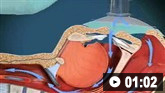
ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგია გადაუდებელი მდგომარეობაა, რომელიც სასწრაფო ყურადღებას საჭიროებს.[70]Cordonnier C, Demchuk A, Ziai W, et al. Intracerebral haemorrhage: current approaches to acute management. Lancet. 2018 Oct 6;392(10154):1257-68.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30319113?tool=bestpractice.com
ჰემატომის გაფართოების შეჩერება სამედიცინო თუ ქირურგიული ჩარევის ძირითადი მიზანია.[21]Al-Shahi Salman R, Frantzias J, Lee RJ, et al. Absolute risk and predictors of the growth of acute spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Neurol. 2018 Oct;17(10):885-94.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laneur/article/PIIS1474-4422(18)30253-9/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30120039?tool=bestpractice.com
საწყისი სტაბილიზაცია და მოთავსება
საწყისი შეფასება და მართვა მიმართული უნდა იყოს სასუნთქი გზების, სუნთქვისა და სისხლის მიმოქცევის სტაბილიზაციისკენ.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებსაც არ შეუძლიათ დამოუკიდებლად სუნთქვა ან აქვთ დაქვეითებული ცნობიერება (გლაზგოს კომის ქულა ≤8), განსახილველია ენდოტრაქეალური ინტუბაცია სასუნთქი გზების დასაცავად.
არტერიული წნევა (BP) ხშირად მომატებულია პრეზენტაციისას და საჭიროებს მკურნალობას. სისტოლური არტერიული წნევის მიზნობრივი დიაპაზონის შენარჩუნება 130-დან 150 მმ Hg-მდე მიზანშეწონილია. რეკომენდირებულია ფრთხილად ტიტრირება არტერიული წნევის მუდმივი გლუვი და მდგრადი კონტროლის უზრუნველსაყოფად, რათა თავიდან იქნას აცილებული სისტოლური არტერიული წნევის პიკი და დიდი ცვალებადობა.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
მწვავე ჰემორაგიული ინსულტის მქონე თითოეული პაციენტი უნდა მოთავსდეს ნევროლოგიურ ინტენსიური თერაპიის განყოფილებაში ჩამოთვლილი პოტენციური რისკების ან საჭიროებების გამო:
საათობრივი ნევროლოგიურ დაკვირვება
ინტუბაცია მექნიკურ ვენტილაციასთან ერთად
დაქვეითებული ცნობიერება
ჰემატომის გაფართოების მაღალი რისკი
არტერიული წნევის მონიტორინგი ან უწყვეტი ინფუზიით მონიტორინგი
გარეგანი ვენტრიკოლოსტომიის კათეტერის საწიროება, ქალასშიდა წნევის მონიტორინგი ან ქირურგიული ჩარევა.
ზოგიერთ პაციენტს ესაჭიროება გარეგანი ვენტრიკულოსტომიის კათეტერის სასწრაფო გაკეთება მწვავე ჰიდროცეფალიის გამო.
სისხლდენის ადგილმდებარეობის მიუხედავად (ნათხემის ან ნათხემის გარე), მიზანშეწონილია ძლიერი სასიცოცხლო ნიშნების მქონე ნევროლოგიურად სტაბილურ პაციენტებზე დაკვირვება, სათანადო ჰიდრატაიცისა და ნუტრიციული სტატუსის უზრუნველყოფის მიზნით.
შეფასება და მკურნალობა საუკეთესოდ მიიღწევა ნევროლოგიურ ინტენსიური თერაპიის განყოფილებაში ან dedicated ინსულტის განყოფილებაში.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[96]Adeoye O, Nyström KV, Yavagal DR, et al. Recommendations for the establishment of stroke systems of care: a 2019 update. Stroke. 2019 Jul;50(7):e187-210.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000173
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31104615?tool=bestpractice.com
[97]Langhorne P, Ramachandra S, Stroke Unit Trialists' Collaboration. Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke: network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 23;(4):CD000197.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD000197.pub4/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32324916?tool=bestpractice.com
[  ]
How does organized inpatient care compare with care on a general medical ward for people with stroke?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.3108/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება[98]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over 16s: diagnosis and initial management. Apr 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng128
]
How does organized inpatient care compare with care on a general medical ward for people with stroke?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.3108/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება[98]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over 16s: diagnosis and initial management. Apr 2022 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng128
რეკომენდებულია, რომ ყველა პაციენტი იყოს დაწესებულებაში მონიტორინგისთვის სადაც ხელმისაწვდომია 24 საათიანი გადაუდებელი ნეიროქირურგიული დახმარება ჰიდროცეფალიის ან მასის ეფექტის მწვავე გაუარესების შემთხვევებში. თუ 24-საათიანი ნეიროქირურგიული დაფარვა ხელმისაწვდომი არ არის, პაციენტი უნდა მოთავსდეს ასეთი სერვისის მქონე კლინიკაში.
ქირურგიული ჩარევა
ქირურგიული ჰემატომის ევაკუაცია კრანიოტომიის, მინიმალური ინვაზიური მიდგომების ან ვენტრიკულოსტომიის საშუალებით მიზნად ისახავს შემდგომი წნევასთან დაკავშირებული დაზიანების თავიდან აცილებას და მეორადი ფიზიოლოგიური და უჯრედული დაზიანებისგან დაცვას.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
სისხლჩაქცევა ნათხემის არეში
პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენა, რომლებიც უარესდება ნევროლოგიურად, ან აქვთ ტვინის ღეროს კომპრესია, ან ჰიდროცეფალია პარკუჭის ობსტრუქციისგან, ან ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მოცულობა ≥15 მლ, ამერიკის გულის ასოციაცია და ამერიკის ინსულტის ასოციაცია (AHA/ASA) რეკომენდებულია სისხლდენის სასწრაფო ქირურგიული მოცილება გარე პარკუჭის დრენაჟით (EVD) ან მის გარეშე. ნაჩვენებია, რომ ამ პაციენტებში ქირურგიული ჩარევა ამცირებს სიკვდილიანობას, მხოლოდ სამედიცინო მენეჯმენტთან შედარებით. ქირურგიული ევაკუაციის ეფექტურობა ფუნქციური შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად, თუმცა, გაურკვეველია და არ არის ნაჩვენები რეტროსპექტულ კვლევებში.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ჰემორაგია ნათხემის გარეთ
შეზღუდული მონაცემები ვარაუდობს, რომ სუპრატენტორული ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებში, რომლეთა მდგომარეობა გაუარესდება, კრანიოტომია ჰემატომის ევაკუაციისთვის შეიძლება ჩაითვალოს სიცოცხლის გადარჩენის ღონისძიებად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, რანდომიზებულმა კვლევებმა, რომლებიც ადარებს სტანდარტულ ქირურგიას (კრანიოტომია) კონსერვატიულ მენეჯმენტთან, არ აჩვენა აშკარა სარგებელი ქირურგიული ჩარევისთვის პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც აქვთ ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენა.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[102]Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Fernandes HM, et al. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2005 Jan 29-Feb 4;365(9457):387-97.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15680453?tool=bestpractice.com
[103]Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Rowan EN, et al; STICH II Investigators. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial lobar intracerebral haematomas (STICH II): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2013 Aug 3;382(9890):397-408.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23726393?tool=bestpractice.com
ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის მინიმალურად ინვაზიური ქირურგია
AHA/ASA-ს რეკომენდაციები მოიცავს შემდეგს:[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ სუპრატენტორული ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენა 20-დან 30 მლ-მდე მოცულობით, GCS ქულები ზომიერ დიაპაზონში (5-12), მინიმალური ინვაზიური ჰემატომის ევაკუაცია ენდოსკოპიური ან სტერეოტაქსიური ასპირაციით თრომბოლიზური გამოყენებით ან მის გარეშე შეიძლება სასარგებლო იყოს სიკვდილიანობის შესამცირებლად მხოლოდ სამედიცინო მენეჯმენტთან შედარებით.
პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ სუპრატენტორული ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენა 20-დან 30 მლ-მდე მოცულობით, GCS ქულები ზომიერ დიაპაზონში (5-12) განიხილება ჰემატომის ევაკუაციისთვის, შეიძლება გონივრული იყოს მინიმალური ინვაზიური ჰემატომის ევაკუაციის არჩევა ჩვეულებრივ კრანიოტომიასთან შედარებით ფუნქციური შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად.
პაციენტებისთვის სუპრატენტორული ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით 20-დან 30 მლ-მდე მოცულობით GCS ქულები ზომიერ დიაპაზონში (5-12), მინიმალური ინვაზიური ჰემატომის ევაკუაციის ეფექტურობა ენდოსკოპიური ან სტერეოტაქტიკური ასპირაციით თრომბოლიზური გამოყენებით ან მის გარეშე ფუნქციური შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად გაურკვეველია.
მინიმალურად ინვაზიური ქირურგიული ჩარევები მოითხოვს ქირურგისა და ცენტრის უნარს და გამოცდილებას, როგორც ამ რეკომენდაციების საფუძველს. ლიტერატურა მხარს უჭერს, რომ მინიმალური ინვაზიური ქირურგია შეიძლება ჩაითვალოს ფუნქციური შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად, ჩვეულებრივ კრანიოტომიასთან შედარებით.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, კრანიოტომიასთან შედარებით მინიმალური ინვაზიური ქირურგიის სიკვდილიანობის სარგებელი გაურკვეველია, რადგან დიდი რანდომიზებული კლინიკური კვლევების შედეგები არ ყოფილა საბოლოო.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
სისტემურმა მიმოხილვებმა და მეტა-ანალიზებმა აჩვენა, რომ პაციენტები, რომლებიც ექვემდებარებიან ადრეულ ევაკუაციას მინიმალური ინვაზიური ტექნიკის გამოყენებით (24 საათის განმავლობაში) უფრო სავარაუდოა, რომ მიაღწიონ ფუნქციურ დამოუკიდებლობას.[104]Scaggiante J, Zhang X, Mocco J, et al. Minimally invasive surgery for intracerebral hemorrhage: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2018 Nov;49(11):2612-20.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.020688
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30355183?tool=bestpractice.com
[105]Tang Y, Yin F, Fu D, et al. Efficacy and safety of minimal invasive surgery treatment in hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2018 Sep 3;18(1):136.
https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-018-1138-9
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30176811?tool=bestpractice.com
[106]Xia Z, Wu X, Li J, et al. Minimally invasive surgery is superior to conventional craniotomy in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018 Jul;115:266-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29730105?tool=bestpractice.com
[107]Cavallo C, Zhao X, Abou-Al-Shaar H, et al. Minimally invasive approaches for the evacuation of intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review. J Neurosurg Sci. 2018 Dec;62(6):718-33.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30160081?tool=bestpractice.com
ერთ-ერთი მეტა-ანალიზის თანახმად, 25-40 მლ მოცულობის ზედაპირული ჰემატომის მქონე პაციენტებში, 72 საათის ფარგლებში მკურნალობის შემთხვევაში, მინიმალურად ინვაზიური ქირურგიული ჩარევა ყველაზე ეფექტურია.[108]Zhou X, Chen J, Li Q, et al. Minimally invasive surgery for spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2012 Nov;43(11):2923-30.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/strokeaha.112.667535
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22989500?tool=bestpractice.com
ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის მინიმალურად ინვაზიური ქირურგიული ჩარევა თრომბოლიზით
მეტა-ანალიზების თანახმად, ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის შემდეგ სტერეოტაქსისის და თრომბოლიზის ერთად ჩატარება ამცირებს სიკვდილობას.[104]Scaggiante J, Zhang X, Mocco J, et al. Minimally invasive surgery for intracerebral hemorrhage: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2018 Nov;49(11):2612-20.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.020688
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30355183?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, შემდგომ ჩატარებულმა ღია ეტიკეტის კვლევამ აჩვენა, რომ მინიმალურად ინვაზიური კათეტერით ევაკუაცია, შემდგომი ალტეპლაზის თრომბოლიზით, არ ზრდის 365-ე დღეს მკურნალობაზე კარგი პასუხის მქონე პაციენტთა რიცხვს, საშუალო და დიდი ზომის ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის მქონე პირებში.[109]Hanley DF, Thompson RE, Rosenblum M, et al. Efficacy and safety of minimally invasive surgery with thrombolysis in intracerebral haemorrhage evacuation (MISTIE III): a randomised, controlled, open-label, blinded endpoint phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019 Mar 9;393(10175):1021-32.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30739747?tool=bestpractice.com
მოიამოიას დაავადება: ცერებრული რევასკულარიზაცია
ცერებროვასკულური შუნტირება შესაძლოა ჩატარდეს მოიამოიას დაავადების მქონე პაციენტებში. მოიამოიას დაავადება არის იშვიათი, პროგრესირებადი ცერებროვასკულური დაავადება, რომელიც გამოწვეულია თავის ტვინის ფუძეში არტერიების დაბლოკვით. მეტა-ანალიზების თანახმად, ქირურგიული შუნტირება უფრო ეფექტურია, ვიდრე კონსერვატიული მკურნალობა ინსულტის პრევენციის კუთხით.[110]Li Q, Gao Y, Xin W, et al. Meta-analysis of prognosis of different treatments for symptomatic moyamoya disease. World Neurosurg. 2019 Jul;127:354-61.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30995556?tool=bestpractice.com
[111]Jeon JP, Kim JE, Cho WS, et al. Meta-analysis of the surgical outcomes of symptomatic moyamoya disease in adults. J Neurosurg. 2018 Mar;128(3):793-9.
https://thejns.org/view/journals/j-neurosurg/128/3/article-p793.xml
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28474994?tool=bestpractice.com
[112]Wang G, Zhang X, Feng M, et al. Efficacy of surgical treatment on the recurrent stroke prevention for adult patients with hemorrhagic moyamoya disease. J Craniofac Surg. 2017 Nov;28(8):2113-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29088693?tool=bestpractice.com
პირდაპირი შუნტირება შესაძლოა დაკავშირებული იყოს უკეთეს კლინიკურ შედეგებთან, ვიდრე არაპირდაპირი შუნტირება.[111]Jeon JP, Kim JE, Cho WS, et al. Meta-analysis of the surgical outcomes of symptomatic moyamoya disease in adults. J Neurosurg. 2018 Mar;128(3):793-9.
https://thejns.org/view/journals/j-neurosurg/128/3/article-p793.xml
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28474994?tool=bestpractice.com
[113]Wei W, Chen X, Yu J, et al. Risk factors for postoperative stroke in adult patients with moyamoya disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2019 May 15;19(1):98.
https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-019-1327-1
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31092214?tool=bestpractice.com
მომატებული ქალასშიდა წნევის მართვა
ინტრაკრანიული ჰემორაგიის მქონე პაციენტებს მომატებული ქალასშიდა წნევის განვითარების რისკი აქვთ, რაც განპირობებულია გაფართოებული ჰემატომის, დაგროვებული შეშუპების ან ჰიდროცეფალიის ეფექტის შედეგად. პაციენტები GCS <8-ით, კლინიკური დასკვნები, რომლებიც მხარს უჭერენ ტრანსტენტორიალურ ჰერნიაციას, ან მნიშვნელოვანი ინტრავენტრიკულური სისხლდენა ან ჰიდროცეფალია, რომელიც ხელს უწყობს ცნობიერების დონის დაქვეითებას, შეიძლება განხილული იყოს ICP მონიტორინგი და მკურნალობა.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
არ გამოიყენება კორტიკოსტეროიდები, რადგან არ არის ეფექტური ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის დროს და ზრდის გართულებების რისკს.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ქირურგიული ჩარევის ან პარკუჭების დრენირების განხილვა
სისხლის პროდუქტებმა ან მასის ეფექტმა შესაძლოა გამოიწვიოს ცერებროსპინური სითხის ვენტრიკულური დინების ობსტრუქცია, ყველაზე ხშირად სილვიის წყალსადენის დონეზე. სისხლის პროდუქტებმა შესაძლოა დაარღვიოს ცერებროსპინური სითხის რეზორბცია arachnoid villis-ის მიერ (ე.ი კომუნიკაციური ჰიდროცეფალია). ამ არასტაბილურ პაციენტებში საჭიროა ოპერაციის ან პარკუჭის დრენაჟის განხილვისათვის ნეიროქირურგიული კონსულტაცია.[102]Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Fernandes HM, et al. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2005 Jan 29-Feb 4;365(9457):387-97.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15680453?tool=bestpractice.com
პარკუჭის გარეგანი შუნტის ჩადგმა
პაციენტებისთვის სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით, დიდი ინტრავენტრიკულური სისხლჩაქცევებით და ცნობიერების დონის დარღვევით, AHA/ASA რეკომენდაციას უწევს გარე პარკუჭის დრენირებას (EVD). ნაჩვენებია, რომ ამ პაციენტებში ქირურგიული ჩარევა ამცირებს სიკვდილიანობას, მხოლოდ სამედიცინო მენეჯმენტთან შედარებით. EVD-ის ეფექტურობა ფუნქციური შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად კარგად არ არის დადგენილი.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის და კლინიკური ჰიდროცეფალიის მქონე პაციენტებისთვის, მხოლოდ EVD, თეორიულად, პოტენციურად საზიანოა, განსაკუთრებით, თუ ბაზალური ცისტერნები შეკუმშულია.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
მხოლოდ EVD შეიძლება იყოს არასაკმარისი, როდესაც ინტრაკრანიალური ჰიპერტენზია აფერხებს თავის ტვინის ღეროს სისხლის მიწოდებას.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ასპირაციის უსაფრთხოების ზომები
მიუხედავად კლინიკური ან ნევროლოგიური სტაბილურობის ან სისხლდენის ადგილმდებარეობისა, ინსულტისას ხშირია ყლაპვის გართულება, ის დაკავშრებულია ასპირაციული პნევმონიის გაზრდილ რისკთან, რომლის ინციდენტობა მერყეობს 20-დან-60%-მდე.[114]Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, et al. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke. 2005 Dec;36(12):2756-63.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.str.0000190056.76543.eb
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16269630?tool=bestpractice.com
[115]Warusevitane A, Karunatilake D, Sim J, et al. Safety and effect of metoclopramide to prevent pneumonia in patients with stroke fed via nasogastric tubes trial. Stroke. 2015 Feb;46(2):454-60.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/strokeaha.114.006639
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25516196?tool=bestpractice.com
გაიდლაინის მიხედვით სანამ პაციენტი დაიწყებს საკვების, სასმელის ან პერორალური მედიკამენტების მიღებას, რეკომენდებულია დისფაგიის სკრინინგი, მეტყველების პათოლოგის ან ჯანმრთელობის მოვლის სხვა სპეციალურად ტრენირებული მომწოდებლის მიერ.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[116]Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):e344-418.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31662037?tool=bestpractice.com
რეკომენდირებულია ადრეული შეფასება დისფაგიის სკრინინგის ფორმალური ინსტრუმენტით.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტები, რომლებიიც საკვებს ვერ იღებენ პერორალურად, უსხამენ იზოტონურ სითხეებს (რათა შემცირდეს ტვინის შეშუპების რისკი) და იღებენ ენტერულ კვებას ნაზოგასტრული, ნაზოდუოდენური, ან პერსკუტანური გასტროტომური მილის საშუალებით.
[  ]
How does percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy compare with nasogastric tube feeding in people with swallowing disturbances?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.1134/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება თუმცა, მაშინაც კი, როდესაც პაციენტის კვება მიმდინარეობს ნაზოგასტრული მილებით, მათ აქვთ ქვედა ეზოფაგური დისფუნქციის, კუჭის რეფლუქსის და ნაზოგასტრული მილის არსებობით მიკროასპირაციის გამწვავების მეორეულად პნევმონიის განვითარების რისკი.[115]Warusevitane A, Karunatilake D, Sim J, et al. Safety and effect of metoclopramide to prevent pneumonia in patients with stroke fed via nasogastric tubes trial. Stroke. 2015 Feb;46(2):454-60.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/strokeaha.114.006639
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25516196?tool=bestpractice.com
]
How does percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy compare with nasogastric tube feeding in people with swallowing disturbances?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.1134/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება თუმცა, მაშინაც კი, როდესაც პაციენტის კვება მიმდინარეობს ნაზოგასტრული მილებით, მათ აქვთ ქვედა ეზოფაგური დისფუნქციის, კუჭის რეფლუქსის და ნაზოგასტრული მილის არსებობით მიკროასპირაციის გამწვავების მეორეულად პნევმონიის განვითარების რისკი.[115]Warusevitane A, Karunatilake D, Sim J, et al. Safety and effect of metoclopramide to prevent pneumonia in patients with stroke fed via nasogastric tubes trial. Stroke. 2015 Feb;46(2):454-60.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/strokeaha.114.006639
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25516196?tool=bestpractice.com
გულყრის მართვა
ანტიკონვულსანტები გამოიყენება კლინიკური გულყრების სამკურნალოდ და შეცვლილი ფსიქიკური სტატუსის მქონე პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც ეეგ-ზე ელექტროგრაფიული გულყრები აქვთ.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის კონტექსტში ახლად დაწყებული კრუნჩხვები შედარებით ხშირია (2.8%-დან 28%-მდე), და ამ კრუნჩხვების უმეტესობა ვლინდება სისხლდენის პირველი 24 საათის განმავლობაში.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
კავშირი კლინიკურ კრუნჩხვებს,ნევროლოგიურ შედეგსა და სიკვდილიანობას შორის გაურკვეველია.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ანტიკონვულსანტების პროფილაქტიკურ გამოყენებას არ გამოუვლენია სარგებელი და შესაბამისად ის არ არის რეკომენდებული.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[117]Chang RS, Leung WC, Vassallo M, et al. Antiepileptic drugs for the primary and secondary prevention of seizures after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 7;2(2):CD005398.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD005398.pub4/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35129214?tool=bestpractice.com
არტერიული წნევის მართვა
ჰიპერტენზია წარმოდგენილია იმ პაციენტთა >70%-ში, რომლებიც წარმოდგენილია მწვავე იშემიური ან ჰემორაგიული ინსულტით და შესაძლოა ასახავდეს ცერებრალურ დაზიანებაზე პასუხს.[118]Bath PM, Woodhouse L, Scutt P, et al; ENOS Trial Investigators. Efficacy of nitric oxide, with or without continuing antihypertensive treatment, for management of high blood pressure in acute stroke (ENOS): a partial-factorial randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015 Feb 14;385(9968):617-28.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(14)61121-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25465108?tool=bestpractice.com
მუდმივი არტერიული მონიტორინგი სასარგებლოა, როდესაც ამ პაციენტებში არტერიული წნევა მომატებულია. არტერიული წნევის დაქვეითება ჰიპოთეზაა ჰემატომის გაფართოების შესამცირებლად, მაგრამ ასევე პოტენციურად ამცირებს ცერებრალური პერფუზიის წნევას (CPP) და ხელს უწყობს იშემიას.[119]Anderson CS, Huang Y, Wang JG, et al. Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction in Acute Cerebral Haemorrhage Trial (INTERACT): a randomised pilot trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008 May;7(5):391-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18396107?tool=bestpractice.com
AHA/ASA-ს რეკომენდაციები მოიცავს შემდეგს:[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც ესაჭიროებათ არტერიული წნევის მკვეთრი დაქვეითება, ფრთხილად ტიტრირება არტერიული წნევის მუდმივი გლუვი და მდგრადი კონტროლის უზრუნველსაყოფად, მწვერვალებისა და დიდი სისტოლური BP (SBP) ცვალებადობის თავიდან აცილების მიზნით, შეიძლება სასარგებლო იყოს ფუნქციური შედეგის გასაუმჯობესებლად.
არტერიული წნევის მკურნალობა ინტრაცერებრული სისხლდენის დაწყებიდან 2 საათის განმავლობაში და მიზნის მიღწევა 1 საათის განმავლობაში შეიძლება სასარგებლო იყოს ჰემატომის გაფართოების რისკის შესამცირებლად და ფუნქციური შედეგის გასაუმჯობესებლად.
პაციენტებში მსუბუქი და ზომიერი სიმძიმის სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით, რომლებსაც აქვთ SBP 150-დან 220 mmHg-მდე, SBP-ის მწვავე დაქვეითება 140 mmHg-მდე სამიზნეზე 130-დან 150 mmHg-მდე შენარჩუნების მიზნით უსაფრთხოა და შეიძლება იყოს გონივრული ფუნქციური შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად. SBP-ის მწვავე დაქვეითება <130 mmHg-მდე პოტენციურად საზიანოა ამ პაციენტებში.
პაციენტებში სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით, რომლებსაც აღენიშნებათ დიდი ან მძიმე ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენა ან მათ, ვისაც ესაჭიროება ქირურგიული დეკომპრესია, არტერიული წნევის ინტენსიური შემცირების უსაფრთხოება და ეფექტურობა კარგად არ არის დადგენილი.
ეს რეკომენდაციები ეფუძნება ორ უდიდეს კვლევას ადრეული ინტენსიური არტერიული წნევის დაქვეითებისთვის ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის შემდეგ (INTERACT2 [ინტენსიური არტერიული წნევის შემცირება მწვავე ცერებრალური სისხლდენის კვლევაში] და ATACH-2 [ცერებრალური მწვავე სისხლდენის ანტიჰიპერტენზიული მკურნალობა II]), მეტა-ანალიზები და INTERACT2 და ATACH-2 კვლევების რამდენიმე პოსტ-ჰოკ ანალიზი.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ერთი რანდომიზებული კონტროლირებადი კვლევის პოსტ-ჰოკ ანალიზმა აჩვენა, რომ დაბალი CPP <60 და <70 mmHg ასოცირდება გაზრდილ სიკვდილიანობასთან და ცუდ ფუნქციურ შედეგებთან, შესაბამისად, ვარაუდობს, რომ არტერიული წნევის ცვლილებები მორგებული უნდა იყოს CPP 60-დან ≥70 mmHg-მდე. პაციენტებში დიდი ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით, ICP-ის მომატებით ან დაქვეითებული CPP.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[120]Qureshi AI, Foster LD, Lobanova I, et al. Intensive blood pressure lowering in patients with moderate to severe grade acute cerebral hemorrhage: post hoc analysis of Antihypertensive Treatment of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage (ATACH)-2 Trial. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;49(3):244-52.
https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/506358
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32585668?tool=bestpractice.com
კოაგულოპათიის შესწორება
ანტიკოაგულანტებთან ასოცირებული სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებში ანტიკოაგულაციის მიღება დაუყოვნებლივ უნდა შეწყდეს და ანტიკოაგულაციის სწრაფი უკუქცევა უნდა მოხდეს რაც შეიძლება მალე. ეს მნიშვნელოვანი ქმედებები აუმჯობესებს გადარჩენას.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ჩარევები, რომელიც ასწორებს ჰიპერკოაგულაციურ მდგომარეობას არის განლეული შედედების ფაქტორების ან თრომბოციტების აღდგენა და სპეციფიკური ფარმაკოლოგიური თერაპიების ანტიდოტები.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
თითოეული ანტიკოაგულანტი აგენტისთვის შესაძლოა ხელმისაწვდომი არ იყოს სპეციფიკური ანტიდოტი; ასეთ დროს, უნდა შეწყდეს მდგომარეობის გამომწვევი აგენტის გამოყენება.
K ვიტამინის ანტაგონისტზე მყოფი პაციენტები (VKA; მაგ., ვარფარინი)
VKA-სთან ასოცირებული სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებში, რომელთა საერთაშორისო ნორმალიზებული თანაფარდობა (INR) არის ≥2.0, რეკომენდებულია 4-ფაქტორიანი პროთრომბინის კომპლექსური კონცენტრატი (PCC) უპირატესობას ანიჭებს ახალ გაყინულ პლაზმას INR-ის სწრაფი კორექციის მისაღწევად და ჰემატომის გაფართოების შეზღუდვის მიზნით.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტებში VKA-სთან ასოცირებული სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით INR 1.3-დან 1.9-მდე, შეიძლება მიზანშეწონილი იყოს 4-ფაქტორიანი PCC-ის გამოყენება INR-ის სწრაფი კორექციის მისაღწევად და ჰემატომის გაფართოების შესაზღუდად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ყველა პაციენტს, რომელსაც აქვს ინტრაკრანიალური სისხლდენა, უნდა მიეცეს K ვიტამინი ინტრავენურად უშუალოდ კოაგულაციის ფაქტორის ჩანაცვლების შემდეგ (PCC ან სხვა), რათა თავიდან აიცილოს INR-ის შემდგომი ზრდა და შემდგომი ჰემატომის გაფართოება.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ფაქტორების კონცენტრატებთან ან რეკომბინანტულ აქტივირებულ VII ფაქტორთან შედარებით, ახლად გაყინული პლაზმა ახდენს INR-ის ნორმალიზებას უფრო ნელა, უფრო ნელა შეჰყავთ და საჭიროებს ინფუზიის უფრო დიდ მოცულობას.[121]Mayer SA, Brun NC, Begtrup K, et al. Recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2005 Feb 24;352(8):777-85.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa042991
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15728810?tool=bestpractice.com
INR უნდა შემოწმდეს ინფუზიის შემდეგ.
ადამიანის 4-ფაქტორიანი პროთრომბინის კომპლექსის კონცენტრატი შეიცავს K ვიტამინზე დამოკიდებულ შედედების II, VII, IX და X ფაქტორებს. აღნიშნული იწვევს საერთაშორისო ნორმალიზებული შეფარდების უფრო სწრაფ აღდგენას მნიშვნელოვნად ნაკლები ინტრავენური მოცულობის ინფუზიით. INR უნდა შემოწმდეს 15-60 წუთის შემდეგ, შემდეგ ყოველ 6-8 საათში პირველი 24-48 საათის განმავლობაში მისი ეფექტის შესაძლო აღდგენის გამო.[122]Frontera JA, Lewin JJ 3rd, Rabinstein AA, et al. Guideline for reversal of antithrombotics in intracranial hemorrhage: executive summary. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and the Society of Critical Care Medicine. Crit Care Med. 2016 Dec;44(12):2251-7.
https://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/Fulltext/2016/12000/Guideline_for_Reversal_of_Antithrombotics_in.16.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27858808?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ INR რჩება მომატებული,უნდა მოიძიოთ სპეციალისტის რჩევა შემდგომი მენეჯმენტის შესახებ. შეიძლება მითითებული იყოს ადამიანისგან მიღებული 4-ფაქტორიანი PCC.
ჰეპარინზე მყოფი პაციენტები
პირველადი ვარიანტი ჰიპოკოაგულაციისთვის, რაც გამოწვეულია ინტრავენურად არაფრაქციული ჰეპარინით არის პროტამინი.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[123]Garcia DA, Baglin TP, Weitz JI, et al. Parenteral anticoagulants: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012 Feb;141(2 suppl):e24-43S.
https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(12)60118-4/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22315264?tool=bestpractice.com
პროტამინის გამოყენება შესაძლებელია დაბალმოლეულური ჰეპარინით გამოწვეული ჰიპოკოაგულაციის აღდგენისთვისაც.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
გაიდლაინებში სპეციფიკური რეკომენდაციები გაწერილია დაბალმოლეკულური ჰეპარინის გამოყენებიდან გასული დროის მიხედვით.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[123]Garcia DA, Baglin TP, Weitz JI, et al. Parenteral anticoagulants: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012 Feb;141(2 suppl):e24-43S.
https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(12)60118-4/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22315264?tool=bestpractice.com
თევზზე ალერგიის ან ვაზექტომიის ან პროტამინის შემცველი ინსულინის ინექციის ანამნეზის მქონე პაციენტებს ანაფილაქსიის რისკი აქვთ და საჭიროა მათი ფრთხილი მონიტორინგი.
თრომბინის პირდაპირი ინჰიბიტორებით მომკურნალე პაციენტები
დაბიგატრანთან ასოცირებული სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებში, იდარუციზუმაბს შეუძლია შეცვალოს დაბიგატრანის ანტიკოაგულაციური ეფექტი.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
იდარუკიზუმაბი არის მონოკლონური ანტისხეულის ფრაგმენტი, რომელიც უკავშირდება დაბიგატრანს და სწრაფად და სრულად ახერხებს დაბიგატრანის ეფექტის უკუქცევას კვლევაში მონაწილე პაციენტთა 88-დან-90%-ში.[124]Pollack CV Jr, Reilly PA, Eikelboom J, et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal. N Engl J Med. 2015 Aug 6;373(6):511-20.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1502000
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26095746?tool=bestpractice.com
როდესაც იდარუციზუმაბი არ არის ხელმისაწვდომი, გააქტიურებული PCC ან PCC შეიძლება ჩაითვალოს ჰემოსტაზის გასაუმჯობესებლად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტებში დაბიგატრან- ან Xa ფაქტორის ინჰიბიტორთან ასოცირებული სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით, თუ პირდაპირი პერორალური ანტიკოაგულანტი მიღებულ იქნა წინა რამდენიმე საათის განმავლობაში, გააქტიურებული ნახშირი შეიძლება იყოს გონივრული შეწოვის თავიდან ასაცილებლად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
არსებობს დავა საუკეთესო მიდგომასთნ დაკავშირებით ინტრაკრანიული ჰემორაგიის მქონე პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებიც იღებენ თრომბინის პირდაპირ ინჰიბიტორს სპეციფიკური ანტიდოტის გარეშე. შემოთავაზებულია არაერთი სტრატეგია, მათ შორის გააქტიურებული ნახშირის გამოყენება პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც ვსინჯავთ თრომბინის პირდაპირი პერორალური ინჰიბიტორის მიღებიდან 2 საათის ფარგლებში. სხვა რეკომენდაციებია: პროთრომბინის კომპლექსის კონცენტრატის, მისი გააქტიურებული ფორმის და გადაუდებელი ჰემოდიალიზის შესრულება.[122]Frontera JA, Lewin JJ 3rd, Rabinstein AA, et al. Guideline for reversal of antithrombotics in intracranial hemorrhage: executive summary. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and the Society of Critical Care Medicine. Crit Care Med. 2016 Dec;44(12):2251-7.
https://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/Fulltext/2016/12000/Guideline_for_Reversal_of_Antithrombotics_in.16.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27858808?tool=bestpractice.com
Xa ფაქტორის ინჰიბიტორებით მომკურნალე პაციენტები
პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც აქვთ უშუალოდ Xa ფაქტორის ინჰიბიტორთან ასოცირებული სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრული სისხლდენა, AHA/ASA რეკომენდაციას იძლევა, რომ რეკომბინანტული კოაგულაციის ფაქტორი Xa (ანდექსანატ ალფა) გონივრულია Xa ფაქტორის ინჰიბიტორების ანტიკოაგულანტული ეფექტის შესაცვლელად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ანდექსანეტ ალფა არის ადამიანის ფაქტორის მოდიფიცირებული Xa ცილა, რომელიც წარმოადგენს Xa ფაქტორის ინჰიბიტორების აპიქსაბანის და რივაროქსაბანის შებრუნებულ აგენტს. ზოგიერთ ქვეყანაში ის შეიძლება გამოყენებულ იქნას Xa ფაქტორის სხვა ინჰიბიტორებისთვის, როგორიცაა ედოქსაბანი და ბეტრიქსაბანი. მულტიცენტრულმა, პროსპექტულმა, ღია ეტიკეტის, ერთი ჯგუფის კვლევამ აჩვენა, რომ ანდექსანეტ ალფათი მკურნალობა ამცირებს ანტი-ფაქტორ Xa-ს აქტივობას მძიმე მწვავე სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებში, რომლებიც იყენებენ Xa ფაქტორის ინჰიბიტორს; პაციენტთა 82%-ს ჰქონდა შესანიშნავი ან კარგი ჰემოსტატური ეფექტურობა 12 საათის განმავლობაში.[125]Connolly SJ, Crowther M, Eikelboom JW, et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 4;380(14):1326-35.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa1814051
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30730782?tool=bestpractice.com
პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც აქვთ უშუალოდ Xa ფაქტორის ინჰიბიტორთან ასოცირებული სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენა, AHA/ASA რეკომენდაციას იძლევა, რომ 4-ფაქტორიანი PCC ან გააქტიურებული PCC ასევე შეიძლება ჩაითვალოს ჰემოსტაზის გასაუმჯობესებლად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
თრომბოლიტიკურ თერაპიაზე მყოფი პაციენტები
იშემიური ინსულტის დროს ალტეპლაზას ინტრავენური შეყვანიდან 24 საათის განმავლობაში სიმპტომატური ინტრაკრანიალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებში, ალტეპლაზას ინფუზია უნდა შეწყდეს.[116]Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):e344-418.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31662037?tool=bestpractice.com
კრიოპრეციპიტატი (რომელიც მოიცავს VIII ფაქტორს) უნდა შეიყვანოთ 10-30 წუთის განმავლობაში.[116]Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):e344-418.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31662037?tool=bestpractice.com
დამატებითი დოზა უნდა დაინიშნოს, თუ ფიბრინოგენის დონე დაბალია (<150 მგ/დლ).[116]Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):e344-418.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31662037?tool=bestpractice.com
ტრანექსამინის მჟავა ან ამინოკაპრონის მჟავა შეიძლება სასარგებლო იყოს ზოგიერთი პაციენტისთვის, მაგრამ განსაკუთრებით მაშინ, როდესაც სისხლის პროდუქტები უკუნაჩვენებია ან უარყოფილია პაციენტის/ოჯახის მიერ ან თუ კრიოპრეციპიტატი დროულად არ არის ხელმისაწვდომი.[116]Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):e344-418.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31662037?tool=bestpractice.com
გასათვალისწინებელია ჰემატოლოგისა და ნეიროქირურგის კონსულტაციები.[116]Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):e344-418.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31662037?tool=bestpractice.com
ქსოვილის პლაზმინოგენის აქტივატორთან დაკავშირებული ჰემორაგიის პროგნოზი არაკეთილსაიმედოა, ხოლო ამ შემთხვევაში კოაგულაციის წარმართვის შესახებ მონაცემები არასაკმარისია. კოაგულოპათიის კომპლექსური ბუნებიდან გამომდინარე განსახილველია ჰემატოლოგთან კონსულტაცია.
თრომბოციტების ტრანსფუზია
სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებიც მკურნალობენ ასპირინით და საჭიროებენ გადაუდებელ ნეიროქირურგიას, AHA/ASA რეკომენდაციას იძლევა, რომ თრომბოციტების გადასხმა შეიძლება სასარგებლო იყოს პოსტოპერაციული სისხლდენისა და სიკვდილიანობის შესამცირებლად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
თრომბოციტების ინფუზია რეკომენდებულია თრომბოციტოპენიისთვის, რათა თრომბოციტების დონემ სისხლში მიაღწიოს >100000 მიკროლიტრზე. არ არსებობს მონაცემები, რომელიც მიუთითებს ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის შემდეგ თრომბოციტების ოპტიმალურ მინიმალურ დონეზე, მაგრამ გონივრულია, რომ სისხლში დონემ მიაღწიოს >100000-ს მიკროლიტრზე გამოვლინებიდან პირველი 24 საათის განმავლობაში, როდესაც ჰემორაგიის გაფართოების რისკი მაღალია.
სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებიც მკურნალობენ ასპირინით და არ არის დაგეგმილი სასწრაფო ოპერაციისთვის, თრომბოციტების გადასხმა პოტენციურად საზიანოა და არ უნდა ჩატარდეს.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[126]Al-Shahi Salman R, Law ZK, Bath PM, et al. Haemostatic therapies for acute spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;(4):CD005951.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD005951.pub4/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29664991?tool=bestpractice.com
ანტიაგრეგანტული მედიკამენტები ამცირებენ თრომბოციტების აქტივობას და პაციენტებს ხდიან მიდრეკილს სისხლჩაქცევების და სისხლდენის გართულებების მიმართ. ეს ფუნქციური შემცირება დაკავშირებულია ადრეული კოლტის ზრდასთან და ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის შემდეგ 3 თვიანი შედეგის გაუარესებასთან.[127]Thompson BB, Bejot Y, Caso V, et al. Prior antiplatelet therapy and outcome following intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review. Neurology. 2010 Oct 12;75(15):1333-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20826714?tool=bestpractice.com
[128]Naidech AM, Jovanovic B, Liebling S, et al. Reduced platelet activity is associated with early clot growth and worse 3-month outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2009 Jul;40(7):2398-401.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/strokeaha.109.550939
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19443791?tool=bestpractice.com
ანტიაგრეგანტული თერაპიის ეფექტების გაზრდის და ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის გაფართოების მინიმიზაციის მიზნით თრომბოციტების ინფუზია იწვევს სიკვდილის ან ქმედუუნარობის უფრო მეტ რისკს, ვიდრე სტანდარტული მკურნალობა (ერთ-ერთი რანდომიზებული კონტროლორებული კვლევის მიხედვით).[126]Al-Shahi Salman R, Law ZK, Bath PM, et al. Haemostatic therapies for acute spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;(4):CD005951.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD005951.pub4/full
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29664991?tool=bestpractice.com
[129]Baharoglu MI, Cordonnier C, Al-Shahi Salman R, et al. Platelet transfusion versus standard care after acute stroke due to spontaneous cerebral haemorrhage associated with antiplatelet therapy (PATCH): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016 Jun 25;387(10038):2605-13.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27178479?tool=bestpractice.com
ცხელების მართვა.
ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის შემდეგ ცხელება ხშირია, განსაკუთრებით პარკუჭშიდა ჰემორაგიის დროს. ცხელების ხანგრძლივი მიმდინარეობა დაკავშირებულია უარეს კლინიკურ შედეგებთან და მიჩნეულია დამოუკიდებელ პროგნოზულ ფაქტორად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
მწვავე იშემიური ინსულტის ან ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის მქონე პაციენტებზე ჩატარებული რანდომიზებული კონტროლირებული კვლევების მონაცემთა შეგროვების შემდგომმა ანალიზმა აჩვენა, რომ პარაცეტამოლით მკურნალობა კლინიკურ შედეგებს აუმჯობესებს პაციენტებში, რომელთა სხეულის საბაზისო ტემპერატურა არის 37°C - 39°C.[130]den Hertog HM, van der Worp HB, van Gemert HM, et al; PAIS Investigators. The Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) In Stroke (PAIS) trial: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase III trial. Lancet Neurol. 2009 May;8(5):434-40.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19297248?tool=bestpractice.com
მულტიცენტრული, რანდომიზებული, ორმაგი ბრმა, პლაცებო-კონტროლირებული კლინიკური კვლევა შეწყდა ნაადრევად, ვინაიდან მონაწილეების ჩართვა მიმდინარეობდა ნელა და დაფინანსება საკმარისი არ იყო.[131]de Ridder IR, den Hertog HM, van Gemert HM, et al. PAIS 2 (Paracetamol [Acetaminophen] in Stroke 2): results of a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Stroke. 2017 Apr;48(4):977-82.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015957
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28289240?tool=bestpractice.com
მიუხედავად საბოლოო მტკიცებულების ნაკლებობისა, ცხელების შესამცირებლად მკურნალობა გონივრულია.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
გლუკოზის კონტროლი
პაციენტებში სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით, AHA/ASA რეკომენდაციას უწევს ჰიპოგლიკემიის (<2,2-3,3 მმოლ/ლ [<40-60 მგ/დლ]) მკურნალობას სიკვდილიანობის შესამცირებლად. პაციენტებში სპონტანური ინტრაცერებრალური სისხლდენით, ზომიერი და მძიმე ჰიპერგლიკემიის მკურნალობა (>10.0-11.1 მმოლ/ლ [>180-200 მგ/დლ]) მიზანშეწონილია შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
კრიტიკულად დაავადებულ პაციენტებში, რომლებსაც აქვთ მუდმივი ჰიპერგლიკემია (≥10.0 მმოლ/ლ [≥180 მგ/დლ] დადასტურებული ორჯერ 24 საათის განმავლობაში), უნდა დაიწყოს ცვლადი სიჩქარის ინტრავენური ინსულინის ინფუზია. გლუკოზის სამიზნე დიაპაზონი 7,8-დან 10,0 მმოლ/ლ-მდე (140-დან 180 მგ/დლ-მდე) რეკომენდებულია ჰიპერგლიკემიის მქონე კრიტიკულად დაავადებული პაციენტების უმეტესობისთვის.[132]American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024 Jan 1;47(supplement_1):S1-4.
https://diabetesjournals.org/care/issue/47/Supplement_1
გლუკოზის სამიზნე დიაპაზონი 6,1-დან 7,8 მმოლ/ლ-მდე (110-დან 140 მგ/დლ-მდე) შეიძლება იყოს შესაბამისი და მისაღები შერჩეულ პაციენტებში (მაგ., კრიტიკულად დაავადებული პოსტოპერაციული პაციენტები), თუ ამის მიღწევა შესაძლებელია მნიშვნელოვანი ჰიპოგლიკემიის გარეშე.[132]American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024 Jan 1;47(supplement_1):S1-4.
https://diabetesjournals.org/care/issue/47/Supplement_1
ICU-ში შეყვანილი პაციენტებისთვის, რომლებსაც აღენიშნებათ მაღალი გლუკოზა, ასევე შეიძლება განიხილებოდეს ინტრავენური ინსულინის პროტოკოლი. იხილეთ ადგილობრივი სპეციალისტის პროტოკოლი ინსულინის დოზირების გაიდლაინებისთვის.
არანამკურნალები ჰიპერგლიკემია დამოუკიდებლად არის დაკავშირებული არაკეთილსაიმედო პროგნოზთან ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის მქონე პაციენტებში.[133]Saxena A, Anderson CS, Wang X, et al. Prognostic significance of hyperglycemia in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: the INTERACT2 Study. Stroke. 2016 Mar;47(3):682-8.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.011627
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26814235?tool=bestpractice.com
[134]Zheng J, Yu Z, Ma L, et al. Association between blood glucose and functional outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018 Jun;114:e756-65.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29555604?tool=bestpractice.com
შესაბამისად, გლუკოზის სწრაფი კორექცია რეკომენდებულია შედეგების გასაუმჯობესებლად მტკიცებულებების ნაკლებობის მიუხედავად.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ფიქრობენ, რომ გლუკოზის კონტროლმა შესაძლოა გაზარდოს ჰიპოგლიკემიის ინციდონტობა, რამაც შესაძლოა გამოიწვიოს უარესი შედეგები. ამიტომ საჭიროა გლუკოზის მჭიდრო მონიტორინგი და თავიდან უნდა იქნას აცილებული ჰიპერგლიკემია და ჰიპოგლიკემია.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
ღრმა ვენების თრომბოზის (DVT) პროფილაქტიკა
ვენური თრომბოემბოლიზმის რისკი იშემიურ ინსულტთან შედარებით შესაძლოა მაღალი იყოს ჰემორაგიული ინსულტის მქონე პაციენტებში.[135]Skaf E, Stein PD, Beemath A, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients with ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Am J Cardiol. 2005 Dec 15;96(12):1731-3.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16360366?tool=bestpractice.com
ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის არსებობა ართულებს ღრმა ვენების თრომბოზის და/ან ფილტვის ემბოლიის პროფილაქტიკისთვის საუკეთესო მიდგომის შერჩევას.
ხანგამოშვებითი პნევმატური კომპრესია მნიშვნელოვნად ამცირებს DVT-ის რისკს ჰემორაგიული ინსულტის შემდეგ და უნდა დაიწყოს ინტრაკრანიალური სისხლდენის მქონე პაციენტებისთვის ჰოსპიტალიზაციისას.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[136]Nyquist P, Bautista C, Jichici D, et al. Prophylaxis of venous thrombosis in neurocritical care patients: an evidence-based guideline. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society. Neurocrit Care. 2016 Feb;24(1):47-60.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26646118?tool=bestpractice.com
[137]Dennis M, Sandercock P, Reid J, et al; CLOTS (Clots in Legs Or sTockings after Stroke) Trials Collaboration. Effectiveness of intermittent pneumatic compression in reduction of risk of deep vein thrombosis in patients who have had a stroke (CLOTS 3): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2013 Aug 10;382(9891):516-24.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(13)61050-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23727163?tool=bestpractice.com
[138]Zhang D, Li F, Li X, et al. Effect of intermittent pneumatic compression on preventing deep vein thrombosis among stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2018 Jun;15(3):189-96.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29729658?tool=bestpractice.com
მხოლოდ მუხლამდე ან ბარძაყამდე სიგრძის კომპრესიული წინდები არ არის სასარგებლო ამ პაციენტებში ვენური თრომბოემბოლიის პროფილაქტიკისთვის.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
რეკომენდებულია პაციენტის ადრეული მობილიზაცია, მაგრამ ეფექტურობა არ არის დამტკიცებული რანდომიზებულ კონტროლირებად კვლევებში.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
განსახილველია დაბალი დოზის არაფრაქციული ან დაბალმოლეკულური ჰეპარინი , იმ შემთხვევაში თუ არ არსებობს სისხლდენის გაგრძელების საშიშროება[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[136]Nyquist P, Bautista C, Jichici D, et al. Prophylaxis of venous thrombosis in neurocritical care patients: an evidence-based guideline. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society. Neurocrit Care. 2016 Feb;24(1):47-60.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26646118?tool=bestpractice.com
[139]Boeer A, Voth E, Henze T, et al. Early heparin therapy in patients with spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 May;54(5):466-7.
https://jnnp.bmj.com/content/jnnp/54/5/466.full.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1865215?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ პაციენტს განუვითარდა ღრმა ვენების თრომბოზი ან ფილტვის ემბოლია, განსახილველია სისტემური ანტიკოაგულაცია ან ქვედა ღრუ ვენის ფილტრის მოთავსება. ჯერჯერობით რისკებისა და სარგებლის მაჩვენებლები დასადგენია. გადაწყვეტილების მიღებისთვის მნიშვნელოვანი ფაქტორებია ჰემორაგიის შემდეგ გასული დრო, ჰემატომის სტაბილურობა, ჰემორაგიის გამომწვევი მიზეზი და პაციენტის კლინიკური ნიშნები.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
რეაბილიტაცია
მრავალი პაციენტი განიცდის გადაადგილების და მობილობის შეზღუდვას, რაც ამცირებს მათი სიცოცხლის ხარისხს. გარდა ამისა, ინსულტის შემდეგ მალე შეიძლება განვითარდეს უძრაობასთან დაკავშირებული გართულებები (მაგ.ღრმა ვენების თრომბოზი, ფილტვის ემბოლია, ასპირაციული პნევმონია).[140]Winstein CJ, Stein J, Arena R, et al. Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2016 Jun;47(6):e98-169.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/str.0000000000000098
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27145936?tool=bestpractice.com
რეაბილიტაციის მიზანია, რომ პაციენტი დაუბრუნდეს მისაღებ სოციალურ და/ან პროფესიულ ცხოვრების წესს. ინსულტის შემდეგ რეკომენდებულია ადრეული რეაბილიტაცია.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[140]Winstein CJ, Stein J, Arena R, et al. Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2016 Jun;47(6):e98-169.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/str.0000000000000098
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27145936?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, ერთ-ერთმა კვლევამ ვერ აღმოაჩინა ძალიან ადრეული, ინტენსიური მობილიზაციის მეტი სარგებელი (მაგ. საწოლიდან ადგომის და მობილობის მრავლობითი სესიები) ინსულტის განვითარებიდან 24 საათის ფარგლებში (იშემიური ან ჰემორაგიული), სტანდარტულ მკურნალობასთან შედარებით.[141]Cumming TB, Churilov L, Collier J, et al. Early mobilization and quality of life after stroke: findings from AVERT. Neurology. 2019 Aug 13;93(7):e717-28.
https://n.neurology.org/content/93/7/e717.long
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31350296?tool=bestpractice.com
[  ]
How does very early mobilization compare with standard care after stroke?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2507/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება[მტკიცებულების დონე B]24cea457-7e11-4cf0-959f-594b1eb09d68ccaBრით განსხვავდება ძალიან ადრეული მობილიზაცია ინსულტის სტანდარტული მოვლისგან? სხვა პატარა კვლევებმა დაადგინა, რომ რეაბილიტაციის დაწყება ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის გამოვლინებიდან 24-48 საათში აუმჯობესებს გადარჩენადობას და ფუნქციურ შედეგებს შემდგომი მეთვალყრეობისას 3-6 თვის შემდეგ.[142]Liu N, Cadilhac DA, Andrew NE, et al. Randomized controlled trial of early rehabilitation after intracerebral hemorrhage stroke: difference in outcomes within 6 months of stroke. Stroke. 2014 Dec;45(12):3502-7.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/strokeaha.114.005661
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25336514?tool=bestpractice.com
]
How does very early mobilization compare with standard care after stroke?/cca.html?targetUrl=https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cca/doi/10.1002/cca.2507/fullსწორი პასუხის ჩვენება[მტკიცებულების დონე B]24cea457-7e11-4cf0-959f-594b1eb09d68ccaBრით განსხვავდება ძალიან ადრეული მობილიზაცია ინსულტის სტანდარტული მოვლისგან? სხვა პატარა კვლევებმა დაადგინა, რომ რეაბილიტაციის დაწყება ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის გამოვლინებიდან 24-48 საათში აუმჯობესებს გადარჩენადობას და ფუნქციურ შედეგებს შემდგომი მეთვალყრეობისას 3-6 თვის შემდეგ.[142]Liu N, Cadilhac DA, Andrew NE, et al. Randomized controlled trial of early rehabilitation after intracerebral hemorrhage stroke: difference in outcomes within 6 months of stroke. Stroke. 2014 Dec;45(12):3502-7.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/strokeaha.114.005661
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25336514?tool=bestpractice.com
ინსულტის მულტიდისციპლინური რეაბილიტაცია
არსებობს მტკიცებულებები, რომ რეაბილიტაციის შედეგები უკეთესია, როდესაც ჩართულია მულტიდისციპლინური გუნდი, რომელსაც გამოცდილება აქვს ინსულტის რეაბილიტაციაში.[143]Sall J, Eapen BC, Tran JE, et al. The management of stroke rehabilitation: a synopsis of the 2019 U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and U.S. Department of Defense clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Dec 17;171(12):916-24.
https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M19-1695
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31739317?tool=bestpractice.com
[144]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stroke rehabilitation in adults. Oct 2023 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng236
პრაქტიკის გაიდლაინები მოიცავს რეკომენდაციებს ინსულტის რეაბილიტაციის ყველა ასპექტის შესახებ, ადრეული მწვავე თერაპიიდან საზოგადოებაში რეინტეგრაციამდე.[9]Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, et al. 2022 Guideline for the management of patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):e282-361.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STR.0000000000000407
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35579034?tool=bestpractice.com
[140]Winstein CJ, Stein J, Arena R, et al. Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2016 Jun;47(6):e98-169.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/str.0000000000000098
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27145936?tool=bestpractice.com
[144]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Stroke rehabilitation in adults. Oct 2023 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng236
ინსულტის შემდეგ პაციენტების დაახლოებით ერთი მესამედი უჩივის აფაზიას. საუბრისა და ენის თერაპია მნიშვნელოვანია იმისთვის, რომ გაიზარდოს კომუნიკაციის ხარისხი. განსხვავებები ფუნქციურ შედეგებში, როდესაც ადარებენ სპეციფიკურ თერაპიულ რეჟიმებს (მაგ. ინტენსივობა, დოზირება და ხანგრძლივობა) კვლავ გამოკვლევის პროცესშია.
ჩარევები მოტორული ფუნქციის გასაუმჯობესებლად
მენტალური პრაქტიკა აღწერს სასწავლო მეთოდს, რომელიც იყენებს აქტივობების კოგნიტიურ რეპეტიციას ამ აქტივობების შესრულების გასაუმჯობესებლად; ინდივიდი არაერთხელ გონებრივად იმეორებს მოქმედებას ან დავალებას თავის წარმოსახვაში (მაგ., ჭიქის აღება ან ხელის გაწვდენა) მოქმედების ან დავალების ფიზიკური შესრულების გარეშე. რანდომიზებული კონტროლირებადი კვლევები მხარს უჭერს მენტალური პრაქტიკის გამოყენებას, გარდა ჩვეულებრივი ფიზიკური სარეაბილიტაციო მკურნალობისა, ინსულტის შემდეგ ზედა კიდურების უკმარისობის გასაუმჯობესებლად.[145]Barclay RE, Stevenson TJ, Poluha W, et al. Mental practice for treating upper extremity deficits in individuals with hemiparesis after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 25;5:CD005950.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005950.pub5
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32449959?tool=bestpractice.com
რამდენიმე კვლევამ შეაფასა ფარმაკოთერაპიის გამოყენება მოტორიკის აღდგენის გასაუმჯობესებლად. ყველაზე ფართოდ იქნა შესწავლილი ამფეტამინები, ლევოდოპა და სეროტონინის უკუმიტაცების შერჩევითი ინჰიბიტორები (SSRI). ფლუოქსეტინი, SSRI, არ აუმჯობესებდა ფუნქციურ შედეგებს რანდომიზებულ კონტროლირებად კვლევებში და მეტა-ანალიზებში პაციენტების მწვავე ინსულტით, მათ შორის ჰემორაგიული ინსულტით.[146]FOCUS Trial Collaboration. Effects of fluoxetine on functional outcomes after acute stroke (FOCUS): a pragmatic, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2019 Jan 19;393(10168):265-74.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(18)32823-X/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30528472?tool=bestpractice.com
[147]AFFINITY Trial Collaboration. Safety and efficacy of fluoxetine on functional outcome after acute stroke (AFFINITY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020 Aug;19(8):651-60.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32702334?tool=bestpractice.com
[148]Legg LA, Rudberg AS, Hua X, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for stroke recovery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 15;11:CD009286.
https://www.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009286.pub4
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34780067?tool=bestpractice.com
ვირტუალური რეალობა ინსულტის შემდგომ პაციენტებს საშუალებას აძლევს შეასრულონ კონკრეტული დავალებები კომპიუტერში წარმოქმნილ ვიზუალურ გარემოში. არსებობს გარკვეული მტკიცებულებები, რომ ვირტუალური რეალობის გამოყენებამ შეიძლება გააუმჯობესოს ფუნქციური ბალანსი, სიარულის სხვადასხვა ასპექტი და სხვა ფუნქციები.[149]Gibbons EM, Thomson AN, de Noronha M, et al. Are virtual reality technologies effective in improving lower limb outcomes for patients following stroke - a systematic review with meta-analysis. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2016 Dec;23(6):440-57.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27237336?tool=bestpractice.com
[150]Palma GC, Freitas TB, Bonuzzi GM, et al. Effects of virtual reality for stroke individuals based on the International Classification of Functioning and Health: a systematic review. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2017 May;24(4):269-78.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27796177?tool=bestpractice.com
 ]
[98]
]
[98] ]
თუმცა, მაშინაც კი, როდესაც პაციენტის კვება მიმდინარეობს ნაზოგასტრული მილებით, მათ აქვთ ქვედა ეზოფაგური დისფუნქციის, კუჭის რეფლუქსის და ნაზოგასტრული მილის არსებობით მიკროასპირაციის გამწვავების მეორეულად პნევმონიის განვითარების რისკი.[115]
]
თუმცა, მაშინაც კი, როდესაც პაციენტის კვება მიმდინარეობს ნაზოგასტრული მილებით, მათ აქვთ ქვედა ეზოფაგური დისფუნქციის, კუჭის რეფლუქსის და ნაზოგასტრული მილის არსებობით მიკროასპირაციის გამწვავების მეორეულად პნევმონიის განვითარების რისკი.[115] ]
[მტკიცებულების დონე B] სხვა პატარა კვლევებმა დაადგინა, რომ რეაბილიტაციის დაწყება ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის გამოვლინებიდან 24-48 საათში აუმჯობესებს გადარჩენადობას და ფუნქციურ შედეგებს შემდგომი მეთვალყრეობისას 3-6 თვის შემდეგ.[142]
]
[მტკიცებულების დონე B] სხვა პატარა კვლევებმა დაადგინა, რომ რეაბილიტაციის დაწყება ინტრაცერებრული ჰემორაგიის გამოვლინებიდან 24-48 საათში აუმჯობესებს გადარჩენადობას და ფუნქციურ შედეგებს შემდგომი მეთვალყრეობისას 3-6 თვის შემდეგ.[142]