Tests
1st tests to order
optical coherence tomography
Test
Should be ordered for all patients at baseline; for patients with exudation, hemorrhages, or microaneurysms in the macular area; and for patients with unexplained visual loss.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomography in macular edema: loss of central foveal depression (yellow arrow), accumulation of fluid within cystoid spaces at fovea (red arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].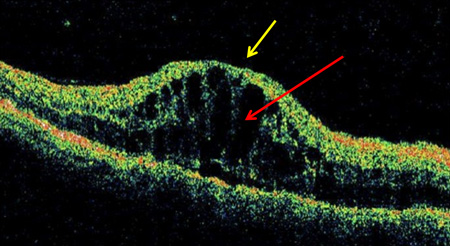 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomogram of normal eye: normal foveal depression at center of macula (yellow arrow), inner retina (toward center of eye; red arrow), outer retina (farther from center of eye; blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomogram of normal eye: normal foveal depression at center of macula (yellow arrow), inner retina (toward center of eye; red arrow), outer retina (farther from center of eye; blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomography in vitreomacular traction: loss of foveal depression with traction on fovea (in direction of yellow arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomography in vitreomacular traction: loss of foveal depression with traction on fovea (in direction of yellow arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
may be used to diagnose: macular edema (intraretinal cystic spaces, increase in centerpoint thickness, increase in central subfield thickness; also, determining whether center-involving or non-center-involving), macular ischemia (disorganization of the retinal inner layers, foveal ganglion cell loss, outer retinal atrophy), vitreomacular traction (posterior hyaloid thickening, tractional retinoschisis), vitreous attachment to neovascularization of retina or optic disk; may also be used to monitor response to treatment of macular edema
fundus photography/wide-field fundus photography
Test
Should be ordered for all patients at baseline, and when there is a change in fundus appearance. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Normal retina left eye: optic disk (white square), macula (white circle), arteriole (red arrow), venule (blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
may be used to assess: retinopathy severity; retinopathy progression
Tests to consider
fluorescein angiography/wide-field fluorescein angiography
Test
Indicated in some patients with diabetic maculopathy, and some patients with severe nonproliferative/proliferative retinopathy.[16]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram in mid-venous phase in diabetic retinopathy with microaneurysms only: microaneurysm (red arrow), optic disk (yellow arrow), macula (white circle)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].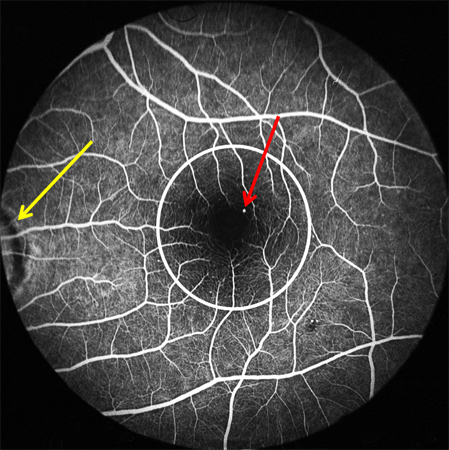 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: microaneurysms (red arrow), intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram of nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: microaneurysms (red arrow), intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].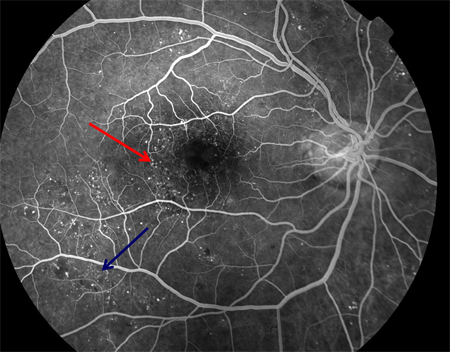 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram in proliferative diabetic retinopathy with macular ischemia: macular ischemia (green circle), capillary nonperfusion (white arrow), optic disk new vessels (red arrow), venous beading (blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram in proliferative diabetic retinopathy with macular ischemia: macular ischemia (green circle), capillary nonperfusion (white arrow), optic disk new vessels (red arrow), venous beading (blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiography in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Vascular component of fibrovascular proliferation (red arrows), capillary nonperfusion (yellow arrow), laser burns (green circle)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiography in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Vascular component of fibrovascular proliferation (red arrows), capillary nonperfusion (yellow arrow), laser burns (green circle)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: new vessels on the optic disk (red arrow), capillary nonperfusion (red rectangle), microaneurysms (green circle), venous beading (blue arrow), intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (yellow arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: new vessels on the optic disk (red arrow), capillary nonperfusion (red rectangle), microaneurysms (green circle), venous beading (blue arrow), intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (yellow arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].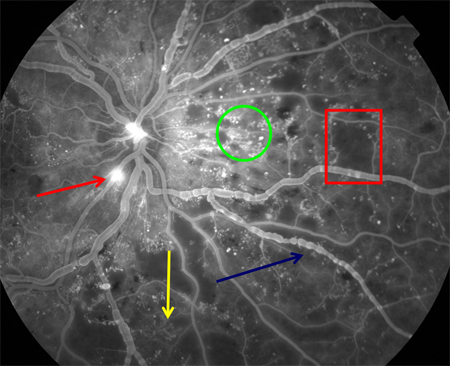 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: new vessels elsewhere (red circle), capillary nonperfusion (white arrow), panretinal laser burns (blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Fluorescein angiogram in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: new vessels elsewhere (red circle), capillary nonperfusion (white arrow), panretinal laser burns (blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].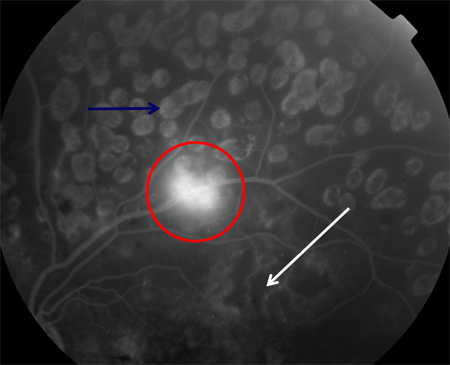
Result
defines macular leakage (versus optical coherence tomography definition of thickness); quantifies macular ischemia; determines extent of capillary nonperfusion; identifies new vessels; determines adequacy of panretinal photocoagulation
optical coherence tomography angiography
Test
Indicated in patients with suspected macular ischemia.[71]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomography in macular edema: loss of central foveal depression (yellow arrow), accumulation of fluid within cystoid spaces at fovea (red arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomogram of normal eye: normal foveal depression at center of macula (yellow arrow), inner retina (toward center of eye; red arrow), outer retina (farther from center of eye; blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomogram of normal eye: normal foveal depression at center of macula (yellow arrow), inner retina (toward center of eye; red arrow), outer retina (farther from center of eye; blue arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomography in vitreomacular traction: loss of foveal depression with traction on fovea (in direction of yellow arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Optical coherence tomography in vitreomacular traction: loss of foveal depression with traction on fovea (in direction of yellow arrow)Courtesy of Moorfields Photographic Archive; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
identifies vascular abnormalities in deep and superficial capillary complexes
B-scan ultrasonography
Test
Should be ordered in patients in whom media opacity (e.g., vitreous hemorrhage) prevents visualization of the fundus.
Result
identifies macular traction retinal detachment, and other major structural derangements of the retina
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer