Differentials
Junctional rhythm
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
In patients with profound first-degree AV block and very long PR intervals, the P wave may encroach so closely on the QRS complexes that they appear to be retrograde P waves, suggesting junctional rhythm. Retrograde P waves in junctional rhythm should be inverted in the inferior leads (II, III, and aVF), whereas in sinus rhythm with profound first-degree AV block, the P waves are upright in those leads.
INVESTIGATIONS
Comparison of numerous ECGs obtained at different times (i.e., days or months apart) may be useful. Baseline ECGs showing profound first-degree AV block may also help make the diagnosis.
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
In patients with profound first-degree AV block and very long PR intervals, the P wave may encroach so closely on the QRS complexes that they appear to be retrograde P waves, suggesting SVT. Retrograde P waves in SVT are frequently inverted in the inferior leads versus upright in sinus rhythm with first-degree AV block.
INVESTIGATIONS
Variations in the heart rate and the PR and RP (QRS to P) intervals suggest against the diagnosis of SVT. Comparison of numerous ECGs may be very useful.
Atrial fibrillation or multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
The irregularity of the RR intervals in type I second-degree AV block may lead to the incorrect diagnosis of atrial fibrillation or MAT. The presence of distinct P waves and the grouped pattern of the RR intervals are characteristic of type I second-degree AV block and are not seen in atrial fibrillation or MAT.
INVESTIGATIONS
Careful inspection of the ECG should allow distinction between these diagnoses.
Sinus rhythm with intact AV conduction
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
In patients with third-degree AV block, if the rate of the junctional escape rhythm is similar to that of the sinus rate, an appearance of sinus rhythm with intact AV conduction may be possible. In most of these cases, with a long enough rhythm strip, the lack of a relationship between the sinus beats and the QRS complexes will become apparent.
INVESTIGATIONS
Examination of a long rhythm strip should allow for the correct diagnosis to be made.
Tachy-brady syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
The RR intervals are irregular and short, suggesting atrial fibrillation with a fast ventricular rate. At the termination of the tachyarrhythmia, the diseased sinus node is slow to take over, resulting in a pause and a slow ventricular rate.
INVESTIGATIONS
There is no AV block. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tachy-brady syndrome due to sinus node disease. Ventricular rate is slow intermittently, but AV block is not seenCourtesy of Dr Sanjiv Petkar; used with permission [Citation ends].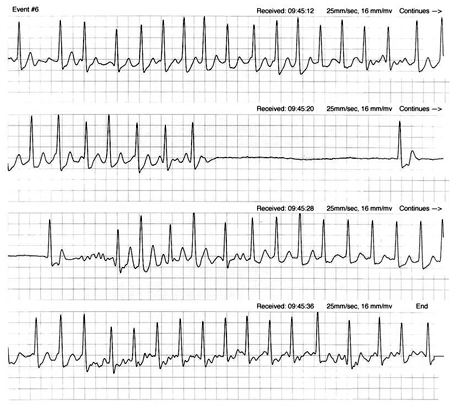
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer