Images and videos
Images
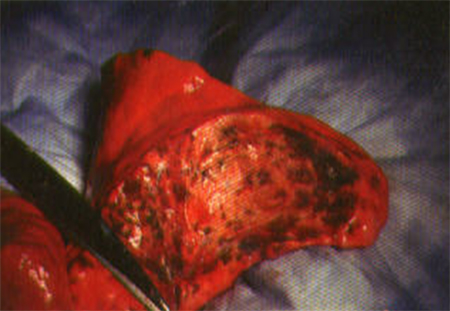
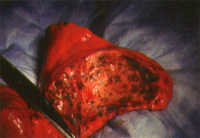
Meconium aspiration syndrome
Cross-section of lung at autopsy showing massive amount of meconium in the airways
From the personal collection of Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:
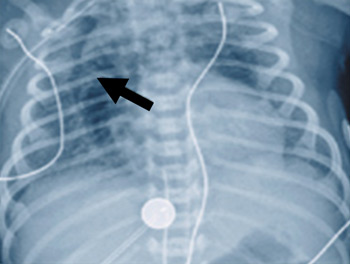
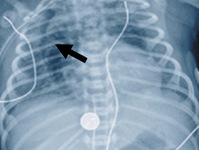
Meconium aspiration syndrome
Pneumomediastinum with spinnaker sail sign (arrow)
From the personal collection of Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:
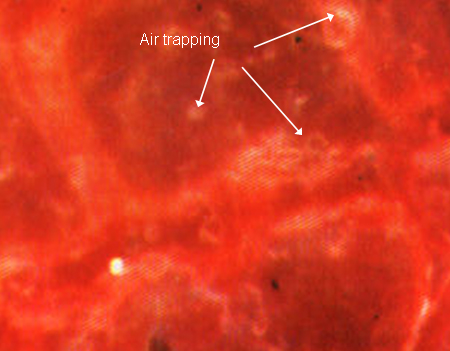
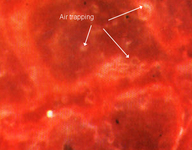
Meconium aspiration syndrome
Air trapping
From the personal collection of Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Meconium aspiration syndrome
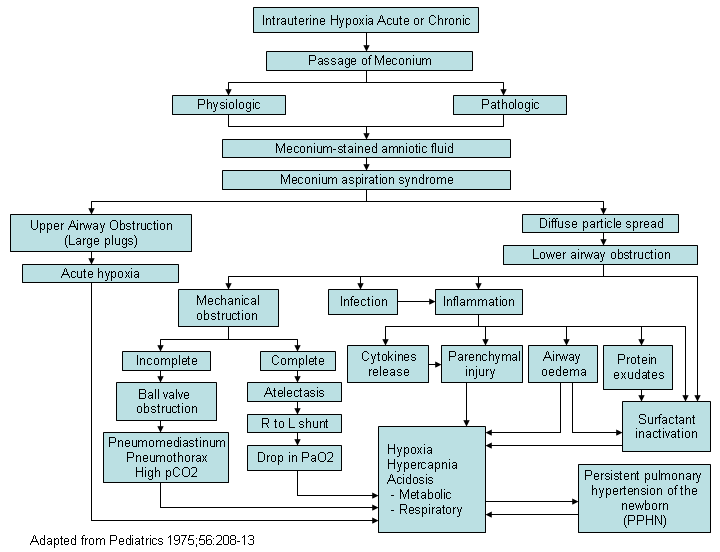
Pathophysiology of meconium aspiration syndrome
Created by Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:
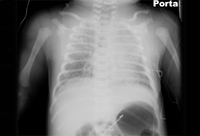
Meconium aspiration syndrome
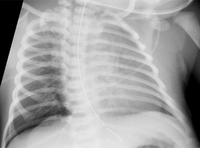
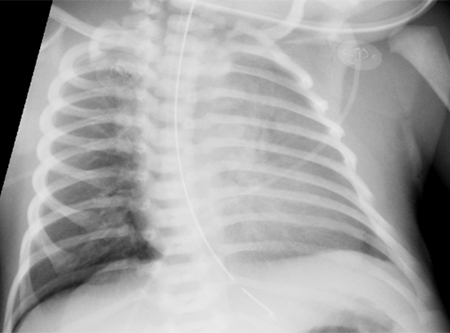
CXR showing air at the base of right lung above the diaphragm, suggestive of pneumothorax in a patient with MAS
From the personal collection of Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Meconium aspiration syndrome
Clinical scoring system for assessing the degree of respiratory distress in the newborn. The physician after assessing the baby using the 5 signs in the left column gives a score of 0 (normal), 1 (mild distress), or 2 (severe distress). Scores for all 5 signs are added, a score of 0 being a normal baby and a score of 10 being very sick. Scores in between correspond to mild to moderate distress
Created by Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Meconium aspiration syndrome
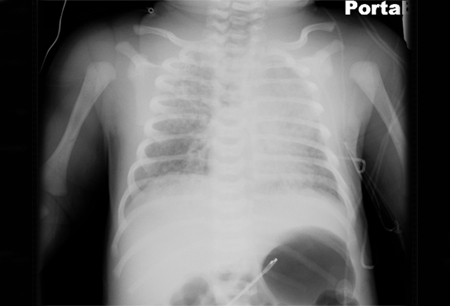
CXR showing patchy infiltrations on both lungs, suggestive of atelectasis in a patient with MAS
From the personal collection of Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Meconium aspiration syndrome
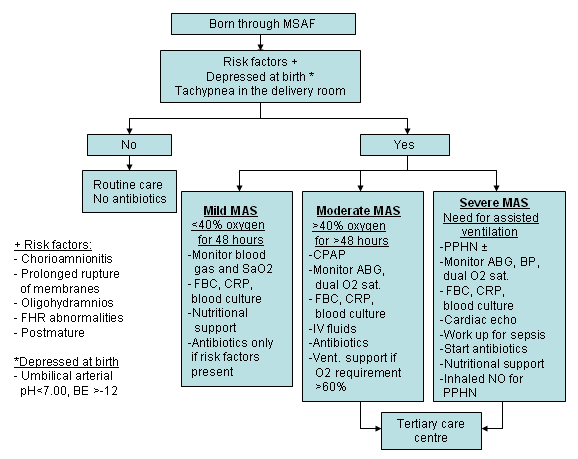
Possible clinical presentations and management of infants born in meconium-stained amniotic fluid (MSAF). BE: base excess; CPAP: continuous positive airway pressure; FHR: fetal heart rate; IV: intravenous; NO: nitric oxide; PPHN: persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn
Created by Dr Vidyasagar and Dr Bhat
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer