Investigations
1st investigations to order
ECG
Test
The diagnosis of atrial fibrillation (AF) requires ECG documentation by at least a single-lead recording during the episode of arrhythmia.[1][2] This test is very accurate in detecting persistent AF. However, where diagnostic uncertainty remains or if rate control needs further evaluation, Holter monitoring or an event recorder (e.g., Cardiomemo) may also be required.[1][80][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atrial fibrillation: P waves are not discernible; the ventricular (QRS complexes) rate is irregularly irregularFrom the collection of Dr Arti N. Shah [Citation ends].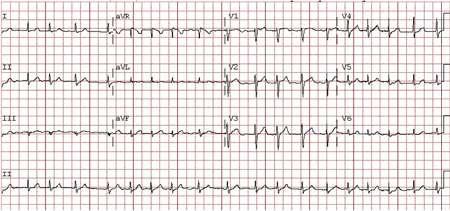
Low-amplitude P waves such as in an atrial tachycardia, especially multifocal atrial tachycardia that may be observed in patients with COPD, may mimic AF.
In patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) such as the permanent pacemakers, AF may be detected as atrial high rate episodes (AHREs). Like clinical AF, CIED-recorded AHRE need to be confirmed by inspection of stored electrogram events because some AHREs may be electrical artefacts/false positives. In patients with CIEDs, if surface ECG shows rapid-paced ventricular rate, underlying AF may not be visible between the paced ventricular complexes and the diagnosis of AF may be missed.
ECG can also be used to screen for a pre-excitation syndrome, such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Result
absent P waves; presence of fibrillatory waves that vary in size, shape, and timing; irregularly irregular QRS complexes
thyroid profile
Test
Thyrotoxicosis may present with atrial fibrillation. Hyperthyroidism can be diagnosed with laboratory work and treated appropriately with medicine, radioablative therapy, or surgery. This is also important when the ventricular rate is difficult to control.[1][2]
Result
suppressed thyroid-stimulating hormone if hyperthyroidism
echocardiogram
Test
Echocardiogram is important to exclude important cardiac pathologies and risk factors for persistent atrial fibrillation such as valvular and pericardial disease, and cardiomyopathies.
Thrombus in the left atrium is more accurately detected with trans-oesophageal echocardiogram compared with transthoracic echocardiogram.[2] All patients who need cardioversion, and have unknown or suboptimal anticoagulation profile, should have a trans-oesophageal echocardiogram first to exclude left atrial thrombus.
Result
may have valvular regurgitation or stenosis, left ventricular or atrial enlargement, peak right ventricular pressure (pulmonary hypertension), left ventricular wall thickness and dysfunction
serum urea and electrolytes (including serum magnesium)
Test
It is important to check serum creatinine as an indicator of renal function. This will influence subsequent management and drug choice and dosing.
Result
may be normal; may be abnormal with renal dysfunction
Investigations to consider
serum transaminases
Test
Liver enzymes may be deranged with alcohol abuse, which is also a risk factor for atrial fibrillation.
Also helpful in choosing anti-arrhythmic agents and their dosages.
Result
may be normal or deranged
prolonged ECG monitoring
Test
Useful to perform over 24 hours (or even 7 days) where diagnostic uncertainty remains. An event recorder (e.g., Cardiomemo) and possibly an insertable/implantable loop recorder may also be required.[94][95]
Mobile health technologies, including smart devices, have become a popular research area for AF detection.[87][88] There are currently >100,000 mobile health apps and ≥400 wearable activity monitors available, but many are not clinically validated and caution is advised for clinical use.[2] If AF is detected by mobile or wearable devices, diagnosis should be confirmed with single-lead or 12-lead ECG analysed by a physician with expertise in ECG rhythm interpretation.[2]
Result
may detect episodes of atrial fibrillation (AF)
fasting blood glucose or HbA1c
Test
Screening for diabetes mellitus as a comorbid condition may be considered.
Result
elevated in diabetes
screening for sleep-disordered breathing (SDB)
Test
Risk factors for SDB should be considered, with screening and diagnosis where indicated. Although polysomnography is the gold standard for diagnosing SDB, home sleep apnoea testing shows promise in diagnosing obstructive sleep apneoa (OSA) in most patients with AF.[45]
Result
may show results consistent with OSA
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer