The incidence of malignant transformation in leukoplakias ranges from 3% to 33% over 10 years.[61]Waldron CA, Shafer WG. Leukoplakia revisited. A clinicopathologic study 3256 oral leukoplakias. Cancer. 1975 Oct;36(4):1386-92.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1175136?tool=bestpractice.com
[62]Wright JM. Oral precancerous lesions and conditions. Semin Dermatol. 1994 Jun;13(2):125-31.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8060824?tool=bestpractice.com
[153]Sciubba JJ. Oral leukoplakia. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1995;6(2):147-60.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7548621?tool=bestpractice.com
[154]Scully C, Cawson RA. Potentially malignant oral lesions. J Epidemiol Biostat. 1996;1:3-12. Rates of transformation to carcinoma vary with the clinical type of leukoplakia. In addition, the overall size of the lesion plays a role in this, with a 5.4 times greater risk of malignancy developing when lesions exceeded 200 mm².[146]Holmstrup P, Vedtofte P, Reibel J, et al. Long-term treatment outcome of oral premalignant lesions. Oral Oncol. 2006 May;42(5):461-74.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16316774?tool=bestpractice.com
[155]Chang JC, Distler SG, Kaplan AM. Tobacco smoke suppresses T cells but not antigen-presenting cells in the lung-associated lymph nodes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 Mar 1;102(3):514-23.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2315919?tool=bestpractice.com
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia is a progressive lesion with high recurrence and low 5-year survival rates.[156]Sciubba JJ, Helman JI. Current management strategies for verrucous hyperkeratosis and verrucous carcinoma. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2013 Feb;25(1):77-82.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23399397?tool=bestpractice.com
While many clinicians advocate that the anatomic site of leukoplakia plays a role in the rate/prevalence of malignant transformation, others state that this concept is not justified. Furthermore, there is no reason to separate tobacco-associated forms of leukoplakia from idiopathic forms in terms of overall management and behavior.[138]van der Waal I, Axell T. Oral leukoplakia: a proposal for uniform reporting. Oral Oncol. 2002 Sept;38(6):521-6.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12167428?tool=bestpractice.com
Most leukoplakias, particularly homogeneous leukoplakias, have low potential for malignant transformation. Those leukoplakias that do progress to carcinoma probably arise within a field of precancerized epithelium consisting of keratinocytes at different stages of cytogenetic transformation.[157]Feller L, Lemmer J. Oral leukoplakia as it relates to HPV infection: a review. Int J Dent. 2012;2012:540561.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3299253
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22505902?tool=bestpractice.com
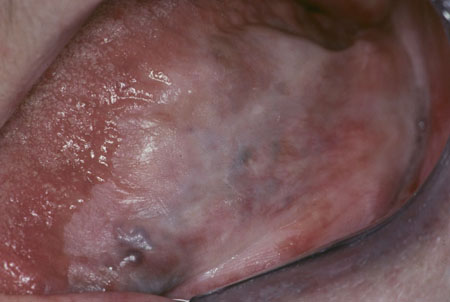
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Homogeneous leukoplakiaCourtesy of Dr James Sciubba; used with permission [Citation ends].