Tests
1st tests to order
CBC
Test
First test to perform. Important to request MCHC and reticulocyte count with suspected hemolytic anemia.
Result
low Hb
MCHC
Test
May indicate the presence of spherocytes and reticulocytes.
Result
increased
reticulocyte count
Test
Indicates appropriate marrow response to anemia. Rise should be 4% to 5%, but may be much higher.[42]
Result
increased reticulocyte percentage (>1.5%), absolute reticulocyte count, and reticulocyte index
peripheral smear
Test
If abnormal forms are found on the peripheral smear, they can aid in diagnosis of specific causes of hemolytic anemia. For example, schistocytes indicate microangiopathic process (disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic uremic syndrome, HELLP syndrome [hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count]) or traumatic process (prosthetic heart valve, footstrike [march] hemolysis). Spherocytes and elliptocytes may indicate hereditary spherocytosis and elliptocytosis. In the setting of liver disease, spur cells are indicative of spur cell anemia. Blister or bite cells can indicate the presence of oxidative damage to the cell. Presence of spherocytes, elliptocytes, schistocytes, or bite or spur cells will often lead to the diagnosis of an underlying hematologic disorder.[43][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Peripheral blood smear with spherocytes, reticulocytes, and a nucleated red blood cellFrom the collection of John Densmore, Department of Medicine, University of Virginia [Citation ends].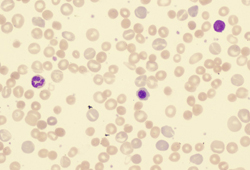 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Peripheral blood smear with red blood cell fragments, or schistocytes (arrow)From the collection of John Densmore, Department of Medicine, University of Virginia [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Peripheral blood smear with red blood cell fragments, or schistocytes (arrow)From the collection of John Densmore, Department of Medicine, University of Virginia [Citation ends].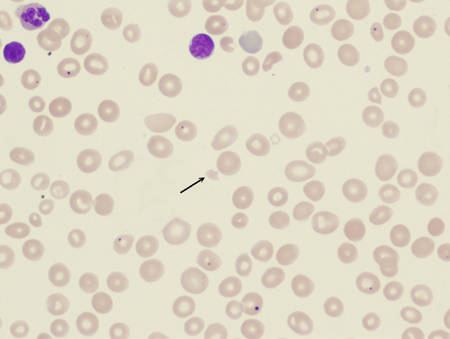
Red blood cell (RBC) inclusions are present in infections such as malaria, babesiosis, and Bartonella infections. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrograph revealing the presence of what were determined to be numbers of intraerythrocytic Babesia sp. ring-form parasitesCDC/ Dr Mae Melvin [Citation ends].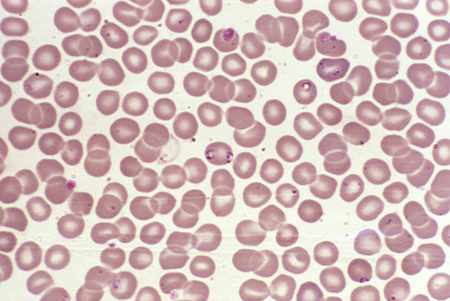 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A photomicrograph of a blood smear showing erythrocytes containing developing Plasmodium vivax parasitesCDC/ Dr Mae Melvin [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A photomicrograph of a blood smear showing erythrocytes containing developing Plasmodium vivax parasitesCDC/ Dr Mae Melvin [Citation ends].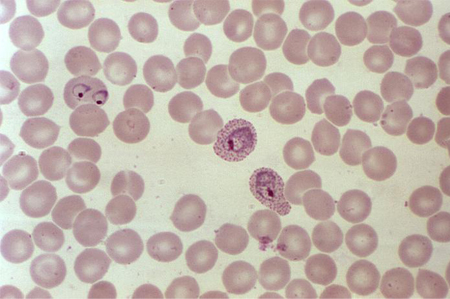
Result
abnormal forms such as schistocytes, spherocytes, elliptocytes, spur cells, blister cells, bite cells, tear drops; RBC inclusions may occur with malaria, babesiosis, and Bartonella infections
unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin
Test
Increased heme catabolism.
Result
elevated, but not >5 mg/dL unless liver function is impaired
LDH
Test
If no other tissue damage is present, serves as a helpful marker. The combination of increased serum LDH and reduced haptoglobin is 90% specific for hemolytic anemia, while the combination of a normal LDH and a haptoglobin of >25 mg/dL (>250 mg/L) is 92% sensitive for ruling out hemolysis.[44][45]
Result
high
haptoglobin
Test
Haptoglobin binds free Hb, with low plasma values suggestive of increased free Hb.
Can be difficult to interpret in the setting of hepatocellular disease and inflammatory states, as these alter the production of haptoglobin. Because haptoglobin is an acute phase reactant, a high level may be the result of a low degree of hemolysis, or of a concomitant inflammatory process.
The combination of increased serum LDH and reduced haptoglobin is 90% specific for hemolytic anemia, while the combination of a normal LDH and a haptoglobin of >25 mg/dL (>250 mg/L) is 92% sensitive for ruling out hemolysis.[44][45]
Result
low
urinalysis
Test
Hemoglobinuria is present in intravascular hemolysis.
Result
dipstick positive for blood, no red blood cells
Tests to consider
direct antiglobulin test (Coombs)
Test
The test is used to detect IgG or complement bound to the red cell surface. The patient's red blood cells are washed and mixed with polyspecific anti-human globulin reagent specific for IgG and the complement protein C3d. The presence of IgG often indicates the presence of a warm antibody, whereas C3d is suggestive of a cold antibody.
Result
positive suggests immune etiology; negative suggests nonimmune etiology
creatinine, BUN
Test
May be elevated due to direct toxic effects of drugs or infection.
Result
elevated in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura or hemolytic uremic syndrome
LFTs
Test
Alcoholic cirrhosis in particular is associated with red blood cell membrane changes and hemolysis.
Result
elevated in liver disease
Donath-Landsteiner antibody
Test
Consider if symptoms are related to exposure to cold and if the test is available.
Result
present in paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
Hb electrophoresis
Test
Indicated in people with African, Mediterranean, or Asian ancestry and/or family members with hemoglobinopathy, who have not previously been tested. Do not repeat hemoglobin electrophoresis in patients who have a prior result, unless the results of interventional therapies are being monitored or to make a more specific diagnosis.[40]
Result
HbS present in sickle cell disease; elevated levels of HbA2 and HbF in beta thalassemia
flow cytometry for CD55/CD59
Test
Testing for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clone.
Result
abnormal
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) fluorescent spot test and spectrophotometry
Test
Can be followed by specific genetic testing.
Result
low G6PD activity
antinuclear antibody
Test
Screen for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), associated with autoimmune hemolytic anemia in up to 10% of cases.
Result
positive if SLE
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer