Investigations
1st investigations to order
ultrasound
Test
First line test.[43][44] Should include both transvaginal and transabdominal views of the pelvis to ensure uterine pathology beyond the limits of the transvaginal probe is detected.[76] Numerous small and diffuse intramural fibroids may appear as subtle heterogeneous echoes within the confines of the myometrium.
Commonly, moderate to large fibroids show gross uterine contour irregularities with a hypoechoic and heterogeneous echotexture.
Large pedunculated subserous fibroids can be difficult to distinguish from solid adnexal masses.
Submucosal fibroids are generally better visualised by transvaginal ultrasound and can still pose a diagnostic dilemma in differentiating these intracavitary lesions from endometrial polyps.
A degenerating fibroid that has outstripped its blood supply can have cystic areas within the fibroid.[77][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Solitary intramural fibroid as shown by transvaginal pelvic ultrasound (TVUS) demonstrating posterior intramural mass lying between a normal-appearing trilaminar endometrial stripe and posterior uterine serosaFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound (TVUS) shows a midline posterior fundal fibroid greatly distorting the endometrial cavityFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound (TVUS) shows a midline posterior fundal fibroid greatly distorting the endometrial cavityFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].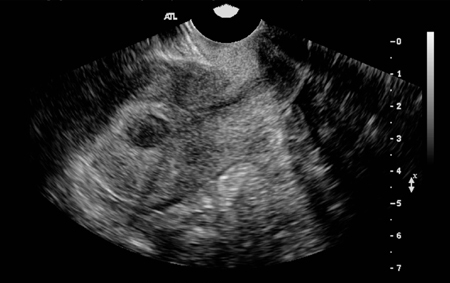
Calcification can also be seen in degenerating fibroids.
Ultrasonographic evaluation does not seem to distinguish fibroids from sarcomas, and adenomyosis may also appear similar.
If the fibroid leads to urinary tract obstruction, renal ultrasonography is required.
Result
sonographic appearance of uterine fibroids variable and depends on location (submucosal, intramural, subserosal), number, and blood supply status; uterus may be symmetrically enlarged or remain normal size
endometrial biopsy
Test
An abnormal endometrial biopsy would show either precursor histology for endometrial carcinoma (simple/complex hyperplasia or simple atypical/complex atypical hyperplasia) or frank endometrial carcinoma.[48]
Result
normal
Investigations to consider
sonohysterography
Test
High sensitivity for the detection of submucous and intramural fibroids.[43][51] For intracavitary lesions detected by transvaginal ultrasound, the biggest challenge is in differentiating endometrial polyps from submucous uterine fibroids; both are space-occupying intracavitary lesions. It is important to keep in mind that endometrial polyps are completely intraluminal in location and can be seen to freely move during injection of saline. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sonohysterography shows several small intracavitary masses suspicious for polypsFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].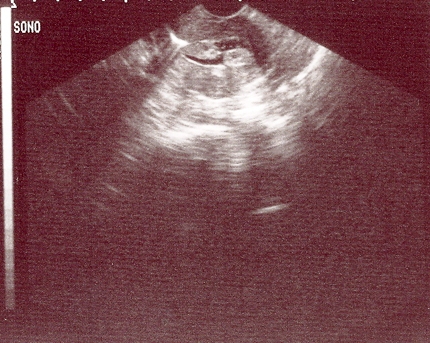
Fibroids are generally less echogenic than polyps and surrounding endometrium and careful examination can frequently reveal continuity with the surrounding myometrium.[53][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sonohysterography demonstrates a posterior submucous uterine fibroid deforming the posterior endometrial cavityFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
intramural and subserosal uterine fibroids; diagnostic criteria similar to that used for transvaginal and transabdominal ultrasound diagnosis
hysteroscopy
Test
Advantages of hysteroscopy include the ability to both visualise space-occupying lesions and obtain a surgical specimen for histologic examination during the same procedure.[46][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hysteroscopic examination of the uterine cavity demonstrates the presence of two contiguous submucous uterine fibroids in this patient with persistent heavy menstrual bleedingFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].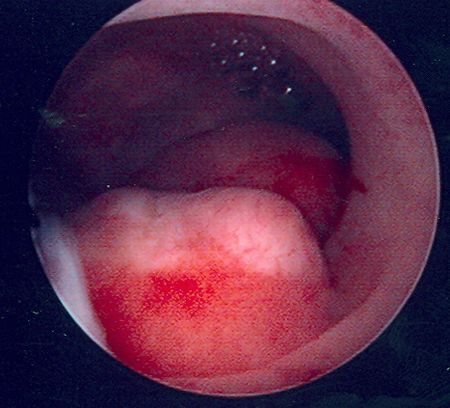 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hysteroscopic image of a large pedunculated submucous uterine fibroidFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hysteroscopic image of a large pedunculated submucous uterine fibroidFrom the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].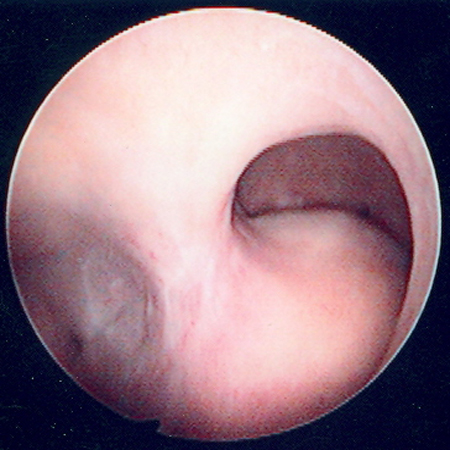
Result
space-occupying lesions of the endometrial cavity such as endometrial polyps and submucous uterine fibroids
MRI
Test
MRI is an excellent non-invasive and non-ionising technique for evaluating atypical cases of pelvic or abdominal masses suspicious for fibroids and can assist in differentiating benign from malignant conditions involving the uterus and adjacent structures.[43]
Result
pelvic or abdominal masses involving the uterus and adjacent structures
laparoscopy
Test
Surgical excision followed by histopathological examination is the standard of care for diagnosis.[72]
Surgery may be needed in cases of suspected malignancies. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Laparoscopy shows the presence of a large right posterolateral subserosal fibroid; note the close proximity of this uterine fibroid to the right ovary (potential for misdiagnosis as an adnexal mass)From the personal collection of Dr M.F. Mitwally and Dr R.J. Fischer; used with permission [Citation ends].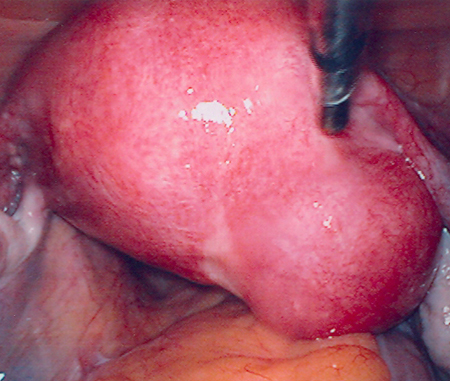
Result
Visualisation of irregular protrusion from uterine surface; if intramural, protrusion minimal; subserosal type has most tissue bulging from surface of uterus, covered by thin layer of serosa and myometrium
Emerging tests
sonoelastography
Test
Diagnostic ultrasound technique that provides a non-invasive means of estimating soft tissue elasticity and stiffness.
Result
differentiates fibroids, adenomyosis, and normal uteri
MR elastography
Test
Non-invasive technique for the assessment of tissue stiffness.[78]
It is more precise than sonoelastography and may be useful for follow-up after treatment of uterine fibroids.
Result
helps predict the response of uterine fibroids to treatment
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer