Investigations
1st investigations to order
ECG
Test
Most useful for initial diagnosis of atrial tachycardia.
The P-wave morphology may be different from that in sinus rhythm when compared with a prior ECG.
Result
regular tachycardia that does not vary in rate; P waves may have an unusual axis
digoxin level
Test
In patients who are on digoxin therapy, focal atrial tachycardia (focal AT) is a classic arrhythmogenic toxic manifestation.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Focal atrial tachycardia in an 88-year-old woman with 2:1 AV nodal block in the setting of digoxin therapy and potassium 2.8 mmol/L (2.8 mEq/L)From the collection of Sarah Stahmer, MD [Citation ends].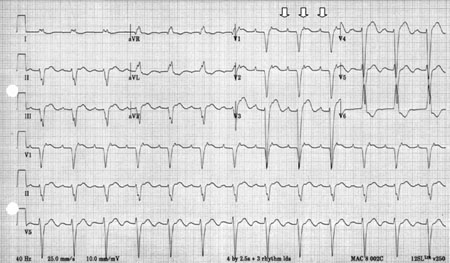
Result
elevated if digoxin toxicity
theophylline level
Test
Result
elevated if theophylline toxicity
CXR
Test
May diagnose underlying cardiopulmonary disease that would predispose the patient to this arrhythmia.
Result
abnormalities suggestive of cardiac disease, such as increased cardiothoracic ratio, lung pathology or evidence of prior cardiac surgery
electrolytes
Test
Should be routinely measured in most patients.
Electrolytes are rarely the primary cause, but abnormality may precipitate focal AT in patients with a predisposition. For example, the patient on digoxin for congestive heart failure may develop this rhythm in the setting of hypokalaemia
Result
hypokalaemia
toxicology screen
Test
When drugs of abuse are suspected, quantitative supportive data can be valuable.
Result
may quantify cocaine, amphetamines, or ethanol use
Investigations to consider
vagal manoeuvres, adenosine
Test
Helpful in differentiating atrial tachycardia from other causes of supraventricular tachycardia.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Response to adenosine 6 mg intravenouslyFrom the collection of Sarah Stahmer, MD [Citation ends].
Result
vagal manoeuvers will either have no effect or cause AV node block (slowing ventricular rate); adenosine causes AV node block and may transiently suppress or rarely terminate tachycardia
thyroid-stimulating hormones
Test
Result
suppressed in hyperthyroidism
echocardiogram
Test
Patients with evidence of haemodynamic compromise or heart failure should have an echo performed as soon as possible.
Result
may show underlying cause such as valvular disease or cardiomyopathy
ambulatory 24-hour (Holter) ECG or event recorder
Test
May be helpful in patients with transient focal AT that occurs several times a week. In patients with less frequent episodes, an event or wearable loop recorder may be more useful than a 24-hour recording.[1]
Result
may record events in patients with transient episodes
electrophysiological study (EPS)
Test
Invasive study that can identify the site of the tachycardia and underlying mechanism.
EPS involving ablation can be curative and may be offered as first-line therapy to select patients.[1]
Result
inducible arrhythmia and mechanism determine the origin of focal AT within the atria
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer