Tests
1st tests to order
ECG
Test
Right ventricular (RV) dilation produces incomplete right bundle branch block and right axis deviation.
RV hypertrophy produces a tall R wave in V1 or qR in V1, an R wave greater than S wave in V1, R wave progression reversal in the precordial leads, and an inverted T wave in the anterior precordial leads.
Right atrial enlargement produces right axis deviation.
Pulmonary regurgitation after repair of tetralogy of Fallot may produce QRS prolongation.
Left ventricular size may also influence QRS duration.[13]
Result
variable nonspecific abnormalities
transthoracic Doppler echocardiogram (TTE)
Test
Should be ordered in any patient where pulmonary regurgitation is suspected.[7]
TTE is useful for determining severity, mechanism, etiology, right ventricular (RV) size and function, other valvular abnormalities, and RV systolic pressure. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Short axis echocardiographic view in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a restrictive right ventricle, and short axis echocardiographic view reveals that the right ventricle is largeFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].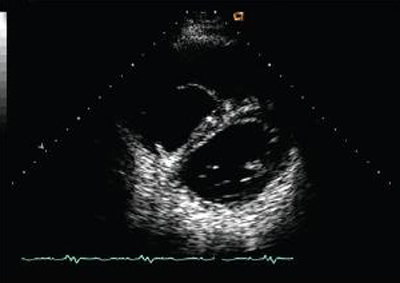 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a nonrestrictive right ventricle, and an ‘‘A’’ wave is not seen in the pulmonary artery Doppler spectrumFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a nonrestrictive right ventricle, and an ‘‘A’’ wave is not seen in the pulmonary artery Doppler spectrumFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].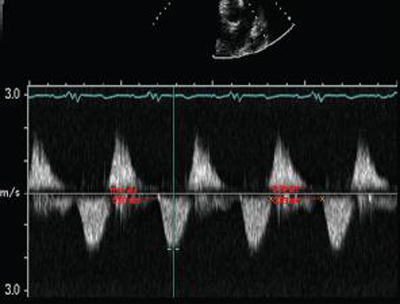 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a restrictive right ventricle, and Doppler shows evidence of restriction with an antegrade "A" wave in the pulmonary arteryFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a restrictive right ventricle, and Doppler shows evidence of restriction with an antegrade "A" wave in the pulmonary arteryFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Short axis echocardiographic view in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a restrictive right ventricle, and short axis echocardiographic view reveals a small right ventricleFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Short axis echocardiographic view in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a restrictive right ventricle, and short axis echocardiographic view reveals a small right ventricleFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].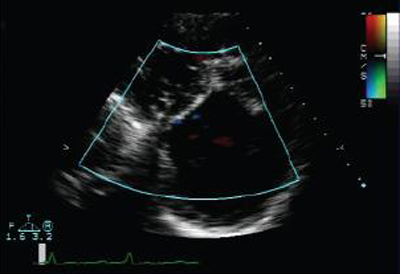 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler echocardiogram in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot, revealing a non-obstructed right ventricular outflow tract. The patient has a restrictive right ventricleFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler echocardiogram in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot, revealing a non-obstructed right ventricular outflow tract. The patient has a restrictive right ventricleFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].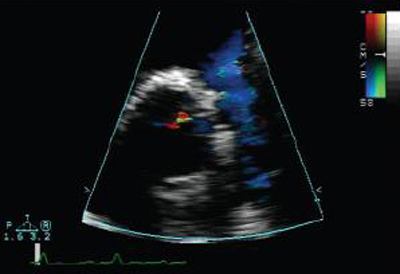 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler echocardiogram in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot, revealing a nonobstructed right ventricular outflow tract. The patient has a nonrestrictive right ventricleFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Doppler echocardiogram in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot, revealing a nonobstructed right ventricular outflow tract. The patient has a nonrestrictive right ventricleFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].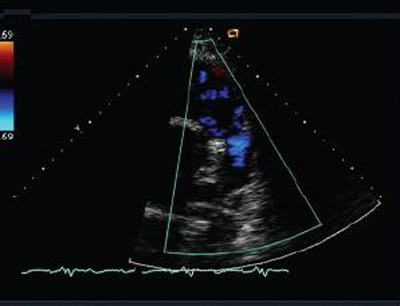 Additionally, it is useful in identifying vegetations on the pulmonary valve. Evidence of tricuspid regurgitation should be taken into consideration.
Additionally, it is useful in identifying vegetations on the pulmonary valve. Evidence of tricuspid regurgitation should be taken into consideration.
Severity of pulmonary regurgitation (PR) is usually assessed by the diameter of the jet at its origin immediately below the valve, in the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT), on the parasternal short axis view. A jet width that occupies >65% of the RVOT is suggestive of severe PR.[8] The continuous-wave Doppler profile of the PR jet in the parasternal short axis view is also fundamental in assessing the presence and severity of PR by TTE.[9]
Result
a regurgitant jet; RV dilation may be present; in mild pulmonary regurgitation, continuous wave Doppler will have slow deceleration, in severe pulmonary regurgitation, steep deceleration returning to baseline by end of diastole
CXR
Test
Appearance of the lung fields depends on the chronicity of the situation. A lot of patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction have normal lung fields because their heart failure is well compensated.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a restrictive right ventricle and the heart is smallFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].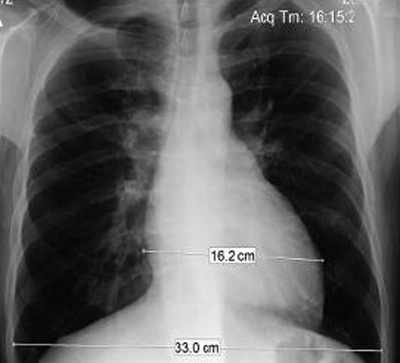
Result
pulmonary artery dilation with clear lung fields; right ventricular dilation
Tests to consider
transesophageal Doppler echocardiogram (TEE)
Test
In general, if TTE indicates severe pulmonary regurgitation, then a TEE would be recommended to better assess the degree and cause of regurgitation. TEE is also indicated in cases where pulmonary regurgitation is suspected but availability of TTE is limited. Rarely, the pulmonary valve leaflets may be difficult to visualize by TEE as the valve lies in the far field from the esophageal position.
TEE is useful for determining severity, mechanism, etiology, right ventricular (RV) size and function, other valvular abnormalities, and RV systolic pressure. Additionally, it is useful in identifying vegetations on the pulmonary valve.[7] Evidence of tricuspid regurgitation should be taken into consideration.
Result
a regurgitant jet; RV dilation may be present
cardiac MRI
Test
Considered the reference standard for quantification of pulmonary regurgitation (PR), right ventricular size and function in people with repaired tetralogy of Fallot. The advantages of cardiac MRI over other imaging modalities in these people include accurate and reproducible measurements of these parameters, excellent image quality in people with a wide range of body sizes, and absence of radiation making it a good choice for longitudinal follow-up.[7][12]
Result
increased PR fraction, increased right ventricular (RV) end-diastolic and RV end-systolic volumes, diminished RV ejection fraction
MRI chest
Test
In patients where the decision to treat pulmonary regurgitation is being considered, an MRI chest may be very helpful. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a restrictive right ventricle, and MRI shows decreased right ventricular volumeFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].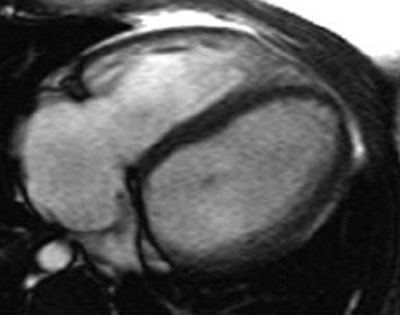 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a nonrestrictive right ventricle, and MRI shows that the right ventricle is dilatedFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a patient with pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The patient has a nonrestrictive right ventricle, and MRI shows that the right ventricle is dilatedFrom: Chaturvedi RR, Redington AN. Heart. 2007 Jul;93(7):880-9; used with permission [Citation ends].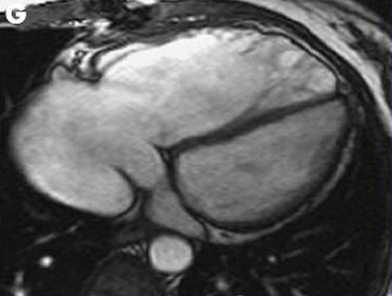
Result
measurement of pulmonary regurgitant fraction, right ventricular (RV) end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes, and RV ejection fraction; anatomy of pulmonary valve and related structures demonstrated
CT scan chest
Test
In patients where the decision to treat pulmonary regurgitation is being considered, a CT scan chest may be very helpful. CT may be an alternative to MRI in patients with contraindications such as pacemakers or other metallic implants.[7]
Result
measurement of pulmonary regurgitant fraction, right ventricular (RV) end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes, and RV ejection fraction; anatomy of pulmonary valve and related structures demonstrated
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer