Tests
1st tests to order
chest x-ray
Test
First-line test ordered in all patients.
Calcified granulomas may represent healed foci of previous infection with the fungus (focal infiltrates).
Unilateral or bilateral interstitial or reticulonodular infiltrates, nodules, mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy, or cavitary lesions are common findings for histoplasmosis pneumonia.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of a patient with histoplasmosis, demonstrating bilateral diffuse reticulonodular infiltratesFrom the personal collection of Dr David L. Goldman [Citation ends].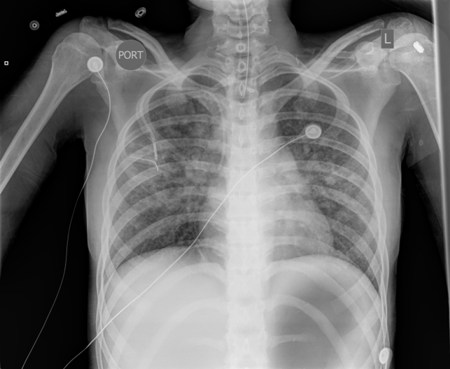
In both immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients, the presence of diffuse interstitial infiltrates on chest x-ray warrants evaluation for disseminated fungal histoplasmosis.
HIV-infected and immunocompromised patients with pulmonary histoplasmosis may present with diffuse bilateral reticulonodular infiltrates indistinguishable from Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
Result
may be normal or show focal infiltrates, hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, calcified granulomas, pulmonary nodules, diffuse interstitial or reticulonodular infiltrates, or cavitary lesions
culture
Test
Culture of pulmonary secretions may be used in all patients. It is the gold standard test to confirm the diagnosis, but can be technically challenging and time consuming.[28] Patients with acute diffuse pneumonia and disseminated histoplasmosis have a high fungal burden; sputum fungal cultures are usually positive in 60% to 85% of cases.[29][30] Patients with acute localized pulmonary disease have a low fungal burden; in these patients, sputum culture has a sensitivity of only 15%.
The fungus grows slowly and may take up to 4 to 6 weeks to grow in culture.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Slant cultures growing Histoplasma capsulatum colonies on 2 different kinds of agarDr Lenore Haley, Public Health Image Library, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Citation ends].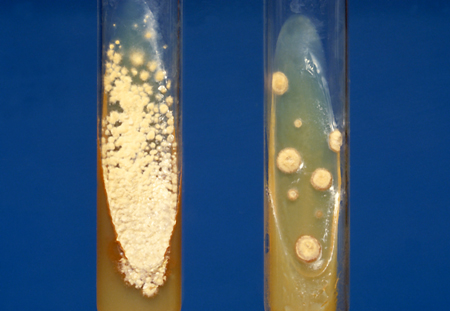
In patients with disseminated disease (e.g., patients with AIDS), culture of the blood using lysis centrifugation bottles increases diagnostic sensitivity when compared with standard culture techniques. Bone marrow culture may also be useful in patients with disseminated disease.[25]
Result
positive for Histoplasma capsulatum
antigen testing
Test
This test provides a rapid diagnosis and is based on the detection of H capsulatum galactomannan. It is useful for patients who are severely ill.[4][28][32]
It is also recommended in patients with HIV who have suspected disseminated histoplasmosis.[32][33]
Patients with acute diffuse pneumonia and disseminated histoplasmosis have a high fungal burden, and the urine antigen test is positive in 75% of patients.[29][30]
Patients with acute localized pulmonary disease have a low fungal burden, and the urine antigen test is positive in only approximately 30% of patients.[36]
Sensitivity of antigen detection in urine is comparable to or better than in serum.[37] It is especially useful in making the diagnosis in immunocompromised patients or those who are severely ill and may not have developed an antibody response.[36] Sensitivity of urine antigen is more than 90% for disseminated disease in immunocompromised patients.[43]
Antigen detection has a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 92% in bronchoalveolar lavage specimens.[38] Testing on CSF can also be performed when indicated.
False-positive results due to cross-reactivity can be seen in patients with blastomycosis, African histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, and Penicillium marneffei infections.
Result
positive for H capsulatum galactomannan antigen
serology (immunodiffusion precipitin test)
Test
Antibody testing is recommended for immunocompetent patients with suspected pulmonary histoplasmosis.[28][32]
The result is positive in 90% of symptomatic patients with acute pulmonary histoplasmosis and nearly 100% with chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis. This test is relatively sensitive but has some limitations because of cross-reactivity.
Measurable antibodies appear 4 to 8 weeks after acute infection and last for 12 to 18 months. This may explain why serology may be negative initially but then positive 1 month later.
Background seropositivity in endemic areas is low; therefore, the immunodiffusion test has a high sensitivity and specificity even in endemic regions.[40]
The result is reported as the presence of M or H bands.[29] H and M antigens are glycoproteins released by the fungus. The M band is found in approximately 76% of patients with acute pulmonary histoplasmosis. The H band is seen in only 20% of infected patients but is associated with severe acute pulmonary histoplasmosis, disseminated infection, and cavitary disease.[29] The M band tends to persist longer than the H band. Its presence can be indicative of acute, chronic or resolved infection.
In patients with AIDS, the sensitivity of serologic tests, including the immunodiffusion test, is reduced to 70%.[2] Likewise, the sensitivity of antibody detection tests is likely to be decreased in other conditions associated with immunosuppression (e.g., organ transplantation or chronic corticosteroid administration).
False positive results can occur in the context of other fungal infections including blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, and aspergillosis.
Result
positive for H capsulatum antibody
serology (complement fixation assay)
Test
Antibody testing is recommended for immunocompetent patients with suspected pulmonary histoplasmosis.[28][32]
Another antibody test, this is quicker and more sensitive than the immunodiffusion test (95% versus 90%) but has a lower specificity due to cross-reactive antibodies induced by other mycotic infections (e.g., coccidioidomycosis, blastomycosis).[40]
Titers between 1:8 and 1:16 are considered low positive and must be interpreted in a clinical context. Titers ≥1:32 or a fourfold rise in titer are highly suggestive of acute infection.[41]
False positive results can occur in the context of other fungal infections including blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, and aspergillosis.
Result
elevated antibody titers
serology (enzyme immunoassay)
Test
Antibody testing is recommended for immunocompetent patients with suspected pulmonary histoplasmosis.[28][32]
Another antibody test, this assay has been reported to be more sensitive than both complement fixation assays and immunodiffusion assays for acute pulmonary histoplasmosis. Sensitivity and specificity reported to be 89% and 92%, respectively. Use of this assay in combination with antigen detection may increase sensitivity.[42] Limitations include cross-reactivity with antibodies to other fungi and decreased sensitivity in immunocompromised patients.
False positive results can occur in the context of other fungal infections including blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, and aspergillosis.
Result
histoplasmosis-specific IgM elevated for the first 3 weeks of illness; IgG remains elevated for 6 weeks
CT scan of chest
Test
In immunosuppressed patients, where the index of suspicion for a fungal process is high and chest x-ray is normal, a CT scan of the chest should be a part of the initial evaluation.
Calcified granulomas may represent healed foci of previous infection with the fungus (focal infiltrates).
Unilateral or bilateral interstitial or reticulonodular infiltrates, nodules, mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy, and cavitary lesions are common findings for histoplasmosis pneumonia.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lung CT scan showing classic "snowstorm" appearance of acute histoplasmosisPublic Health Image Library, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Citation ends].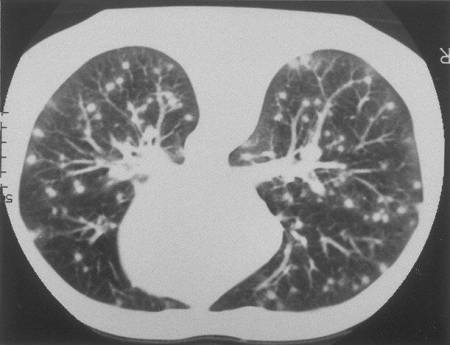
In both immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients, the presence of diffuse interstitial infiltrates on chest x-ray warrants evaluation for disseminated fungal histoplasmosis.
HIV-infected and immunocompromised patients with pulmonary histoplasmosis may present with diffuse bilateral reticulonodular infiltrates indistinguishable from pneumocystis pneumonia.
Result
may be normal or show focal infiltrates, hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, calcified granulomas, pulmonary nodules, diffuse interstitial infiltrates, reticulonodular infiltrates, focal lobar infiltrates, and cavitary lesions
CBC
Test
Immunocompetent patients with histoplasmosis pneumonia may demonstrate only mild anemia.
Patients with progressive disseminated histoplasmosis may have evidence of anemia, neutropenia, pancytopenia, and thrombocytopenia due to disseminated infection involving the reticuloendothelial system.
Result
anemia; pancytopenia; neutropenia; thrombocytopenia
LFTs
Test
Elevated LFTs in the setting of histoplasmosis infection suggest the presence of disseminated disease.
Baseline LFTs are helpful if treatment with azole antifungals will be initiated, due to the drugs' risk of hepatotoxicity.
Result
normal or elevated enzymes
Tests to consider
tissue biopsy
Test
Tissue should be obtained whenever possible to allow for histopathologic diagnosis via fungal stains and fungal culture.[4]
Periodic acid-Schiff or Grocott methenamine silver staining may be used.[4]
Allows rapid diagnosis but sensitivity of histopathology will vary according to the burden of disease and degree of immunosuppression.[4]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Methenamine silver stain revealing Histoplasma capsulatum fungi in lung tissue Dr Edwin P. Ewing, Jr., Public Health Image Library, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Citation ends].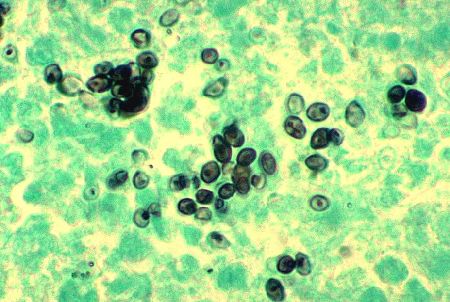 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histopathologic changes associated with histoplasmosis of the lungDr Martin Hicklin, Public Health Image Library, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histopathologic changes associated with histoplasmosis of the lungDr Martin Hicklin, Public Health Image Library, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Citation ends].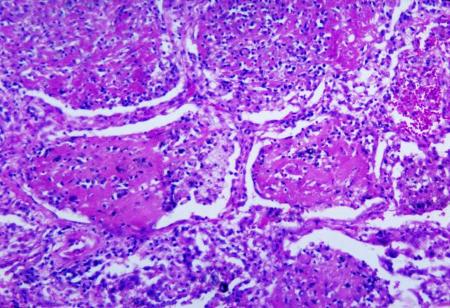
Result
H capsulatum appear as relatively small (2-4 microns), ovoid, intracellular yeast. Granulomatous inflammation may be caseating or noncaseating.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer