Tests
1st tests to order
serum TSH
Test
Suppressed by high levels of thyroid hormones.
Rarely, a high TSH level indicates pituitary origin of hyperthyroidism.
Result
decreased in primary hyperthyroidism
serum creatinine
Test
Multifactorial mechanisms in diminished renal function can lead to gynecomastia.
Result
elevated in renal impairment
serum LFTs
Test
Because of decreased testosterone catabolism in the face of hepatic insufficiency, more testosterone is available for conversion to estrogen, resulting in gynecomastia.
Result
elevated in liver disease
Tests to consider
serum total testosterone
Test
Decreased testosterone and elevated LH indicates primary testicular failure, either congenital (e.g., Klinefelter syndrome) or acquired (e.g., orchitis).
Decreased testosterone and normal or decreased LH indicates pituitary or hypothalamic disease.
Elevated testosterone and high estradiol indicate exogenous androgen or androgen resistance (testicular feminization syndrome).
Assays and normal ranges vary. Testosterone is ideally measured by a specific assay such as liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.[64]
Measure in the morning when testosterone levels are highest.[27][64]
A free testosterone level, measured by equilibrium dialysis, may be helpful in assessing the bioavailability of male hormone if total testosterone is equivocal.
Result
low level suggests hypogonadism
serum LH
Test
Decreased testosterone and elevated LH indicates primary testicular failure.
Decreased testosterone and normal or decreased LH indicates pituitary or hypothalamic disease.
Result
elevated in primary hypogonadism and decreased or inappropriately normal in secondary hypogonadism
serum estradiol
Test
May be elevated along with serum sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) if estrogen exposure, or an estrogenizing testicular or adrenal tumor.
May be elevated along with testosterone in exogenous androgen exposure, androgen resistance, testicular tumor, or beta human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)-producing tumor.
Result
may be elevated from obesity (especially severe obesity), exogenous estrogen exposure, or feminizing tumor
serum sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG)
Test
Elevated if estrogen exposure, hyperthyroidism, liver disease, or genetically high SHBG.
Result
may be elevated
serum free testosterone
Test
Test by equilibrium dialysis confirms low levels when total testosterone is equivocal.
Result
low level suggests hypogonadism
serum beta hCG
Test
Elevated if testicular tumor or ectopic tumor hCG production.[3]
Levels of hCG should be measured in the blood.
Result
may be elevated with trophoblastic tumor
serum dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEAS)
Test
Precursor molecule to sex hormones.
Highly specific to adrenal tissues.
Useful to detect excess adrenal activity as seen in adrenal cancer or hyperplasia.
Result
may be elevated in adrenal tumor
serum prolactin
Test
Excess prolactin suppresses GnRH with resultant hypogonadism.
Also may be elevated in hypothyroidism and in response to some antipsychotic drugs.
Result
may be elevated with pituitary tumor, disorders affecting the pituitary stalk, hypothyroidism, renal failure, or antipsychotic drugs
mammogram
Test
Breast imaging is indicated when the clinical exam is equivocal.[3][65] Suspicious features on ultrasound may prompt mammography.[65][66]
Mammography can also differentiate between breast glandular tissue (true gynecomastia) and adipose tissue (pseudogynecomastia). Mammography has 92% to 100% sensitivity and 90% to 96% specificity for the detection of breast carcinoma.[67][68]
Result
tissue enlargement in gynecomastia may be nodular, dendritic, or diffuse glandular
core biopsy of breast (if cancer suspected)
Test
Biopsy is prompted by any irregular, rubbery, hard, fixed, or eccentric (not subareolar) mass; overlying nipple, areola, or skin abnormality; or axillary adenopathy. These findings are suggestive of breast cancer.[3][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology: breast cancer; nests of malignant ductal carcinoma invading tissue; 10X magnificationFrom Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center pathology collection [Citation ends].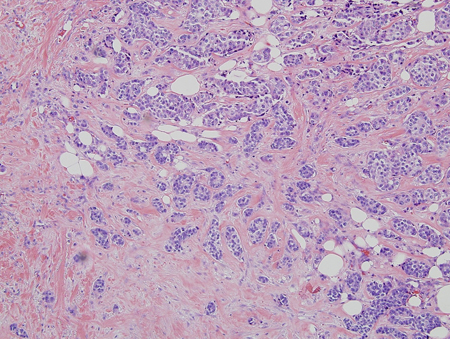
Histologic findings of clusters of ducts (with epithelial hyperplasia if acute, and dilation alone when chronic), edema, or inflammatory cells on a fibrous background indicate gynecomastia.
Result
may confirm malignancy
testicular ultrasound
abdominal CT/MRI (if adrenal adenoma or carcinoma suspected)
Test
Should be performed if an adrenal adenoma or carcinoma is suspected based upon elevations of DHEAS and estradiol, or clinical findings suggesting concomitant glucocorticoid and/or mineralocorticoid excess.[4]
Result
may show adrenal mass
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer