Tests
1st tests to order
esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Test
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is the initial diagnostic test of choice to visually assess the esophagus. EGD should be ordered in all patients with suspected eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).[1][3][4]
Endoscopic signs are nonspecific (and not formally part of the diagnostic criteria), but can be highly suggestive of EoE.[1][3] Findings can be formally graded with the EoE Endoscopic Reference Score (EREFS), which accounts for the 5 most typical EoE endoscopic features (which also form the acronym): edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and strictures.[82]
Endoscopy can appear normal in a number of patients (most commonly children).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopic findings including white plaques, linear furrows, and edemaFrom the collection of Dr Evan S. Dellon [Citation ends].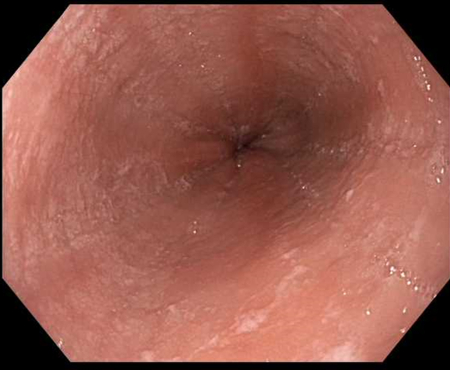 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopic findings including esophageal rings, linear furrows, edema, mild white plaques, and narrowingFrom the collection of Dr Evan S. Dellon [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopic findings including esophageal rings, linear furrows, edema, mild white plaques, and narrowingFrom the collection of Dr Evan S. Dellon [Citation ends].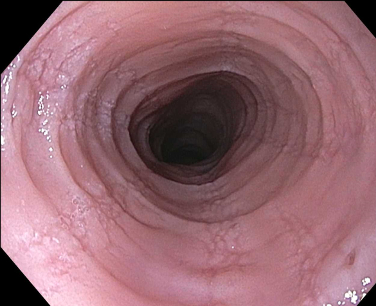
Result
fixed esophageal rings; focal esophageal strictures; diffuse esophageal narrowing; edema or congestion of the mucosa with loss of normal vascular markings; linear furrows; white plaques or exudates (which correlate with the histologic finding of eosinophilic microabscesses); crêpe-paper mucosa (mucosa fragility where the esophageal mucosa tears from insufflation or passage of the scope); may be normal in some cases
esophageal biopsy
Test
Biopsies are obtained during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD). In the US, at least 2-4 biopsies are taken, and in Europe at least 6 biopsies are taken, with 6 considered the gold standard.[1][4][83] Eosinophilic infiltrate in EoE is patchy, and an increasing number of biopsies maximizes diagnostic sensitivity.[1][3][84][85][86][87][88]
If a patient presents with food bolus obstruction, sufficient biopsies should be taken at the time of endoscopy to ensure a diagnosis of EoE is not missed - if the obstruction has spontaneously cleared or insufficient diagnostic biopsies have been obtained at the index endoscopy, elective endoscopy should be arranged before discharge.[4]
Recommendations in the UK also specify that biopsies be taken from targeted (taken from visibly abnormal areas) and non-targeted areas.[4]
On histologic examination, the convention is to quantify the peak eosinophil count in the most inflamed area of the esophageal epithelium.[1][2][3] The standard size of a high-power field is 0.3 mm², and UK guidelines recommend an updated peak eosinophil count of ≥15 per 0.3 mm² is used.[4]
Other supporting histologic features include basal zone hypertrophy, lamina propria fibrosis, surface layering of eosinophils, eosinophil degranulation, and eosinophil microabscesses.[89] These, and several other features, have been developed into an EoE Histologic Scoring System (HSS).[89][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Esophageal biopsy showing a diffuse eosinophilic epithelial infiltrate as well as basal cell hyperplasia and spongiosisFrom the collection of Dr Evan S. Dellon [Citation ends]. UK guidelines recommend that concomitant histologic features be included in the histologic description, with the peak eosinophil count, to aid diagnosis of EoE.[4]
UK guidelines recommend that concomitant histologic features be included in the histologic description, with the peak eosinophil count, to aid diagnosis of EoE.[4]
Result
peak eosinophilic count ≥15 eosinophils per high-power microscopy field (or ≥15 eosinophils per 0.3 mm²); concomitant features, including basal cell hyperplasia, edema (sponginosis), eosinophil microabscesses, layering and degranulation, and subepithelial sclerosis, may be present
CBC with differential
Test
A mild to moderate peripheral eosinophilia may be seen in EoE.
Grossly raised peripheral eosinophil count is rarely seen and suggests the patient should be evaluated for other systemic causes.
Result
may show peripheral eosinophilia
Emerging tests
transnasal endoscopy
esophageal string test
Test
Minimally invasive esophageal sampling technique where a capsule containing a string is swallowed, and the string that is attached to the capsule is held outside of the mouth. The capsule dissolves and the string remains in the esophagus where it absorbs inflammatory factors related to EoE.
After an hour, the string is removed and sent to a specialized laboratory where the inflammatory factors can be measured.
Initial studies showed that these factors correlate extremely well with the same factors measured in esophageal biopsies, and further work indicates the esophageal string test may provide a safe and minimally invasive way of disease monitoring.[92][93]
Result
elevated levels of eosinophil granule protein and other inflammatory factors
cytosponge
Test
Minimally invasive esophageal sampling technique where a capsule containing a sphere-shaped cytology mesh (sponge) is swallowed, and an attached string retained outside of the mouth.
After 5 minutes, the capsule dissolves, which releases the sponge, and the string is used to pull the sponge through the esophagus where it collects a tissue sample before it is removed from the mouth. The sample can then be assessed for levels of esophageal eosinophils in a standard pathology laboratory.
A preliminary study showed excellent correlation between the eosinophil levels in the sponge sample and in matched endoscopic biopsy samples.[94] Additional studies are ongoing and indicate that cytosponge is a safe, well tolerated and accurate way to assess histologic activity.[95]
Result
increased levels of esophageal eosinophils
Esophageal physiological testing
Test
Several studies have shown that mucosal impedance is lower in EoE than in other esophageal conditions such as erosive and nonerosive reflux disease and achalasia, and that this low impedance is seen throughout the entire esophagus.[64][66][96]
A minimally invasive approach to measurement of mucosal impedance is not currently available.
UK guidelines recommend esophageal physiological testing for patients with EoE who remain symptomatic even though they have received appropriate treatment, have no evidence of fibrostenotic disease at endoscopy and are in histologic remission.[4]
Result
lower impedance pattern is suggestive of EoE
EoE diagnostic panel
Test
A 94-gene expression panel that uses a single esophageal biopsy to yield a summary gene expression score. This score has been shown to discriminate EoE cases from non-EoE controls (including patients with GERD) with a high degree of accuracy.[61][97]
This test is currently being commercialized and ongoing studies are evaluating the role of this test in diagnostic algorithms.
Result
gene expression score suggestive of EoE
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer