Complications
May be present at diagnosis. More common in adolescents and adults, and patients with a prolonged duration of symptoms prior to diagnosis, suggesting that the condition can progress with worsening fibrosis.
Strictures can be focal, multifocal, or diffuse (narrowing).[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopic findings including esophageal rings, linear furrows, edema, mild white plaques, and narrowingFrom the collection of Dr Evan S. Dellon [Citation ends].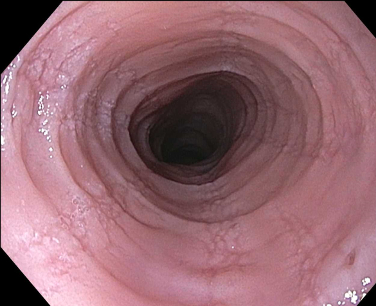
Treated with endoscopic dilation.
Local irritation from medication deposition and/or esophageal candidiasis are commonly reported adverse effects of corticosteroid therapy, but candidiasis resolves on treatment and does not require topical corticosteroids to be stopped.[118] These effects are seen in up to 15% to 20% of patients.[28] The systemic exposure to topical corticosteroid is thought to be very small because of poor absorption from the gastrointestinal tract (fluticasone), or a very high first-pass rate of hepatic metabolism (budesonide). Some cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported, mostly among patients on higher corticosteroid doses who use other inhaled or intranasal corticosteroids to treat concomitant atopic disease.[133][134] Long-term studies assessing the adrenal axis in both adults and children are needed, as well as additional data assessing the effect on growth and bone mineral density in children.[112]
Common complication in adolescents and adults, occurring in up to one third of patients.[13][14][15][178][179]
More common in patients with a prolonged duration of symptoms prior to diagnosis.
An episode can be transient (lasting only a few minutes) or prolonged. In the most severe cases, the food will become stuck and urgent esophagogastroduodenoscopy is required to remove the bolus.
Complications of endoscopic removal include esophageal injury, rupture, or perforation.
Although faltering growth may occur in infants and young children with EoE, long-term growth or final height deficit is not associated with EoE.
A life-threatening, but rare, complication.
May be spontaneous, secondary to food impaction, or due to endoscopic complications.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer