Differentials
Atrial flutter with variable atrioventricular (AV) conduction
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
History and physical examination may be similar to atrial fibrillation patients.
INVESTIGATIONS
ECG tracing to examine all leads for flutter waves: ECG shows more discrete, uniform atrial activity, such as the typical saw tooth pattern described for typical atrial flutter.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atrial flutter: typical saw-tooth appearance of the flutter waves in the inferior leads (leads II, III, and aVF) indicates typical counterclockwise atrial flutter; the ventricular (QRS complexes) rate is variableFrom the collection of Dr Arti N. Shah [Citation ends].
Multifocal atrial tachycardia
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Often seen in severely ill patients with pulmonary disease.
INVESTIGATIONS
ECG tracing: more than three different but distinct P-wave morphologies associated with varying PR intervals and RR intervals.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Multifocal atrial tachycardia: there are P waves of multiple (at least 3) different morphologiesFrom the collection of Dr Arti N. Shah [Citation ends].
Atrial tachycardia with variable AV conduction
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
There may be no difference in signs and symptoms.
INVESTIGATIONS
ECG tracing: discrete regular P waves often different from the sinus P waves.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atrial tachycardia: bursts of atrial tachycardia (10 beats in the middle section of the rhythm strip II at bottom) follows sinus complexesFrom the collection of Dr Arti N. Shah [Citation ends].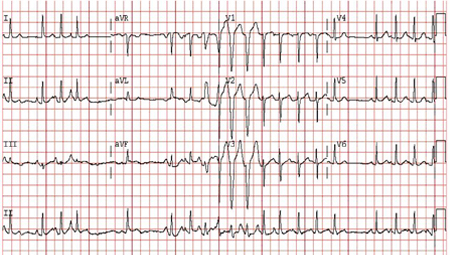
Sinus rhythm with premature atrial contractions or with premature ventricular contractions
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
There may be no difference in signs and symptoms.
INVESTIGATIONS
ECG tracing: sinus with premature atrial or ventricular complexes.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sinus rhythm with premature atrial complexesFrom the collection of Dr Arti N. Shah [Citation ends].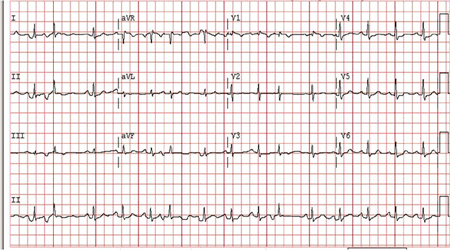 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sinus rhythm with premature ventricular complexesFrom the collection of Dr Arti N. Shah [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sinus rhythm with premature ventricular complexesFrom the collection of Dr Arti N. Shah [Citation ends].
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of orthostatic intolerance (palpitations, lightheadedness, blurred vision, presyncope and syncope, tremor, generalised weakness, fatigue) and an increase in heart rate on standing.
Non-orthostatic symptoms may include dyspnoea, gastrointestinal symptoms (bloating, nausea, diarrhoea, constipation, and abdominal pain), headache, sleep disturbance, cognitive impairment, chest pain, and bladder disturbance.
The patient may also have signs and symptoms of associated comorbidities, such as those of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and autoimmune diseases, particularly Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and coeliac disease.
INVESTIGATIONS
10-minute standing test: patient’s heart rate will typically increase by ≥30 bpm (≥40 bpm in patients aged 12-19 years) after changing position from supine to standing, and no orthostatic hypotension (sustained drop in systolic blood pressure by ≥20 mmHg).
24-hour Holter monitor: can help confirm the diagnosis by demonstrating the association between tachycardia and orthostatic changes.
Tilt-table test: may be used if the diagnosis is unclear following initial assessment or if the patient is not able to perform a 10-minute standing test. A positive test demonstrates orthostatic tachycardia with changing position.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer