Differentials
Syphilis infection
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Ulcers (chancres) are typically solitary, indurated, and painless.
Causes painless inguinal lymphadenopathy, which is usually bilateral.
May occur with Haemophilus ducreyi in a mixed infection.
More commonly associated with systemic symptoms such as fever and rash.[70]
Condyloma latum is often accompanied by a rash.
INVESTIGATIONS
Combination of both non-treponemal (non-specific) and treponemal (specific) tests.
A positive first test aids in the diagnosis of syphilis infection.
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Lesions form vesicles.
Ulcers are shallower than chancroid lesions with a clean base.
Lymphadenopathy is usually bilateral and not fluctuant.
May occur with H ducreyi in a mixed infection.
More commonly associated with systemic symptoms such as fever, headache, and malaise.[70]
INVESTIGATIONS
HSV DNA detected by polymerase chain reaction testing and viral culture.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tzanck test specimen showing multi-nucleated giant cells, indicating the presence of herpes virusAdapted from J. Miller, Public Health Image Library, CDC (1975) [Citation ends].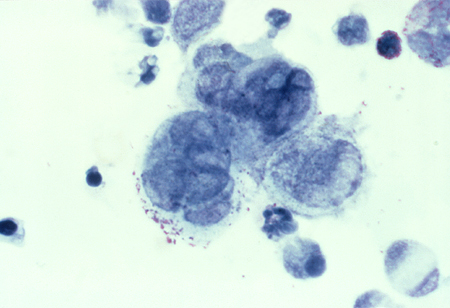
Lymphogranuloma venereum
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Tender inguinal lymphadenopathy without associated genital ulcerations.
Lesions, if present, are painless.[70]
INVESTIGATIONS
Culture or polymerase chain reaction from bubo aspirate positive for Chlamydia trachomatis.
Mpox
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Recent travel to Africa or recent close contact (including sexual contact) with someone who has Mpox is likely to be present.[71]
Patients typically present with a characteristic rash that progresses in sequential stages at the same stage of development over all affected areas of the body. The rash often affects the palms and soles. It may be associated with fever, lymphadenopathy, backache, and myalgia.
Rash lesions may also be atypical, localised to the genital, perineal/perianal, or perioral areas without spreading further.
INVESTIGATIONS
Polymerase chain reaction of skin lesion material: positive for monkeypox or Orthopoxvirus DNA.
Granuloma inguinale
Traumatic ulceration
INVESTIGATIONS
Diagnosis is clinical.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
No distinguishing characteristics.
INVESTIGATIONS
Polymerase chain reaction, culture, and serology for infections are negative.
Biopsy of the lesion provides definitive diagnosis.
Behcet's syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Oral lesions are more common.
Systemic symptoms such as fever, arthralgias, uveitis, and abdominal pain are common.[70]
INVESTIGATIONS
Pathergy test is positive, leading to pustule formation within 48 hours.
Cutaneous drug reaction
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Recent history of antibiotic use or chemotherapy.[70]
INVESTIGATIONS
Skin biopsy is diagnostic.
Crohn's disease
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Patients have predominantly peri-anal lesions.
More likely to have systemic symptoms, such as fever, diarrhoea, weight loss, and abdominal pain.
Inguinal lymphadenopathy is uncommon.[70]
INVESTIGATIONS
Colonoscopy and biopsy are diagnostic.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer