მიუხედავად იმისა, რომ გარკვეული კლინიკური ნიშნები და ლაბორატორიული მონაცემები სეპტიკური ართრიტის მიმანიშნებელია, არ არსებობს ერთი ცალკეული ფაქტორი, რომელიც 100%-იანი სპეციფიკურობით ან მგრძნობელობით ხასიათდება. სწორი დიაგნოზისთვის აუცილებელია კლინიკური ეჭვის მიტანა პროფესიონალის მიერ, რომელიც გამოცდილია ძვალკუნთოვანი დაავადებების სფეროში. თუ კლინიკური ეჭვი მაღალია, აუცილებელია სავარაუდო სეპტიკური ართრიტის მკურნალობა, სისხლის ანალიზებისა და მიკრობიოლოგიური კვლევების მიუხედავად.[11]Coakley G, Mathews C, Field M, et al. BSR and BHPR, BOA, RCGP and BSAC guidelines for management of the hot swollen joint in adults. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Aug;45(8):1039-41.
http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/45/8/1039
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16829534?tool=bestpractice.com
თუ ინფექციის ნიშნებით ან სიმპტომებით წარმოდგენილი პაციენტის მდგომარეობა მკვეთრად გაუარესდება, ექიმებმა უნდა განიხილონ სეფსისის არსებობის შესაძლებლობა და სასწრაფოდ მოახდინონ სისტემური შეფასება იმ პირთა გამოსავლენად, რომელთაც აქვთ მდგომარეობის გაუარესების მაღალი რისკი ორგანოების დისფუნქციის გამო შეფასება, ადგილობრივი პროტოკოლების მიხედვით.[12]National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Sepsis: recognition, diagnosis and early management. Sep 2017 [internet publication].
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng51
[13]Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 2021 Nov 1;49(11):e1063-143.
https://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/Fulltext/2021/11000/Surviving_Sepsis_Campaign__International.21.aspx
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34605781?tool=bestpractice.com
იხ სეფსისი მოზრდილებში დასეფსისი ბავშვებში.
ანამნეზი
სეპტიკური ართრიტი, როგორც წესი, ვლინდება მხურვალე, შეშუპებული, მტკივნეული სახსრის (ან სახსრების) ხანმოკლე ანამნეზით, რასაც თან ერთვის მოძრაობის შეზღუდვა.[3]Weston VC, Jones AC, Bradbury N, et al. Clinical features and outcome of septic arthritis in a single UK health district 1982-1991. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Apr;58(4):214-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1752863/pdf/v058p00214.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10364899?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Gupta MN, Sturrock RD, Field M. A prospective 2-year study of 75 patients with adult-onset septic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001 Jan;40(1):24-30.
http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/40/1/24
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11157138?tool=bestpractice.com
გამოვლინება შეიძლება უფრო თანდათანობითი იყოს დაბალი ვირულენტობის მიკროორგანიზმის, ტუბერკულოზის ან სახსრის პროთეზის არსებობის შემთხვევაში.[4]Gupta MN, Sturrock RD, Field M. A prospective 2-year study of 75 patients with adult-onset septic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001 Jan;40(1):24-30.
http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/40/1/24
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11157138?tool=bestpractice.com
[5]Gupta MN, Sturrock RD, Field M. Prospective comparative study of patients with culture proven and high suspicion of adult onset septic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Apr;62(4):327-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1754487/pdf/v062p00327.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12634231?tool=bestpractice.com
სახსრის ძირითადი დაავადების კონტექსტში, სეპტიკურ სახსარზე ეჭვი უნდა მივიტანოთ იმ შემთხვევაში, თუ სიმპტომები დაზიანებულ სახსრში არ შეესატყვისება სხვა ადგილებში აღმოჩენილ დაავადების აქტივობას. შემთხვევათა 22%-ში სეპტიკური ართრიტი პოლიართრიტულია (მოიცავს რამდენიმე სახსარს).[2]Kaandorp CJ, Dinant HJ, van de Laar MA, et al. Incidence and sources of native and prosthetic joint infection: a community based prospective survey. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 Aug;56(8):470-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1752430/pdf/v056p00470.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9306869?tool=bestpractice.com
[6]Dubost JJ, Soubrier M, De Champs C, et al. No changes in the distribution of organisms responsible for septic arthritis over a 20 year period. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Mar;61(3):267-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1754020/pdf/v061p00267.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11830437?tool=bestpractice.com
რისკფაქტორები
სეპტიკური ართრიტის რისკფაქტორებია: რევმატოიდული ართრიტი, ოსტეოართრიტი, ხელოვნური სახსრები, დაბალი სოციეკონომიკური სტატუსი, ნარკოტიკების ინტრავენური მოხმარება, ალკოჰოლიზმის მოხმარებასთან დაკავშირებული დაავადებები, დიაბეტი, წარსულში სახსარშიდა კორტიკოსტეროიდების ინექცია, კანის დაწყლულება. სქესობრივად აქტიურ პციენტებში შეიძლება ეჭვი მივიტანოთ გონოკოკურ ართრიტზე.[2]Kaandorp CJ, Dinant HJ, van de Laar MA, et al. Incidence and sources of native and prosthetic joint infection: a community based prospective survey. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 Aug;56(8):470-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1752430/pdf/v056p00470.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9306869?tool=bestpractice.com
[3]Weston VC, Jones AC, Bradbury N, et al. Clinical features and outcome of septic arthritis in a single UK health district 1982-1991. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Apr;58(4):214-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1752863/pdf/v058p00214.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10364899?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Gupta MN, Sturrock RD, Field M. A prospective 2-year study of 75 patients with adult-onset septic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001 Jan;40(1):24-30.
http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/40/1/24
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11157138?tool=bestpractice.com
[6]Dubost JJ, Soubrier M, De Champs C, et al. No changes in the distribution of organisms responsible for septic arthritis over a 20 year period. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Mar;61(3):267-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1754020/pdf/v061p00267.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11830437?tool=bestpractice.com
[7]Sharp JT, Lidsky MD, Duffy J, et al. Infectious arthritis. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Oct;139(10):1125-30.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/485744?tool=bestpractice.com
[8]Meijers KA, Dijkmans BA, Hermans J, et al. Non-gonococcal infectious arthritis: a retrospective study. J Infect. 1987 Jan;14(1):13-20.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3819454?tool=bestpractice.com
MRSA-ს ინციდენტობა იზრდება მსოფლიოს მრავალ რეგიონში.[14]Arnold SR, Elias D, Buckingham SC, et al. Changing patterns of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis and septic arthritis: emergence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006 Nov-Dec;26(6):703-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17065930?tool=bestpractice.com
განსაკუთრებით მაღალი რისკი აღენიშნებათ ჰოსპიტალიზებულ პაციენტებს, მოხუცთა საცხოვრებლების ბინადრებს, ფეხის წყლულების ან შარდის ბუშტის კათეტერის მქონე პაციენტებს. ტუბერკულოზური ართრიტი უფრო და უფრო ხშირია და მასზე უნდა ვიეჭვოთ იმუნოკომპრომისულ პირებში და იმ რეგიონებში მცხოვრებ ადამიანებში, სადაც ტუბერკულოზი პრევალენტურია.
გამოკვლევა
ინფიცირებული სახსრისათვის დამახასიათებელი ნიშნებია შეშუპება, სიმხურვალე, მტკივნეულობა და მოძრაობის მნიშვნელოვანი შეზღუდვა. ცხელების არსებობა ან არარსებობა არ არის სახსრის ინფიცირების სანდო მაჩვენებელი.[3]Weston VC, Jones AC, Bradbury N, et al. Clinical features and outcome of septic arthritis in a single UK health district 1982-1991. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Apr;58(4):214-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1752863/pdf/v058p00214.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10364899?tool=bestpractice.com
[4]Gupta MN, Sturrock RD, Field M. A prospective 2-year study of 75 patients with adult-onset septic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001 Jan;40(1):24-30.
http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/40/1/24
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11157138?tool=bestpractice.com
[5]Gupta MN, Sturrock RD, Field M. Prospective comparative study of patients with culture proven and high suspicion of adult onset septic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Apr;62(4):327-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1754487/pdf/v062p00327.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12634231?tool=bestpractice.com
[6]Dubost JJ, Soubrier M, De Champs C, et al. No changes in the distribution of organisms responsible for septic arthritis over a 20 year period. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Mar;61(3):267-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1754020/pdf/v061p00267.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11830437?tool=bestpractice.com
ლაბორატორული გამოკვლევები
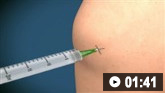
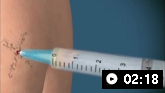
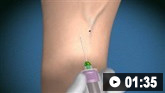
სეპტიკურ ართრიტზე ეჭვის შემთხვევაში აუცილებელია სახსრის ასპირაცია სინოვიური სითხის ნიმუშის ასაღებად მანამ, სანამ ანტიმიკრობული თერაპია დაიწყება.[10]Earwood JS, Walker TR, Sue GJC. Septic arthritis: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2021 Dec 1;104(6):589-97.
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2021/1200/p589.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34913662?tool=bestpractice.com
მარტივი ასპირაციის უკუჩენებას წარმოადგენს სახსრის პროთეზის არსებობა. მსგავს შემთხვევებში რეკომენდებულია ინვაზიური პროცედურის ჩატარება სტერილურ პირობებში საოპერაციოში. შესაბამისად, რეკომენდებულია ქირურგ-ორთოპედთან მიმართვა. ორთოპედთან მიმართვა ასევე რეკომენდებულია შესაძლო ტუბერკულოზური ართრიტის მქონე პაციენტებში. დიაგნოზის დასადასტურებლად შეიძლება საჭირო გახდეს სინოვიუმის ბიოფსია.
სახსრის ასპირაციის აბსოლუტური უკუჩვენებას არ წარმოადგენს არც მფარავი ცელულიტი არც ანტიკოაგულაცია. სპეციალისტის დახმარება საჭიროა, ნებისმიერ ასეთი მდგომარეობის დროს, თუ ექიმი თავს გრძნობს არაკომფორტულად ართროცენტეზის ჩასატარებლად
სინოვიური სითხე დაუყოვნებლივ უნდა გაიგზავნოს გრამის წესით შესაღებად, სისხლის თეთრი უჯრედების რაოდენობრივი ანალიზისთვის და შემდგომში კულტივირებისათვის. თავდაპირველი გამოვლენისას, ანტიბიოტიკოთერაპიის დაწყებამდე, ასევე რეკომენდებულია სისხლის კულტივირება.
შრატში სისხლის თეთრი უჯრედების რაოდენობრივი ანალიზი, ედს და C-რეაქტიული ცილა შეიძლება დაგვეხმაროს დიაგნოსტირებასა და მკურნალობის მონიტორინგში. შესაბამისად, აღნიშნული გამოკვლევები რეკომენდებულია რუტინულად, სეპტიკურ ართრიტზე ეჭვის შემთხვევაში.
შეიძლება განისაზღვოს ელექტროლიტები და ჩატარდეს ღვიძლის ფუნქციური სინჯი სისტემური სეფსისის არსებობის გამოსავლენად.
თუ ანამნეზის ან გასინჯვის მიხედვით ეჭვია ალტერნატიულ, არასახსროვან ინფექციაზე, საჭიროა შესაბამისი ნიმუშების აღება და კულტივირება.
პროკალციტონინი (PCT) დაგეხმარებათ ბაქტერიული ინფექციის იდენტიფიცირებაში და სერიული შეფასება შეიძლება მიუთითებდეს თერაპის პასუხზე.[21]Sager R, Kutz A, Mueller B, et al. Procalcitonin-guided diagnosis and antibiotic stewardship revisited. BMC Med. 2017 Jan 24;15(1):15.
https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-017-0795-7
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28114931?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, შრატში პროკალციტონინი (PCT) ჯერ კიდევ არ არის რეკომენდებული, როგორც რუტინული დიაგნოსტიკური საშუალება.[22]Mathews CJ, Coakley G; British Society for Rheumatology. Hot joint update 2017. Mar 2017 [internet publication].
https://www.rheumatology.org.uk/Portals/0/Documents/Guidelines/Audit%20tools/Hot_Joint_guideline_update_2017.pdf
რადიოლოგიური კვლევები
სეპტიკური ართრიტის დიაგნოსტირებისათვის სანდო რადიოლოგიური კვლევები არ არსებობს.[23]Nijhof MW, Oyen WJ, van Kampen A, et al. Evaluation of infections of the locomotor system with indium-111-labeled human IgG scintigraphy. J Nucl Med. 1997 Aug;38(8):1300-5.
http://jnm.snmjournals.org/cgi/reprint/38/8/1300
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9255172?tool=bestpractice.com
[24]Karchevsky M, Schweitzer ME, Morrison WB, et al. MRI findings of septic arthritis and associated osteomyelitis in adults. Am J Roentgenol. 2004 Jan;182(1):119-22.
http://www.ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/ajr.182.1.1820119
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14684523?tool=bestpractice.com
თუმცა, რეკომენდებულია ბაზისურად მიმოხილვითი რენტგენოგრაფია, რათა განისაზღვროს სახსრის ფონური დაავადება გამოვლენისას.[25]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: suspected osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, or soft tissue infection (excluding spine and diabetic foot). 2022 [internet publication].
https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/3094201/Narrative
მრტ შესაძლოაო დაგვეხმაროს, თუ არსებობს ეჭვი ასოცირებულ ოსტეომიელიტზე.[25]American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: suspected osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, or soft tissue infection (excluding spine and diabetic foot). 2022 [internet publication].
https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/3094201/Narrative
მენჯის შესაძლო სეფსისის შემთხვევაში სახსრის ასპირაცია ულტრაბგერის კონტროლით ტარდება.