Differentials
Breast cancer
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Gynecomastia is not a premalignant condition.
Risk of both gynecomastia and breast cancer is increased in high estrogen states.
Men with family history of the BRCA2 gene mutation, prostate cancer, or Klinefelter syndrome are at higher risk.
Malignancy should be considered if the breast mass is unilateral, although gynecomastia can be unilateral and breast cancer bilateral.
Breast cancer is usually painless, but not always. The mass may be eccentric (10% to 30%) rather than subareolar. The mass often is irregular, rather than smooth; rubbery or hard rather than firm; and fixed rather than mobile.
Any overlying nipple deformity or ulceration or discharge; red, thickened, or ulcerated overlying skin; or axillary adenopathy raises suspicion for malignancy.
INVESTIGATIONS
Any eccentric, irregular, hard, or fixed mass, or associated nipple or skin abnormality, or axillary adenopathy, mandates a biopsy.
A core biopsy is preferred.[69][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology: breast cancer; nests of malignant ductal carcinoma invading tissue; 10X magnificationFrom Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center pathology collection [Citation ends].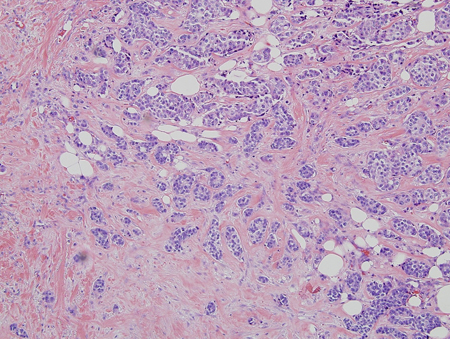
Mammography has 92% to 100% sensitivity and 90% to 96% specificity for the detection of breast carcinoma.[67][68]
Benign breast masses
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Bilateral or painful masses more likely benign.
INVESTIGATIONS
Breast biopsy demonstrates histologic findings of the underlying disorder.
Rare nonmalignant conditions include lipoma, lupus mastitis, granulomatous mastitis, hemangioma, or hamartoma.
Pseudogynecomastia
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Pincer-like compression of the breast against the chest wall reveals no mound of firm breast tissue extending beyond the nipple.
INVESTIGATIONS
Not usually necessary.
Mammogram or ultrasound can differentiate gynecomastia from adipose tissue and is helpful if cosmetic surgery is planned.[70]
Metastatic tumor
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
History of smoking, unexplained weight loss, liver disease, or cancer may be clues to metastatic activity.
Malignancy should be considered if the breast mass is unilateral, although gynecomastia can be unilateral and breast cancer bilateral.
Any overlying nipple deformity or ulceration or discharge; red, thickened, or ulcerated overlying skin; or axillary adenopathy raises suspicion for malignancy.
INVESTIGATIONS
Breast biopsy demonstrates histologic findings of the primary disorder.
Rare malignancies include metastases from lung, prostate, or liver cancer; Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma; or plasmacytoma.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer