Differentials
Common
Gastritis
History
use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; burning epigastric pain often relieved by food; may be aggravated by recent stress or anxiety
Exam
tenderness to palpation in the epigastrium or normal examination
1st investigation
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
gastritis; antral mucosal biopsies may reveal H pylori infection, which requires antibiotic therapy; may confirm aetiology such as eosinophilic gastritis
Other investigations
- Helicobacter pylori urea breath test:
positive
More
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
History
typical: heartburn and regurgitation; atypical: minimal epigastric burning or regurgitation; nausea predominates; morning nausea common
Exam
tenderness in the epigastrium on palpation or normal examination
1st investigation
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
may be normal or reveal oesophageal inflammation ranging from erythema to frank ulceration
More
Other investigations
- ambulatory pH monitoring:
confirms acid reflux if endoscopy normal; pH >4 more than 4% of the time is abnormal
More
Peptic ulcer disease
History
use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; burning epigastric pain often relieved by food
Exam
tenderness to palpation in the epigastrium or normal examination
1st investigation
- Helicobacter pylori urea breath test:
positive
More - upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
reveals gastritis, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, or duodenitis; antral mucosal biopsies reveal H pylori infection, which requires antibiotic therapy
Other investigations
Acute gastroenteritis
History
diarrhoea; abdominal pain; low-grade fever in viral disease; high-grade fever with toxicity in bacterial aetiology
Exam
diffuse abdominal tenderness to palpation; signs of volume depletion (altered mental status, poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, sunken eyes, irritability, and hypotension)
1st investigation
- serum electrolytes:
low sodium and potassium
Other investigations
- stool culture:
may identify microbial agent; usually unrevealing
More
Food poisoning
History
diarrhoea, abdominal pain; symptoms develop within several hours to days following meal; symptoms may improve or persist for weeks leading to chronic disease
Exam
epigastric tenderness; lower abdominal tenderness to palpation; signs of volume depletion (altered mental status, poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, sunken eyes, irritability, and hypotension)
1st investigation
- serum electrolytes:
low sodium and potassium
Other investigations
- stool culture:
may reveal Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella
Chronic post-viral nausea and vomiting
History
symptoms become chronic after acute viral or bacterial gastroenteritis
Exam
epigastric tenderness; signs of volume depletion (altered mental status, poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, sunken eyes, irritability, and hypotension)
1st investigation
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
normal
Other investigations
- solid meal gastric emptying study:
gastroparesis
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
Migraine
History
recurrent nausea and/or vomiting in the presence of headache and disturbed vision
Exam
no neurological findings but abdomen may be tender due to vomiting/retching
1st investigation
- no initial test:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
- CT head:
may exclude alternate diagnosis
- MRI head:
may exclude alternate diagnosis
Motion sickness
History
precipitating event (e.g., car, aeroplane, or boat ride)
Exam
normal
1st investigation
- no initial test:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
- autonomic nervous system tests:
may provoke the symptoms
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
History
brief, sudden, episodic vertigo
Exam
normal neurological exam
1st investigation
- Dix-Hallpike manoeuvre:
positive
Other investigations
Stroke (embolic/ischaemic/haemorrhagic)
History
transient nausea, loss of vision, instability, dizziness
Exam
focal neurological deficits
1st investigation
- CT head:
oedema or infarct in brain
Other investigations
Hypercalcaemia
History
alterations of mental status, abdominal pain, constipation, muscle pains, polyuria, headache
Exam
normal
1st investigation
- calcium:
elevated; >2.63 mmol/L (>10.5 mg/dL)
- parathyroid hormone:
suppressed (non-hyperparathyroid diagnoses such as malignancy) or elevated (hyperparathyroidism)
Other investigations
Hypothyroidism
Gastric outlet obstruction
History
history of peptic ulcer disease; vomitus is yellow gastric juice or may contain blood; upper abdominal pain is prominent
Exam
epigastric tenderness and/or distension; a rigid abdomen with rebound tenderness suggests concurrent bowel perforation and acute peritonitis
1st investigation
- upper gastrointestinal series:
gastric distension
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
reveals the site and cause of obstruction
More
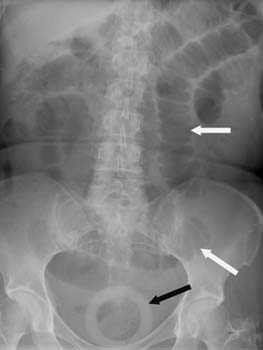
Small bowel obstruction
History
bilious vomiting; peri-umbilical location of pain
Exam
peri-umbilical tenderness; abdominal distension; bowel sounds high pitched or absent; rigid abdomen with rebound tenderness suggests concurrent bowel perforation and acute peritonitis
1st investigation
- acute abdominal series:
air fluid levels in small bowel
More
Colonic obstruction
History
lower abdominal pain with or without distension; faeculent vomitus
Exam
tenderness and/or distension in lower abdomen; bowel sounds may be absent; a rigid abdomen with rebound tenderness suggests concurrent bowel perforation and acute peritonitis
1st investigation
- acute abdominal series:
distended colon proximal to site of obstruction; air fluid levels in small bowel
More
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
reveals site of colonic obstruction; free air under the diaphragm indicating perforation
- colonoscopy:
may reveal mucosal lesion that may narrow the bowel lumen
Choledocholithiasis
History
right upper quadrant (RUQ) or epigastric pain, postprandial symptoms
Exam
RUQ tenderness; may have jaundice
1st investigation
- abdominal ultrasound:
stones in gallbladder or bile duct
Other investigations
Cholecystitis
History
history of prior biliary colic; right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain; may have fever or referred right shoulder pain
Exam
may have positive Murphy sign (right subcostal tenderness, worse after deep inspiration); may have tender RUQ mass; possible jaundice
1st investigation
- CBC:
elevated WBC count
- LFTs:
cholestatic pattern
- ultrasound RUQ:
may show thickened gallbladder wall with calculi or pericholecystic fluid collection
Other investigations
Post-gastrointestinal surgery
History
previous surgery (fundoplication, oesophagectomy, gastrojejunostomy [Bilroth I or II], or bariatric operation); epigastric discomfort; bloating; regurgitation after oesophagectomy with early satiety
Exam
epigastric tenderness; tender scars, positive Carnett's sign (occurs when a combination of pressure on the scar and flexion of the head clearly exacerbates the patient's typical pain)[19]
1st investigation
- upper endoscopy:
mechanical obstruction at site of surgery, mucosal abnormalities, or normal
Other investigations
- gastric emptying study:
gastroparesis or disordered gastric emptying
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
Severe constipation
History
constipation; altered bowel habits; abdominal pain; pain on defecation
Exam
tender abdomen; palpable abdominal mass
1st investigation
- acute abdominal series:
dilated loops of bowel; faecal loading in right colon
Other investigations
- anorectal manometry:
dyssynergia, impaired/absent recto-anal inhibitory reflex, abnormal rectal sensation (hypo- or hypersensitivity)
- transit studies:
retention of >20% of radio-opaque markers on an abdominal x-ray performed 120 hours after ingestion of the capsule indicates slow colonic transit; retention of a wireless motility capsule for >59 hours after capsule ingestion also provides an accurate assessment of colonic transit time
- defecography:
incomplete evacuation of the rectum, poor rectal stripping wave, abnormal perineal descent
Irritable bowel syndrome
History
altered bowel habits (alternating constipation and diarrhoea), bloating, abdominal pain and distension, stress-related symptoms
Exam
normal in most patients; abdominal tenderness in some cases
1st investigation
- no initial test:
diagnosis of exclusion
Other investigations
- acute abdominal series:
dilated loops of bowel
- colonoscopy:
may demonstrate alternate diagnosis such as inflammatory bowel disease or neoplasm
More
Cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS)
History
onset in childhood; migraine common; symptom-free weeks
Exam
normal
1st investigation
- no initial test:
clinical diagnosis
More
Other investigations
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
- endoscopy:
normal
- solid meal gastric emptying study:
normal
More
Gastric dysrhythmias
Gastroparesis
History
nausea, early satiety, fullness, and vomiting of undigested food; all symptoms are worse after ingestion of meals; history of diabetes or Parkinson's disease
Exam
succussion "splash" rarely detected; weight loss, orthostatic hypotension
1st investigation
- solid meal gastric emptying study:
>60% after 2 hours or >10% after 4 hours after consumption of the meal
- non-digestible capsule test:
diagnosis is confirmed if capsule not emptied within 5 hours after it is ingested
More
Other investigations
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
- endoscopy:
no evidence of mucosal inflammation
Bacterial peritonitis
History
abdominal pain; nausea or vomiting ranges from mild to severe; fever low grade to severe; recent abdominal surgery
Exam
rigid abdomen with rebound tenderness
1st investigation
- acute abdominal series:
air under diaphragm indicates perforation
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
air under diaphragm, ascites; thickened bowel wall, intra-abdominal fluid or masses
Anorexia nervosa
History
abnormalities in body image, depression, amenorrhoea, or psychosocial dysfunction
Exam
cachexia; signs of volume depletion (altered mental status, poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, sunken eyes, irritability, and hypotension), signs of malnutrition (loss of subcutaneous fat, apathy and lethargy, pallor, depigmentation, enlarged abdomen, winged scapula, flaky skin, bipedal oedema)
1st investigation
- solid meal gastric emptying study:
gastroparesis
Other investigations
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
Bulimia nervosa
History
abnormalities in body image, depression, other psychosocial dysfunction
Exam
normal examination; possible signs of volume depletion (altered mental status, poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, sunken eyes, irritability, and hypotension) and malnutrition (loss of subcutaneous fat, apathy and lethargy, pallor, depigmentation, enlarged abdomen, winged scapula, flaky skin, bipedal oedema); may have teeth enamel erosion from repeated vomiting
1st investigation
- solid meal gastric emptying study:
normal
Other investigations
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
Pregnancy
History
sexually active; missed period; morning nausea
Exam
pelvic examination may reveal gravid uterus or pelvic masses that suggest an alternate diagnosis; may have signs of volume depletion in hyperemesis gravidarum
1st investigation
- urine or blood tests for pregnancy:
positive
- ultrasound pelvis:
confirms pregnancy, rules out ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy, or any other structural abnormalities that suggest pelvic inflammatory disease (e.g., tubo-ovarian abscess)
Other investigations
- thyroid function tests:
may show suppressed thyroid-stimulating hormone in hyperemesis gravidarum
Drug-induced
History
symptoms not related to eating or bowel movements; onset days to weeks after starting the medicine; symptoms recur 3 to 4 days after re-initiation of medicine (e.g., chemotherapy agents); causative medications include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antidepressants, anti-arrhythmics, opioids, chemotherapy, oestrogen/progesterone, theophylline, digoxin, lubiprostone, metformin, exenatide
Exam
epigastric tenderness may be present with NSAIDs
1st investigation
- therapeutic trial:
nausea resolves on cessation of medicine
More
Other investigations
Nephrolithiasis
History
flank pain, may radiate to groin; dysuria
Exam
costovertebral angle tenderness
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
microscopic or gross haematuria
- noncontrast CT abdomen:
size and location of stones
Other investigations
Uraemia
History
existing renal disease or diabetes; fatigue, anorexia, weight loss; severe cases may have muscle cramps, pruritus, mental and visual disturbances; increased thirst
Exam
oedema; sallow skin; pallor; occult gastrointestinal bleed; hypertension
1st investigation
- 24-hour urine creatinine clearance:
<10 to 20 mL/minute
More - renal profile:
hyperkalaemia; acidosis; hypocalcaemia; hyperphosphataemia
- ultrasound kidneys:
large kidneys in hydronephrosis, obstructions; small kidneys in chronic irreversible damage
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
size and morphology of the kidneys, lymph nodes
Idiopathic functional dyspepsia or post-prandial distress syndrome
History
vague epigastric discomfort, early satiety, and prolonged fullness
Exam
normal
1st investigation
- no initial test:
diagnosis of exclusion
Other investigations
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
excludes structural lesions or inflammation
Uncommon
Acute coronary syndrome
History
may have cardiac risk factors such as hypertension or diabetes; may have previous myocardial infarction or stable angina; chest pain; diaphoresis; dyspnoea
Exam
may have hypotension or hypertension; may have rales, oedema, or abnormal heart sounds
1st investigation
- ECG:
ST-T wave changes, ischaemic changes, or dysrhythmia
- troponin levels:
elevated
Other investigations
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
History
nausea onset with change in position (e.g., supine to upright), lightheadedness
Exam
usually normal; absence of dehydration
1st investigation
- autonomic nervous system testing:
blood pressure and/or pulse rate do not increase in response to upright tilt, and nausea is provoked during the test
More
Other investigations
Meniere's disease
History
vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, aural fullness, drop attacks
Exam
nystagmus, positive Romberg's test, inability to tandem walk
1st investigation
- audiometry:
low-frequency, unilateral sensorineural hearing loss
Other investigations
Acoustic neuroma
History
asymmetrical hearing loss, tinnitus
Exam
nystagmus, imbalance
1st investigation
- audiometry:
asymmetrical sensorineural/retrocochlear hearing loss
Other investigations
- CT head:
unilateral acoustic meatus enlargement on bone windows
- MRI head:
uniformly enhanced, dense mass extending into internal acoustic meatus; absence of dural tail
Traumatic brain injury
History
head trauma; headache, confusion
Exam
may have focal neurological deficit
1st investigation
- CT head:
may show fracture or intracranial bleed
Other investigations
- MRI head:
may show fracture or intracranial bleed
Meningitis
History
headache, neck stiffness, fever, altered mental status, photophobia, seizures
Exam
rash, papilloedema, Kernig's or Brudzinski's sign
1st investigation
- lumbar puncture with cerebrospinal examination:
low glucose, high protein; may reveal infectious aetiology
More
Other investigations
- blood cultures:
may show infecting organism
Brain abscess
History
headache, stiff neck, altered mental status
Exam
may have focal neurological deficit; Kernig's or Brudzinski's sign
1st investigation
- MRI head:
one or more ring-enhancing lesions
Other investigations
- blood cultures:
may show infecting organism
Complex partial seizures
History
nausea, bizarre smells, unusual sensations or experience (rising epigastric experience, fear, deja vu, or an 'out-of-body' sensation); appearance of being in a daydream, or staring blankly
Exam
normal neurological examination between episodes
1st investigation
- EEG:
abnormalities in temporal lobe electrical rhythm
Other investigations
Central nervous system tumours
History
unexplained headache, change in vision or motor function, poor coordination, ataxia
Exam
focal neurological abnormalities; abdominal examination is normal
1st investigation
- CT head:
area of hypodensity; enhancement with contrast depending on type or grade of the tumour; hyperdensity if calcification or haemorrhage present
Other investigations
Primary adrenal insufficiency (acute or chronic)
History
chronic symptoms; no abdominal pain; may have diarrhoea; may be on chronic corticosteroid medicine
Exam
normal abdominal examination; orthostatic hypotension
1st investigation
- fasting cortisol:
82.8 nanomols/L (<3 micrograms/dL)
More
Other investigations
- cosyntropin stimulation test:
poor cortisol response to adrenocorticotropic hormone (peak <497 nanomols/L; <18 micrograms/dL)
More
Hyperthyroidism
History
heat intolerance; tremors; weight loss
Exam
tachycardia; brisk reflexes; enlarged thyroid
1st investigation
- free T4 and/or free T3:
elevated
- thyroid-stimulating hormone:
suppressed
Other investigations
Hypopituitarism
History
possible galactorrhoea; headache or visual field defects; weakness; dizziness; infertility; symptoms of hypothyroidism
Exam
absent axillary and pubic hair; orthostasis; reduced muscle mass; delayed return of reflexes
1st investigation
- thyroid function tests:
low free T4 with normal or low thyroid-stimulating hormone
- adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation test:
inadequate cortisol response
- serum follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinising hormone:
low
- serum prolactin:
may be elevated
Other investigations
- MRI head:
may show pituitary tumour or sellar abnormality
Heat stroke
History
older age; cognitive comorbidities; use of diuretics, antihypertensives, anticholinergics, phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants; altered mental status
Exam
core temperatures >40°C (>104°F)
1st investigation
- serum chemistries:
variable abnormalities
- serum creatine phosphokinase:
may be elevated if rhabdomyolysis
Other investigations
Acute pancreatitis
History
history of alcohol use or cholelithiasis; abdominal pain
Exam
tachycardia or orthostasis if volume-depleted; abdominal tenderness or distension
1st investigation
- serum lipase or amylase:
elevated (3 times the upper limit of normal)
More
Other investigations
- abdominal ultrasound:
may show pancreatic inflammation, peri-pancreatic stranding, calcifications, or fluid collections
More - abdominal CT with oral and intravenous contrast:
may show diffuse or segmental enlargement of the pancreas with irregular contour and obliteration of the peri-pancreatic fat, necrosis, or pseudocysts
More - magnetic imaging/magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP):
findings may include stones, tumours, diffuse or segmental enlargement of the pancreas with irregular contour and obliteration of the peri-pancreatic fat, necrosis, or pseudocysts
More
Bariatric surgery sequelae
History
intolerance of oral intake 3 to 6 weeks following surgery (suggests stricture); possible dysphagia
Exam
the obese abdomen may be difficult to examine; may be tachycardia, fever, and signs of respiratory distress
1st investigation
- upper endoscopy:
demonstrates stricture
More
Other investigations
- gastric emptying study:
>60% after 2 hours or >10% after 4 hours after consumption of the meal is considered to be delayed gastric emptying
Primary pseudo-obstruction
History
symptoms mimic mechanical gastrointestinal obstruction; there may be a history of laparotomy with no evidence of mechanical obstruction
Exam
abdomen distended and tympanitic; bowel sounds usually absent
1st investigation
- acute abdominal series:
air fluid levels; dilated stomach, duodenum, colon
- full thickness gastrointestinal biopsy:
may help identify the pathophysiology of pseudo-obstruction
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
dilated stomach, duodenum, small bowel, colon; no site of obstruction located
Secondary pseudo-obstruction
History
history of lupus, scleroderma, myotonic dystrophy or other striated muscle disorders; symptoms mimic mechanical gastrointestinal obstruction; there may be a history of laparotomy with no evidence of mechanical obstruction
Exam
abdomen distended and tympanitic; bowel sounds usually absent; sclerodactyly, malar rash
1st investigation
- antinuclear antibodies, double-stranded (ds)DNA, Smith antigen:
may be positive
- acute abdominal series:
air fluid levels; dilated stomach, duodenum, colon
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
dilated stomach, duodenum, small bowel, colon; no site of obstruction
- full thickness gastrointestinal biopsy:
may help identify the pathophysiology of pseudo-obstruction
Abdominal abscess
History
abdominal pain; symptoms range from mild to severe; low-grade fever; recent abdominal surgery; night sweats; fatigue; history of cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and ascites
Exam
abdominal tenderness and/or mass; ascites and enlarged liver and spleen
1st investigation
- CT abdomen:
intra-abdominal abscess; ascites
Other investigations
Carcinomatous peritonitis
History
known gastrointestinal cancer; abdominal pain; symptoms range from mild to severe; low-grade fever; recent abdominal surgery
Exam
cachexia; firm abdomen; palpable abdominal mass
1st investigation
- CT abdomen:
ascites, thickened bowel wall, intra-abdominal fluid or masses
Other investigations
- abdominal paracentesis with biopsy:
histology of aspirated abdominal fluid and biopsied mass or peritoneum confirms cancer diagnosis
Stomach cancer
History
nausea, vomiting, and early satiety evolve slowly over weeks or months; weight loss; symptoms suggest mucosal inflammation, dyspepsia, or gastroparesis
Exam
appears ill; cachexia; epigastric tenderness
1st investigation
- upper gastrointestinal barium series:
polypoid or ulcer-like gastric mass
- upper gastrointestinal endoscopy:
biopsy reveals cancer
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
gastric mass; enlarged lymph nodes
Ovarian cancer
History
nausea, vomiting, and early satiety evolve slowly over weeks or months; symptoms of dyspepsia or gastroparesis; weight loss; middle-aged woman
Exam
appears ill; cachexia; pelvic mass
1st investigation
- pelvic ultrasound:
presence of solid, complex, septated, multiloculated mass; high blood flow
- CT abdomen:
ovarian mass; enlarged lymph nodes
- CA-125:
may be positive
More
Other investigations
Renal cancer
History
nausea, vomiting, and early satiety evolve slowly over weeks or months; symptoms of dyspepsia or gastroparesis; unexplained weight loss, haematuria; low back pain
Exam
appears ill; cachexia; abdominal mass
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
gross or microscopic haematuria
- abdominal/pelvic ultrasound:
abnormal renal cyst/mass, lymphadenopathy, and/or other visceral metastatic lesions
- abdominal CT scan:
renal mass; enlarged lymph nodes
Other investigations
Small cell lung cancer
History
history of smoking; weight loss; shortness of breath; cough; haemoptysis; nausea, vomiting, and early satiety evolves slowly over weeks or months; symptoms of dyspepsia or gastroparesis
Exam
appears ill with cachexia; respiratory wheeze or decreased breath sounds
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
central mass, hilar lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion
More - CT chest:
mass in the lung
Other investigations
- paraneoplastic antibodies:
increased
More
Pancreatic cancer
History
weight loss, anorexia, abdominal discomfort, back pain
Exam
may have jaundice or abdominal mass
1st investigation
- abdominal ultrasound:
pancreatic mass, dilated bile ducts, liver metastases
- abdominal CT:
confirms pancreatic mass and extent of spread
Other investigations
Chronic mesenteric ischaemia
History
post-prandial nausea, fullness, and early satiety; symptoms worse 30 to 60 minutes after ingestion of food; weight loss
Exam
diffuse abdominal tenderness; abdominal bruit
1st investigation
- mesenteric duplex ultrasound:
confirms blood flow disturbance in the superior mesenteric artery or coeliac artery
- CT angiogram:
confirms site of blood vessel stenosis
Other investigations
- solid meal gastric emptying study:
confirms gastroparesis if present
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
Cannabinoid hyperemesis
History
age <50 years; cannabis use usually for >2 years and >once per week; may have abdominal pain; may have relief of symptoms with warm showers or baths
Exam
non-specific
1st investigation
- no initial test:
diagnosis is clinical: tests may be required to rule out other causes of nausea and vomiting
Other investigations
- gastric emptying studies:
may be delayed
More - autonomic nervous system testing:
may provoke the symptoms
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
Chronic nausea and vomiting after antibiotics or anaesthetics
History
chronic symptoms develop after exposure to antibiotics or anaesthesia agents
Exam
epigastric tenderness
1st investigation
- no initial test:
clinical diagnosis
Other investigations
- gastric electrical activity:
may show abnormalities of frequency, amplitude, and/or propagation
- solid meal gastric emptying study:
normal or gastroparesis
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer