MA, BM BCh, MD, FRCP
Consultant Neurologist
Addenbrookes Hospital
Cambridge
UK
Declarações
PM declares that he has no competing interests.
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal