Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- increased risk of exposure to HPV
- immunocompromise
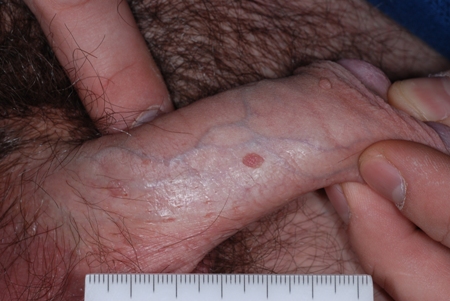
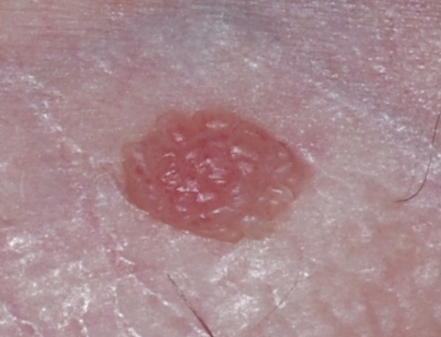
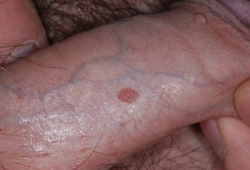
- sessile exophytic papillomas
Risk factors
- intercourse at an early age
- increasing number of lifetime sexual partners
- young sexually active adults
- increasing number of partner's lifetime sexual partners
- immunocompromise
Diagnostic tests
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Natalia Mendoza, MD
Pariser Dermatology Specialist
Williamsburg
VA
Disclosures
NM declares that she has no competing interests.
Stephen K. Tyring, MD, PhD, MBA
Clinical Professor
Departments of Dermatology, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics and Internal Medicine
University of Texas Health Science Center
Houston
TX
Disclosures
SKT declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Natalia Mendoza and Dr Stephen K. Tyring would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Brenda L. Pellicane, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
BLP declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Angela Moore, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor
University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston
Galveston
TX
Disclosures
AM declares that she has no competing interests.
Steve Baguley, FRCP, MSc
Consultant Genitourinary Physician
Woolmanhill Hospital
Aberdeen
Scotland
UK
Disclosures
SB declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer