Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- advanced age
- ethnicity
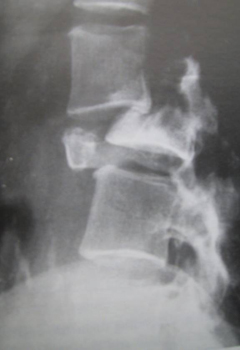
- previous osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
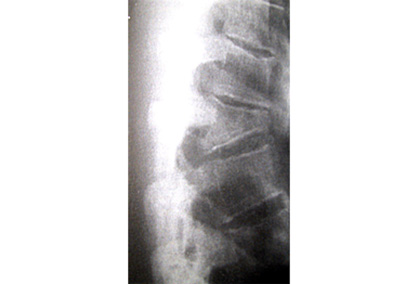
- acute back pain
- asymptomatic
Other diagnostic factors
- history of long-term corticosteroid use
- bone-losing medications
- kyphotic deformity
- loss of lumbar lordosis
- localised tenderness
- loss of standing height
- loss of sagittal balance
Risk factors
- older age
- previous osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- low body weight
- recent weight loss
- family history of low bone mass/osteoporotic fractures
- smoking
- white or Asian race
- postmenopausal status
- secondary amenorrhoea
- alcohol (>2 units/day)
- corticosteroid use
- glucocorticoid excess
- hyperthyroidism
- vitamin D deficiency
- low calcium intake
- rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune connective tissue diseases
- endocrine disorders (e.g., hypogonadism, hyperparathyroidism, hyperprolactinaemia, acromegaly, hypercortisolism, hyperthyroidism)
- gastrointestinal diseases (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease, coeliac disease, malabsorption syndromes, post-bariatric surgery)
- liver diseases (e.g., biliary sclerosis, sclerosing cholangitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis)
- dietary disorders (e.g., anorexia nervosa/bulimia, inadequate diet, total parenteral nutrition)
- neurological disorders (e.g., stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injury, long-term immobilisation)
- renal disease
- type 1 diabetes mellitus
- organ transplantation
- bone-losing medications
Diagnostic investigations
Investigations to consider
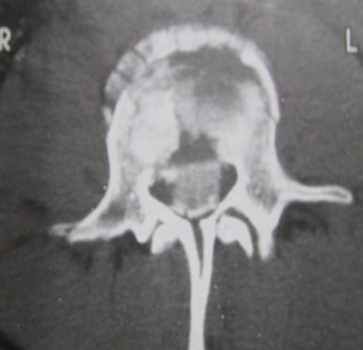
- CT spine
- MRI spine
- technetium-99m (Tc-99m) whole-body bone scan (bone scintigraphy)
- single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/CT
- bone densitometry scan
- CT myelogram
- FBC
- bone profile (including serum calcium and alkaline phosphatase)
- C-reactive protein
- blood cultures
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Nasir A. Quraishi, LLM, FRCS
Consultant Spine Surgeon & Honorary Clinical Associate Professor
Centre for Spinal Studies and Surgery
Queen’s Medical Centre
Nottingham
UK
Disclosures
NAQ declares that he has no competing interests.
Opinder Sahota, FRCP, DM, FHEA
Professor of Orthogeriatric Medicine & Consultant Physician
Queen's Medical Centre
Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust
Nottingham
UK
Disclosures
OS declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Nasir A. Quraishi and Dr Opinder Sahota would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Jeremy Fairbank, previous contributor to this topic.
Peer reviewers
Kee D. Kim, MD
Professor of Neurological Surgery
University of California
Davis
CA
Disclosures
KDK declares that he has no competing interests.
Micky Malhotra, MBBS, DTCD, MD, MRCP
Consultant Physician
Wrightington, Wigan & Leigh NHS Foundation Trust
Wigan
UK
Disclosures
MM declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer