Tests
1st tests to order
chest x-ray
Test
In pneumonitis or pneumonia resulting from aspirated gastric contents, there are patchy, bilateral airspace consolidations with a perihilar and basilar distribution.[48] The most commonly involved areas are the superior and posterobasal segments of the right lower lobe and the posterior segment of the right upper lobe because of their dependent location in the supine position. If the patient is in a different position, other segments can be involved.
X-ray changes are usually apparent within 2 hours of aspiration but if pneumonia develops, opacities can become apparent days later and take weeks to resolve. See Aspiration pneumonia.
Barium aspiration should be confirmed by CXR.[70][71][72][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A. Portable upright chest x-ray before aspiration; B. Chest x-ray 1 hour after aspiration, showing bilateral diffuse alveolar infiltrates, worse at the bases on the right sideFrom the collection of Dr Henri Colt [Citation ends].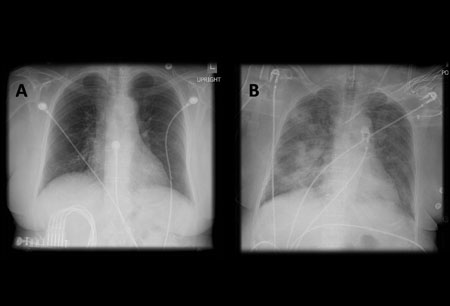 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barium aspiration. A barium swallow was conducted in a 53-year-old woman. Imaging revealed hyperdense airway-centered material in the left lower lobe consistent with barium aspiration bronchiolitis. A tracheoesophageal fistula was confirmedFrom the collection of Dr Augustine Lee; used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, all rights reserved [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Barium aspiration. A barium swallow was conducted in a 53-year-old woman. Imaging revealed hyperdense airway-centered material in the left lower lobe consistent with barium aspiration bronchiolitis. A tracheoesophageal fistula was confirmedFrom the collection of Dr Augustine Lee; used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, all rights reserved [Citation ends].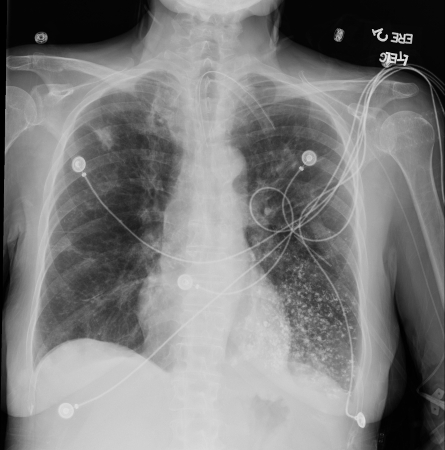
An estimated 25% of cases may not be apparent on CXRs relative to CT imaging.[68]
Result
patchy, bilateral airspace consolidations; barium may be identified by hyperdense opacities in the mid and lower lungs, sometimes outlining the tracheobronchial tree, and more distally, with a bronchiolocentric or centrilobular pattern
Tests to consider
chest CT
Test
In cases of aspirated gastric contents, opacities may be seen in dependent segments of the lung. Chest CT scanning precisely delineates the location of the lobar and segmental opacities. In advanced cases, the findings may be indistinguishable from those of acute respiratory distress syndrome. See Acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Aspiration of fat (exogenous lipoid pneumonia) or contrast material can sometimes be determined by measuring the tissue attenuation on CT scans. Lung abscess and empyema are potential complications of aspiration that are visualized better with CT than with plain chest x-ray.[73] See Lung abscess and Empyema.
Although CXR is sufficient in most cases of aspiration, a CT chest should be ordered if foreign body aspiration is suspected (to plan extraction) or if the patient fails to improve with initial therapy (to rule out empyema or lung abscess).
Chest CT is superior compared with CXR in the detection of aspiration pneumonia, and if initial CXR is inconclusive, CT should be ordered.[68]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lipoid pneumonia. A 77-year-old woman with dysphagia and achalasia following a stroke presented with recurrent lung infiltrates, including a persisting right middle lobe lesion. Hounsfield units (HU) measurement was -157, consistent with lipoid pneumonia. Comparative subcutaneous fat and aorta (blood/tissue) HU are shownFrom the collection of Dr Augustine Lee, used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, all rights reserved [Citation ends].
Result
opacities in dependent segments
bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage
Test
Bronchoscopy is indicated if aspirated material is particulate or potentially obstructive, or if there is radiographic evidence of lobar or segmental collapse, in order to clear the airway. In addition, bronchoscopy can be used to collect quantitative cultures on bronchoalveolar lavage or protected specimen brush, which can be used to guide antibiotic therapy, particularly in patients who fail to respond to empiric antibiotic treatment.
Cytologic analysis can pick up unusual tumors that can appear pneumonic on imaging. When the differential is broader, a bronchoscopic biopsy may occasionally be employed for interstitial pneumonias and other considerations, though not often in the acute setting.[75] Finally, a careful bronchoscopic exam may be important to identify a tracheoesophageal fistula that may be complicating cancer, surgery, radiation, or trauma.
In cases of aspiration of barium sulfate, especially if a patient has hypoxia or respiratory distress, early bronchoscopy should be performed to remove the barium from the airway, but there is some risk of disseminating the contrast to unaffected airways. Deaths have been reported in patients who aspirated barium and for whom bronchoscopy was not performed for airway clearance.[24][74][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bronchoscopy showing barium aspiration in a lung transplant patient in the right mainstem bronchus after a barium swallow studyFrom the collection of Dr Kamran Mahmood [Citation ends].
Result
airway erythema; particulate matter, barium may be seen; protected brush specimens can be used to identify, confirm, or refute the presence of an infection; eosinophils or tumor cells may be present
CBC
Test
Performed if pneumonia develops after the aspiration of gastric contents.
Result
leukocytosis
arterial blood gases
Test
Aspiration may cause hypoxia.
Result
reduced oxygen tension
blood culture
Test
In the context of small bowel obstruction, where there is a high risk of bacterial translocation, bacterial contamination of gastric juice, and sepsis, the initiation of antibiotics should be considered up front and should be adjusted when pathogens are identified.[2][79] See Small bowel obstruction and Sepsis in adults.
Result
growth of causative bacterial species
thoracentesis
Test
Thoracentesis for microscopy, culture, and sensitivity should be considered if there is concern for a complicated parapneumonic effusion. See Pleural effusion and Empyema.
Result
growth of causative bacterial species
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer