Deve-se suspeitar de dissecção da aorta quando for relatada uma dor abdominal, torácica ou dorsalgia abrupta do tipo dilacerante ou cortante.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
Normalmente os pacientes descrevem a dor como intensa, "em facada" ou "aguda", máxima no início.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Errar o diagnóstico pode ser catastrófico, daí a importância de se obter a história aguda para impulsionar investigações adicionais.[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
[27]Sutherland A, Escano J, Coon TP. D-dimer as the sole screening test for acute aortic dissection: a review of the literature. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Oct;52(4):339-43.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18819176?tool=bestpractice.com
A apresentação típica é de um paciente do sexo masculino, na faixa dos 50 anos de idade, mas essa afecção pode ocorrer em pacientes mais jovens com síndrome de Marfan, síndrome de Ehlers-Danlos ou outros distúrbios do tecido conjuntivo.[14]Bossone E, LaBounty TM, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes: diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):739-49d.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29106452?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Outros cenários de alto risco incluem história familiar de doença aórtica ou doença do tecido conjuntivo, doença aórtica ou aneurisma da aorta torácica conhecidos e manipulação prévia da aorta (incluindo cirurgia cardíaca).[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
A maioria dos pacientes tem hipertensão prévia, geralmente mal controlada.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
Os pacientes mais jovens podem apresentar uma doença do tecido conjuntivo ou história recente de levantamento de pesos ou uso de cocaína. Em virtude da gravidade da doença, o diagnóstico deve ser considerado nos pacientes jovens, mesmo quando os fatores predisponentes estiverem ausentes.
Sinais e sintomas
O início agudo de dor intensa no tórax ou nas costas anuncia dissecção aguda da aorta em 80% a 90% dos pacientes.[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
A dor associada à dissecção da aorta pode ser retroesternal, interescapular ou ocorrer na coluna lombar.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bossone E, LaBounty TM, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes: diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):739-49d.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29106452?tool=bestpractice.com
Embora a descrição clássica nos livros-texto seja de dor aguda "dilacerante" ou "cortante", os pacientes costumam relatar o início abrupto de uma dor intensa "aguda" ou "em facada", máxima no início.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
A dor torácica anterior geralmente está associada com uma dissecção ascendente; a dor interescapular geralmente ocorre com uma dissecção descendente.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bossone E, LaBounty TM, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes: diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):739-49d.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29106452?tool=bestpractice.com
A dor pode migrar ao longo do tórax ou abdome, e a localização da dor pode mudar com o tempo à medida que a dissecção se estende.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bossone E, LaBounty TM, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes: diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):739-49d.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29106452?tool=bestpractice.com
Uma minoria dos pacientes apresenta síncope e ausência de dor.[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
É importante reconhecer que nenhum sintoma isolado de dissecção da aorta é patognomônico para a afecção, pois eles coincidem com distúrbios cardíacos, pulmonares, abdominais e musculoesqueléticos.
Os pacientes podem estar hemodinamicamente estáveis ou em estado de choque hipovolêmico.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Diferenças de pressão arterial nos membros superiores ou deficit de pulsação nos membros inferiores devem ser investigados.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Um déficit nos pulsos é particularmente comum em uma dissecção proximal afetando o arco aórtico.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
O déficit pode ser unilateral ou bilateral, dependendo do nível de separação da túnica íntima.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
Um déficit de pulso também pode estar presente em dissecções da aorta mais distais (por exemplo, da aorta descendente) e, em alguns casos, pode levar à isquemia aguda do membro. No entanto, déficits de pulso são menos comuns do que em dissecções mais proximais.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
Uma diferença na pressão arterial sistólica maior que 20 mmHg entre os dois braços é um sinal importante de dissecção da aorta.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Déficits neurológicos podem indicar envolvimento dos vasos cerebrais ou intercostais. Pode haver estado mental deprimido, dor nos membros, parestesias, fraqueza, ou paraplegia. Podem estar presentes sintomas de isquemia visceral. Ocasionalmente, pode ser encontrado um sopro diastólico em decrescendo, indicando insuficiência aórtica. Pode haver sintomas ou sinais de insuficiência cardíaca, tamponamento pericárdico ou um derrame pleural esquerdo.[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
Consulte Derrame pleural.
Uma revisão sistemática identificou deficit neurológico, hipotensão e deficit de pulso como os três achados de exame clínico com as razões de probabilidade positiva mais altas para dissecção da aorta.[28]Ohle R, Kareemi HK, Wells G, et al. Clinical examination for acute aortic dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad Emerg Med. 2018 Apr;25(4):397-412.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/acem.13360
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29265487?tool=bestpractice.com
Exames diagnósticos
A escolha dos exames para a investigação diagnóstica da dissecção aguda é baseada no estado hemodinâmico do paciente, na probabilidade de dissecção da aorta e na disponibilidade e experiência local.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
A investigação inicial inclui um ECG e enzimas cardíacas para descartar o infarto do miocárdio.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bossone E, LaBounty TM, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes: diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):739-49d.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29106452?tool=bestpractice.com
Consulte Infarto do miocárdio com supradesnivelamento do segmento ST
Isquemia ou infarto do miocárdio podem estar presentes em 10% a 15% dos pacientes com dissecção da aorta, o que pode mascarar o diagnóstico de dissecção.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
Também devem ser solicitados exames de sangue incluindo um perfil metabólico completo e um hemograma completo, tipagem sanguínea e prova cruzada. Apesar da alta sensibilidade, o dímero D não é recomendado como a única ferramenta de rastreamento para dissecção aguda da aorta; enquanto o dímero D negativo pode ser útil para descartar a dissecção da aorta em pacientes de baixo risco, particularmente quando usado em uma ferramenta de suporte à decisão integrada, um dímero D positivo carece de especificidade quando usado isoladamente.[29]Asha SE, Miers JW. A systematic review and meta-analysis of D-dimer as a rule-out test for suspected acute aortic dissection. Ann Emerg Med. 2015 Oct;66(4):368-78.
http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(15)00118-3/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25805111?tool=bestpractice.com
[30]Baez AA, Cochon L. Improved rule-out diagnostic gain with a combined aortic dissection detection risk score and D-dimer Bayesian decision support scheme. J Crit Care. 2017 Feb;37:56-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27632799?tool=bestpractice.com
No entanto, o dímero D terá valor ao se considerar o diagnóstico diferencial (por exemplo, embolia pulmonar).[27]Sutherland A, Escano J, Coon TP. D-dimer as the sole screening test for acute aortic dissection: a review of the literature. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Oct;52(4):339-43.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18819176?tool=bestpractice.com
Outros biomarcadores com potencial para auxiliar no diagnóstico de dissecção da aorta incluem proteína C-reativa, produtos de degradação da elastina, calponina e cadeia pesada da miosina do músculo liso, mas nenhum deles foi validado.[31]Ranasinghe AM, Bonser RS. Biomarkers in acute aortic dissection and other aortic syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010 Nov 2;56(19):1535-41.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21029872?tool=bestpractice.com
Em pacientes com suspeita de dissecção da aorta, a angiotomografia (ATG) é recomendada como exame de imagem diagnóstica inicial, devido a sua grande disponibilidade, precisão e velocidade, bem como a extensão do detalhe anatômico fornecido.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Fleischmann D, Afifi RO, Casanegra AI, et al. Imaging and surveillance of chronic aortic dissection: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Mar;15(3):e000075.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/HCI.0000000000000075
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35172599?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bossone E, LaBounty TM, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes: diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):739-49d.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29106452?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Expert Panel on Cardiac Imaging., Kicska GA, Hurwitz Koweek LM, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Suspected acute aortic syndrome. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021 Nov;18(11s):S474-S481.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2021.09.004
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34794601?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Upchurch GR Jr, Escobar GA, Azizzadeh A, et al. Society for Vascular Surgery clinical practice guidelines of thoracic endovascular aortic repair for descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2021 Jan;73(1s):55S-83S.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.05.076
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32628988?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]Czerny M, Schmidli J, Adler S, et al. Editor's Choice - current options and recommendations for the treatment of thoracic aortic pathologies involving the aortic arch: an expert consensus document of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) & the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Feb;57(2):165-98.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30692-0/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30318395?tool=bestpractice.com
A ATG tem sensibilidade superior a 90% e especificidade superior a 85% para síndromes aórticas agudas, incluindo a dissecção da aorta.[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
A ATG também mostra a extensão completa da dissecção e, em alguns casos, o local da ruptura de entrada. A ATG pode detectar a presença e o mecanismo de envolvimento do vaso ramificado da aorta, bem como a patência dos vasos, sinais de má perfusão, derrame pericárdico e hemopericárdio, hematoma periaórtico ou mediastinal e derrame pleural.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Para os pacientes que não podem receber contraste iodado, a TC sem contraste é uma alternativa aceitável.
O diagnóstico de dissecção da aorta é feito pela imagem de uma separação da túnica íntima separando 2 lúmens. Se o falso lúmen estiver completamente trombosado, o deslocamento central da separação da túnica íntima, a calcificação ou a separação das camadas intimais são sinais definitivos de dissecção da aorta. A TGA permite visualizar a extensão da dissecção e o envolvimento dos ramos laterais.
Uma radiografia torácica simples não é suficientemente sensível ou específica para a dissecção da aorta para ser usada como uma ferramenta diagnóstica. Uma radiografia torácica pode revelar outras causas de dor torácica aguda.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Expert Panel on Cardiac Imaging., Kicska GA, Hurwitz Koweek LM, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Suspected acute aortic syndrome. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021 Nov;18(11s):S474-S481.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2021.09.004
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34794601?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Upchurch GR Jr, Escobar GA, Azizzadeh A, et al. Society for Vascular Surgery clinical practice guidelines of thoracic endovascular aortic repair for descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2021 Jan;73(1s):55S-83S.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2020.05.076
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32628988?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Um alargamento do mediastino ou derrame pleural pode indicar dissecção da aorta, mas tem valor diagnóstico limitado, principalmente se a dissecção estiver confinada à aorta ascendente; a radiografia torácica está normal em até 40% dos pacientes com dissecção da aorta.[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
[14]Bossone E, LaBounty TM, Eagle KA. Acute aortic syndromes: diagnosis and management, an update. Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):739-49d.
https://www.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx319
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29106452?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]Czerny M, Schmidli J, Adler S, et al. Editor's Choice - current options and recommendations for the treatment of thoracic aortic pathologies involving the aortic arch: an expert consensus document of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) & the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019 Feb;57(2):165-98.
https://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(18)30692-0/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30318395?tool=bestpractice.com
[35]von Kodolitsch Y, Nienaber CA, Dieckmann C, et al. Chest radiography for the diagnosis of acute aortic syndrome. Am J Med. 2004 Jan 15;116(2):73-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14715319?tool=bestpractice.com
A ecocardiografia transtorácica (ETT) pode ser usada no pronto-socorro, na unidade de terapia intensiva (UTI) ou na sala de cirurgia para dissecções agudas proximais se o paciente estiver clinicamente instável e se houver qualquer dúvida sobre o diagnóstico, ou se a TGA estiver indisponível ou for contraindicada.[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
[32]Expert Panel on Cardiac Imaging., Kicska GA, Hurwitz Koweek LM, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Suspected acute aortic syndrome. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021 Nov;18(11s):S474-S481.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2021.09.004
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34794601?tool=bestpractice.com
[36]Nazerian P, Vanni S, Morello F, et al. Diagnostic performance of focused cardiac ultrasound performed by emergency physicians for the assessment of ascending aorta dilation and aneurysm. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 May;22(5):536-41.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25899650?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
A ETT pode mostrar derrame pericárdico ou regurgitação aórtica, e, às vezes, um retalho da dissecção pode ser visualizado; entretanto, imagens mais completas do arco aórtico requerem uma ecocardiografia transesofágica ou uma ATG.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
Para dissecções do tipo A (ascendentes), a ecocardiografia transesofágica também pode ser feita na UTI ou na sala de cirurgia para confirmar o diagnóstico e para melhor avaliar a valva aórtica.[11]Gulati M, Levy PD, Mukherjee D, et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the evaluation and diagnosis of chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021 Nov 30;144(22):e368-e454.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001029
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34709879?tool=bestpractice.com
A sensibilidade e a especificidade são maiores que para ETT.
A ressonância nuclear magnética (RNM) é usada com mais frequência como modalidade de imagem de acompanhamento nos pacientes com incerteza diagnóstica.[4]Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA guideline for the diagnosis and management of aortic disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Dec 13;80(24):e223-e393.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36334952?tool=bestpractice.com
A angiografia por ressonância magnética é o exame mais preciso, sensível e específico para a dissecção da aorta, mas ela raramente é usada no quadro agudo porque é mais difícil de ser realizada que a TGA.[2]Lombardi JV, Hughes GC, Appoo JJ, et al. Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS) and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) reporting standards for type B aortic dissections. J Vasc Surg. 2020 Mar;71(3):723-47.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2019.11.013
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32001058?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
Para dissecções do tipo B (descendentes), se a terapia medicamentosa falhar e a cirurgia se tornar necessária, a ultrassonografia intravascular intraoperatória ajuda a definir a morfologia da dissecção e auxilia no plano de tratamento.
Se o paciente apresentar um achado incidental de dissecção crônica (como alargamento do mediastino ou botão aórtico proeminente na radiografia torácica), o diagnóstico é confirmado por imagem transversal, como ATG, ETT ou RNM.[24]Fleischmann D, Afifi RO, Casanegra AI, et al. Imaging and surveillance of chronic aortic dissection: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Mar;15(3):e000075.
https://www.doi.org/10.1161/HCI.0000000000000075
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35172599?tool=bestpractice.com
[10]Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, et al; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 1;35(41):2873-926.
https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/41/2873/407693/2014-ESC-Guidelines-on-the-diagnosis-and-treatment
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173340?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) de um homem de 71 anos de idade mostrando aneurisma dissecante tipo II da aorta ascendente. Um hematoma em torno do segmento proximal da aorta ascendente (painéis A-D) comprimiu a artéria pulmonar direita, quase obstruindo sua patência e limitando a perfusão do pulmão recíprocoStougiannos PN, Mytas DZ, Pyrgakis VN. The changing faces of aortic dissection: an unusual presentation mimicking pulmonary embolism. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.2006.104414 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) 3D, dissecção distalDo acervo de Dr. Eric E. Roselli; usado com permissão [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) 3D, dissecção distalDo acervo de Dr. Eric E. Roselli; usado com permissão [Citation ends].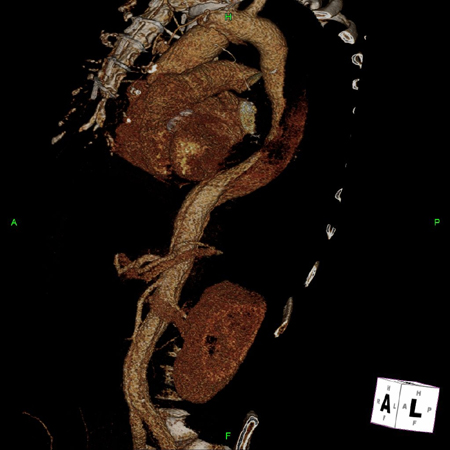 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) mostrando aneurisma dissecante em um paciente de 45 anos de idade com síndrome de Marfan com dor torácicaSanyal K, Sabanathan K. Chest pain in Marfan syndrome. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0431 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) mostrando aneurisma dissecante em um paciente de 45 anos de idade com síndrome de Marfan com dor torácicaSanyal K, Sabanathan K. Chest pain in Marfan syndrome. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0431 [Citation ends].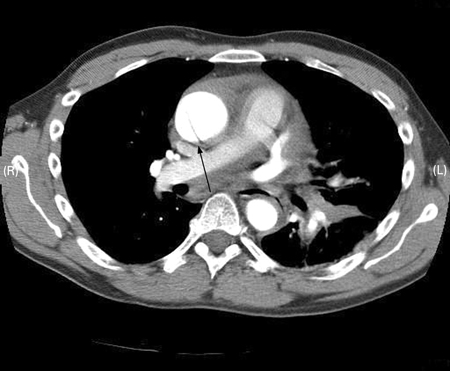 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ecocardiografia transesofágica (secção transversal da aorta) mostrando uma dissecção circunferencial da aorta ascendente em um paciente de 30 anos de idade com características de síndrome de MarfanBouzas-Mosquera A, Solla-Buceta M, Fojón-Polanco S. Circumferential aortic dissection. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.2007.049908 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ecocardiografia transesofágica (secção transversal da aorta) mostrando uma dissecção circunferencial da aorta ascendente em um paciente de 30 anos de idade com características de síndrome de MarfanBouzas-Mosquera A, Solla-Buceta M, Fojón-Polanco S. Circumferential aortic dissection. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.2007.049908 [Citation ends].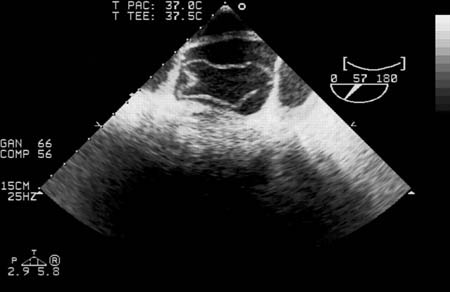
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) 3D, dissecção distalDo acervo de Dr. Eric E. Roselli; usado com permissão [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) 3D, dissecção distalDo acervo de Dr. Eric E. Roselli; usado com permissão [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) mostrando aneurisma dissecante em um paciente de 45 anos de idade com síndrome de Marfan com dor torácicaSanyal K, Sabanathan K. Chest pain in Marfan syndrome. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0431 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tomografia computadorizada (TC) mostrando aneurisma dissecante em um paciente de 45 anos de idade com síndrome de Marfan com dor torácicaSanyal K, Sabanathan K. Chest pain in Marfan syndrome. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0431 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ecocardiografia transesofágica (secção transversal da aorta) mostrando uma dissecção circunferencial da aorta ascendente em um paciente de 30 anos de idade com características de síndrome de MarfanBouzas-Mosquera A, Solla-Buceta M, Fojón-Polanco S. Circumferential aortic dissection. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.2007.049908 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ecocardiografia transesofágica (secção transversal da aorta) mostrando uma dissecção circunferencial da aorta ascendente em um paciente de 30 anos de idade com características de síndrome de MarfanBouzas-Mosquera A, Solla-Buceta M, Fojón-Polanco S. Circumferential aortic dissection. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.2007.049908 [Citation ends].