Tests
1st tests to order
ECG
Test
Should be the first test requested. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atrial fibrillationFrom the collections of Arti N. Shah and Bharat K. Kantharia [Citation ends].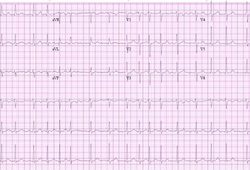
The ECG may also show evidence of possible underlying causes, such as left ventricular hypertrophy or previous myocardial infarction.
P waves that have been replaced by a saw-tooth appearance in the inferior limb leads, and QRS complexes that are regularly (typically 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 P to QRS ratio) irregular are characteristic of atrial flutter. Abnormal and variable morphology P waves can occur in atrial tachycardia.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Atrial flutterFrom the collections of Arti N. Shah and Bharat K. Kantharia [Citation ends].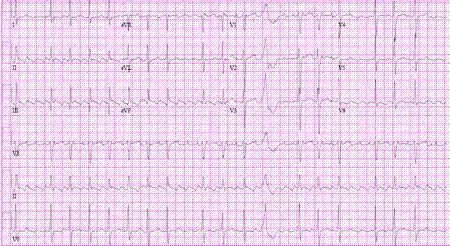 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Multifocal atrial tachycardiaFrom the collections of Arti N. Shah and Bharat K. Kantharia [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Multifocal atrial tachycardiaFrom the collections of Arti N. Shah and Bharat K. Kantharia [Citation ends].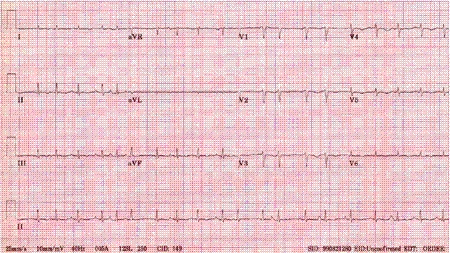 Patients with concomitant severe atrioventricular conduction block (inherent or drug-induced [e.g., digoxin toxicity]) may have bradycardia and regular ventricular escape rhythm resulting in regular QRS complexes. In patients with pacemakers, ECG may exhibit regular ventricular paced complexes. In these patients the atrial rhythm will still show irregular fibrillatory waves from AF.
Patients with concomitant severe atrioventricular conduction block (inherent or drug-induced [e.g., digoxin toxicity]) may have bradycardia and regular ventricular escape rhythm resulting in regular QRS complexes. In patients with pacemakers, ECG may exhibit regular ventricular paced complexes. In these patients the atrial rhythm will still show irregular fibrillatory waves from AF.
Result
absent P waves; presence of fibrillatory waves that vary in size, shape, and timing; irregularly irregular QRS complexes confirm the diagnosis of AF
serum electrolytes
Test
Routine biochemistry should be done to assess for the presence of other comorbid conditions, and to assess electrolyte and metabolic status.
Also helpful in choosing antiarrhythmic agents and their dosages.
Result
may show high or low potassium, or low magnesium
cardiac biomarkers
Test
Myocardial ischemia may be a cause or consequence of AF.
Troponin levels may be elevated in patients presenting with AF. The high-sensitivity (hs) troponin level is independently associated with a raised risk of stroke, cardiac death, and major bleeding and improves risk stratification beyond the CHA₂DS₂-VASc score.[82][83]
Result
elevated troponins and CK-MB with myocardial ischemia
thyroid function tests
Test
Thyrotoxicosis may present with AF: suppressed thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) with elevated free T4 and/or T3.[81]
Result
suppressed TSH in thyrotoxicosis
CXR
Test
CXR in patients who are otherwise healthy and presenting with new-onset AF (e.g., secondary to alcohol ingestion) may be normal.
Pneumonia, pericarditis, or heart failure may precipitate new-onset AF.
Result
may show cardiomegaly, in particular left atrial enlargement; signs of heart failure; other precipitating pathology, such as pneumonia
transthoracic echocardiogram
Test
May show abnormalities, such as left ventricular hypertrophy, left atrial enlargement, segmental or global wall motion abnormalities, valvular stenotic or regurgitation abnormalities, cardiomyopathy with low left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), or pericardial disease.[84]
Echocardiogram in patients who are otherwise healthy and presenting with new-onset AF (e.g., secondary to alcohol ingestion) may be normal.
Result
may show dilated left atrium; valvular disease; low LVEF; diastolic dysfunction
transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
Test
TEE is necessary in patients presenting with new-onset AF, where the exact onset of AF is unclear, and cardioversion is necessary to restore sinus rhythm.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transesophageal echocardiogram showing left atrial appendage clot. LA=left atrium; LAA=left atrial appendage; LV=left ventricleFrom the collection of Dr Bharat Kantharia [Citation ends].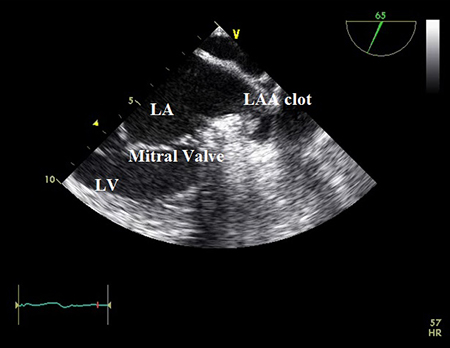
The presence of atrial thrombus increases the risk of embolic stroke.
Result
may show presence of atrial thrombus
Investigations to avoid
coronary CT angiography
Tests to consider
electrophysiologic study
Test
May show accessory bypass tract that causes arrhythmias, such as in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, or other arrhythmias such as atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia and atrial tachycardia.
Result
may show accessory aberrant pathways or other arrhythmias
exercise stress tests
Test
Exercise echocardiography and the exercise nuclear imaging stress test are both useful to determine structural abnormalities of the heart and assess for coronary artery disease (CAD), for assessing adequate rate control, and to determine whether there is a “use dependence” proarrhythmic effect (i.e., when channel-blocking agents have greater effect at faster heart rates, and thus can have proarrhythmia at faster rate) of class Ic antiarrhythmic agents.[85] However, do not use these tests routinely in the initial diagnosis of AF. If there are no symptoms or signs of cardiovascular disease then cardiac imaging beyond a transthoracic echocardiogram is rarely needed.[86]
A treadmill exercise stress test may also be useful for risk stratification for risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. The sudden loss of preexcitation delta waves at faster heart rate during exercise stress test indicates that the antegrade conduction property of the accessory bypass tract is weaker, and the risk of sudden cardiac death from AF is therefore lower.
Result
detection of structural abnormalities or CAD
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer