Child-Pugh-Turcotte (CPT)[64]Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964;1:1-85.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4950264?tool=bestpractice.com
[65]Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4541913?tool=bestpractice.com
One of the most commonly used scoring systems to determine disease severity in cirrhosis.[64]Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964;1:1-85.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4950264?tool=bestpractice.com
[65]Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4541913?tool=bestpractice.com
The CPT score is based on the presence of ascites and hepatic encephalopathy, serum bilirubin, albumin, and clotting (prothrombin time and international normalised ratio [INR]) and is divided into Child A, B, and C with increasing disease severity.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Child-Pugh-Turcotte scoring systemFrom the collection of Dr Keith Lindor; used with permission [Citation ends].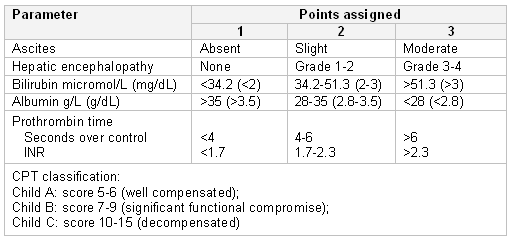
Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)[68]Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001 Feb;33(2):464-70.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11172350?tool=bestpractice.com
A more recent scoring system for the determination of severity in cirrhosis, the MELD score is electronically calculated from the serum bilirubin, sodium, creatinine, and clotting (INR and prothrombin time) by a specific computer programme.[67]Kim WR, Biggins SW, Kremers WK, et al. Hyponatremia and mortality among patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. N Engl J Med. 2008 Sep 4;359(10):1018-26.
http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa0801209#t=article
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18768945?tool=bestpractice.com
[68]Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001 Feb;33(2):464-70.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11172350?tool=bestpractice.com
[
MELDNa scores (for liver transplantation listing purposes, not appropriate for patients under age 12 years) (SI units)
Opens in new window
]
This is the classification system used for the allocation of livers for transplantation in the US.
Hepatorenal syndrome-acute kidney injury (HRS-AKI)
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is an absolute increase in serum creatinine of ≥26.4 micromoles/L (≥0.3 mg/dL) in less than 48 hours, or a percentage increase in serum creatinine of at least 1.5-fold from baseline in less than 7 days, or a reduction in urine output of 0.5 mL/kg/h for more than 6 hours.[88]European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018 Aug;69(2):406-60.
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(18)31966-4/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29653741?tool=bestpractice.com
[89]Angeli P, Gines P, Wong F, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. Gut. 2015 Apr;64(4):531-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308874
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25631669?tool=bestpractice.com
[90]Flamm SL, Wong F, Ahn J, et al. AGA clinical practice update on the evaluation and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Dec;20(12):2707-16.
https://www.cghjournal.org/article/S1542-3565(22)00829-1/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36075500?tool=bestpractice.com
AKI has three stages, as defined by the International Club of Ascites (ICA-AKI criteria):[91]Wong F. Acute kidney injury in liver cirrhosis: new definition and application. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016 Dec;22(4):415-22.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5266339
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27987536?tool=bestpractice.com
Stage 1: an increase in serum creatinine ≥26.4 micromoles/L (≥0.3 mg/dL) or an increase in serum creatinine ≥1.5-fold to twofold from baseline at diagnosis of AKI
Stage 2: an increase in serum creatinine greater than twofold to threefold from baseline
Stage 3: an increase of serum creatinine greater than threefold from baseline or serum creatinine ≥352 micromoles/L (≥4.0 mg/dL) with an acute increase ≥26.4 micromoles/L (≥0.3 mg/dL) or initiation of renal replacement therapy.
European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) guidelines recommend using an adapted staging system for AKI that splits AKI stage 1 into stage 1A and 1B according to a serum creatinine value of <133 micromoles/L (<1.5 mg/dL) or ≥133 micromoles/L (≥1.5 mg/dL), respectively.[88]European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018 Aug;69(2):406-60.
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(18)31966-4/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29653741?tool=bestpractice.com
International Club of Ascites (ICA) diagnostic criteria for HRS-AKI:[89]Angeli P, Gines P, Wong F, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. Gut. 2015 Apr;64(4):531-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308874
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25631669?tool=bestpractice.com
Cirrhosis with ascites
Diagnosis of AKI according to ICA-AKI criteria
Increase in serum creatinine ≥26.4 micromoles/L (≥0.3 mg/dL) within 48 hours, or
A percentage increase serum creatinine ≥50% from baseline which is known, or presumed, to have occurred within the prior 7 days.
No response after 2 consecutive days of diuretic withdrawal and plasma volume expansion with albumin
Absence of shock
No current or recent use of nephrotoxic drugs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, aminoglycosides, or iodinated contrast media)
No macroscopic signs of structural kidney injury. Structural kidney injury is indicated by proteinuria (>500 mg/day), micro-haematuria (>50 red blood cells per high-power field), and/or abnormal renal ultrasonography.
