Tests
1st tests to order
ECG
Test
ECG analysis in acute heart failure shows atrial fibrillation in approximately 35% of cases.[15]
ECG abnormality is found in almost all cases of heart failure. If the ECG is completely normal then alternate diagnosis should be considered.[39][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: ECG showing left ventricular hypertrophy with sinus tachycardiaFrom the private collections of Syed W. Yusuf, MBBS, MRCPI, and Daniel Lenihan, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].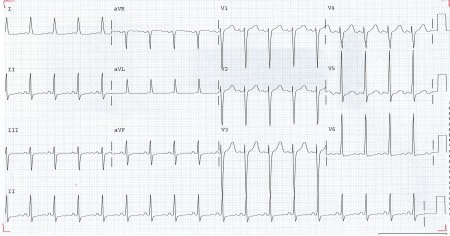
Result
arrhythmia, ischemic ST and T wave changes
chest x-ray
Test
Pulmonary congestion on chest x-ray is present in up to 76% of patients with acute decompensated heart failure.[11][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of acute pulmonary edema showing increased alveolar markings, fluid in the horizontal fissure, and blunting of the costophrenic anglesFrom the private collections of Syed W. Yusuf, MBBS, MRCPI, and Daniel Lenihan, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].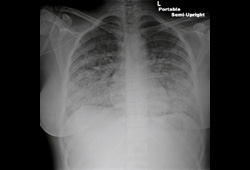 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of acute pulmonary edema showing increased alveolar markings and bilateral pleural effusionsFrom the private collections of Syed W. Yusuf, MBBS, MRCPI, and Daniel Lenihan, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of acute pulmonary edema showing increased alveolar markings and bilateral pleural effusionsFrom the private collections of Syed W. Yusuf, MBBS, MRCPI, and Daniel Lenihan, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].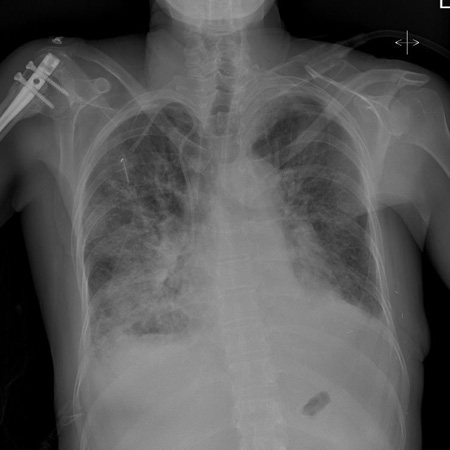
Result
cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion, pleural effusion, valvular or pericardial calcification
Hb
Test
Suggests anemia as a precipitating cause. Check iron status before discharge.
Result
low
thyroid function test
Test
Hypo- or hyperthyroidism can cause acute heart failure.
Result
abnormal
B-type natriuretic peptide
Test
If >500 picograms/mL, dyspnea likely to be due to heart failure.
If <100 picograms/mL, unlikely to be caused by heart failure.
If 100 to 500 picograms/mL, further investigations are required.[42]
In patients presenting with suspected acute heart failure, a finding of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) <100 picograms/mL, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) <300 picograms/mL, and mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide (MR-proANP) <120 picograms/mL makes the diagnosis of acute heart failure unlikely.[1]
Result
>500 picograms/mL
troponin
Test
Elevated in acute cardiac ischemia.
Also elevated in over 50% of cases of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema without evidence of infarction.[47]
Result
elevated
echocardiography
Test
In clinical practice, many centers consider a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of >50% as normal.
Guidelines from the American Society of Echocardiography state an LVEF of 52% to 72% in men and 54% to 74% in women is considered as normal. An LVEF of 41% to 51% in men and 41% to 53% in women is mildly abnormal. In both men and women, an LVEF of 30% to 40% is moderately abnormal and an LVEF of <30% is severely abnormal.[61]
In approximately one third of patients with acute heart failure, LVEF is preserved at ≥45%.[14]
Result
abnormal systolic and diastolic function; valvular and pericardial disease, may reveal underlying cause
electrolyte panel with BUN, serum creatinine, glucose
Test
Initial baseline blood tests should include serum electrolytes, BUN, serum creatinine, and glucose.
Result
baseline levels
lipid profile
Test
For assessment of baseline cardiovascular risk.
Result
baseline levels
Tests to consider
lung ultrasound
cardiac catheterization
Test
Left heart cardiac catheterization (coronary angiogram) is needed in cases where significant coronary artery disease is thought to be a contributing factor.[2]
Right heart catheterization and pulmonary artery catheter monitoring is not routinely recommended, but may be helpful if: systolic blood pressure remains low or symptoms persist despite treatment; fluid status, perfusion, or systemic or pulmonary vascular resistance is uncertain; renal function worsens with therapy; parenteral vasoactive agents are required.[2]
Result
coronary artery stenosis, abnormal coronary artery flow and left ventricular function, abnormal right ventricular function, elevated left ventricular end diastolic pressure, pulmonary hypertension
endomyocardial biopsy
Test
Indicated in patients with rapidly progressive clinical heart failure or worsening ventricular dysfunction that persists despite appropriate medical treatment, where clinical findings suggest acute myocarditis, or where a myocardial infiltrative process (e.g., light chain amyloidosis) or cardiac rejection after heart transplantation is suspected.[2]
Result
inflammatory infiltrate
cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR)
Test
Can be useful for establishing the etiology of heart failure. Allows differentiation between ischemic and nonischemic origins of heart failure, and myocardial fibrosis/scars can be visualized. In addition, CMR allows the characterization of myocardial tissue and is useful for the diagnosis of myocarditis and helping to exclude other etiologies of heart failure (e.g., amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, Chagas disease, Fabry disease, noncompaction cardiomyopathy, and hemochromatosis).
Result
ischemic cardiomyopathy tends to cause late gadolinium enhancement in the subendocardium or transmurally and follows a vascular distribution; in nonischemic cardiomyopathy, the late gadolinium enhancement is often located in the midwall or epicardial regions and does not correspond to any particular coronary artery distribution; in myocarditis, the CMR findings include myocardial edema, wall motion abnormalities, and patchy myocardial late gadolinium enhancement involving the subepicardial regions; in cardiac amyloidosis, the myocardial hyper-enhancement on late gadolinium enhancement typically appears as global subendocardial; CMR can detect myocardial iron deposits through T2-star (T2*) technique, in which the affected myocardium will appear dark (reduced T2*)
nuclear medicine imaging
Test
Single-photon emission CT (SPECT) or positron emission tomography (PET) may be useful in assessing ischemia and myocardial viability. 3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid (DPD) scintigraphy may be useful for the detection of transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis.[1][2]
Result
ischemia, mixed ischemia/scar or scar tissue; in patients with transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis, a DPD scintigraphy may show myocardial tracer uptake
cardiac CT (coronary CT angiogram)
Test
Noninvasive means to visualize the coronary anatomy in patients with heart failure.
Result
coronary stenosis
additional biomarkers
Test
Measuring the concentration of certain biomarkers can provide important information about disease severity and helps not only in the detection and diagnosis of heart failure but also in management and prognosis. In addition to natriuretic peptides and troponin, useful biomarkers include soluble suppressor of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin-6, cystatin-C, galectin-3, and procalcitonin.[50]
Result
presence and concentration of biomarkers varies; refer to local guidelines
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer