Differentials
Atrial flutter
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Clinical history and physical exam may not be useful to differentiate from AF.
INVESTIGATIONS
ECG shows absence of P waves, presence of characteristic flutter waves that give typical saw-tooth appearance in the inferior limb leads, and QRS complexes that are regularly (typically 2:1, 3:1, 4:1) irregular. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atrial flutterFrom the collections of Arti N. Shah and Bharat K. Kantharia [Citation ends].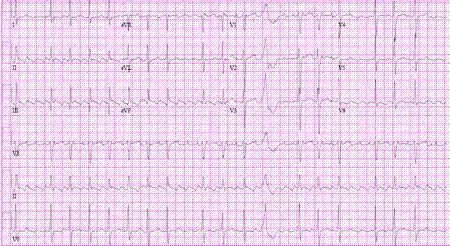
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Usually presents at younger age (teens or early 20s).
Often precipitated by exercise.
INVESTIGATIONS
Classic ECG has shortened PR interval and delta wave on the QRS complex, which may degenerate into AF. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atrial fibrillation with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndromeFrom the collections of Arti N. Shah and Bharat K. Kantharia [Citation ends].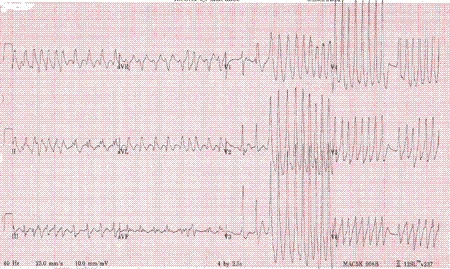
An electrophysiologic study with view to curative ablation procedure is suggested for patients with ECG changes suggestive of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome who present with AF and rapid ventricular rate.
Atrial tachycardia
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Clinical history and physical exam may not be useful to differentiate from AF. However, atrial tachycardia (in particular, multifocal atrial tachycardia) is more common in patients with severe COPD.
INVESTIGATIONS
ECG shows abnormal P waves. In multifocal atrial tachycardia, there are at least 3 different morphologies of P waves. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Multifocal atrial tachycardiaFrom the collections of Arti N. Shah and Bharat K. Kantharia [Citation ends].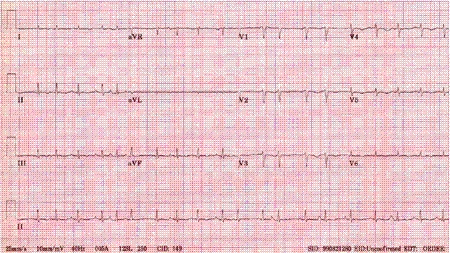
Ventricular/atrial ectopic beats
SIGNS / SYMPTOMS
Clinical history and physical exam may not be useful to differentiate from AF.
INVESTIGATIONS
ECG shows underlying normal sinus rhythm, with additional, randomly occurring, ventricular or atrial ectopic complexes.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer