History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
positive family history
short stature
May be a presenting feature.
Childhood growth tends to follow the third centile, but the pubertal growth spurt is often attenuated or absent.[32]
dysmorphic facial features
Irrespective of the age of the patient, specific facial features are seen.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Young male with Noonan syndrome, seen at age 3 months (A), 2 years (B), 6 years (C), and 17 years (D)From the collection of Judith E. Allanson [Citation ends].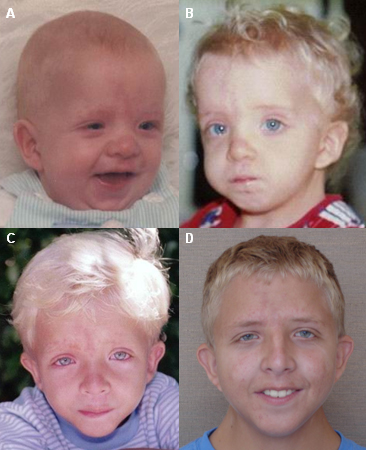 These include wide-spaced and down-slanting eyes with vivid blue or blue-green irides; low-set, posteriorly rotated ears; an inverted triangular-shaped face with small chin; and a broad or webbed neck.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Female with Noonan syndrome seen at age 4 months (A), 4 years (B), and as an adult (C)From the collection of Judith E. Allanson [Citation ends].
These include wide-spaced and down-slanting eyes with vivid blue or blue-green irides; low-set, posteriorly rotated ears; an inverted triangular-shaped face with small chin; and a broad or webbed neck.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Female with Noonan syndrome seen at age 4 months (A), 4 years (B), and as an adult (C)From the collection of Judith E. Allanson [Citation ends].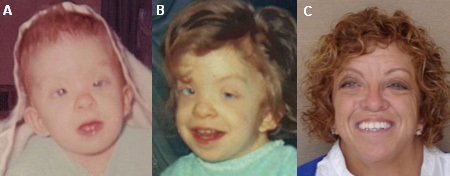
cryptorchidism
Undescended testes are presenting features in most boys (60% to 69%), and may be associated with delayed puberty.[1]
cardiac anomalies
Pulmonary valve stenosis and/or dysplasia, septal defects, and other less common structural cardiac defects are cardinal features of NS.[30]
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may develop in utero, at birth, or in infancy or childhood.
delayed puberty
easy bruising or bleeding
uncommon
lymphedema
Less than 20% of cases have a lymphatic abnormality.[29]
Dorsal limb lymphedema may be present at birth, contributing to increased birth weight, and resolving in childhood.
Lymphatic dysplasias, causing limb edema, pulmonary or intestinal lymphangiectasia, and scrotal or penile edema, are less common and may present at any age.
Treatment is challenging, and specialist referral is required.
pigmentary anomalies
Café au lait patches, lentigines, nevi, and keratosis are seen.
sparse or absent eyebrows and lashes
Associated with mutations in SOS1, BRAF, and MAP2K1 genes in most instances.
splenomegaly
Enlargement of the spleen has been observed and may be a feature of myelodysplasia.
Other diagnostic factors
common
abnormalities identified prenatally
During pregnancy, the most common features suggesting a diagnosis of NS are polyhydramnios (excess of amniotic fluid) and cystic hygroma (cystic lymphatic lesion).[29][46][47][48]
Other features noted on ultrasound include scalp edema, increased nuchal translucency, pleural or pericardial effusion, ascites, and/or hydrops (fluid in body cavities).[46][49]
chest deformity
A broad chest with wide-spaced, low nipples and a particular pectus deformity (carinatum superiorly and excavatum inferiorly) is frequently seen.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest demonstrating typical pectus deformity with a marked inferior excavatum and subtle superior carinatumFrom the collection of Judith E. Allanson [Citation ends].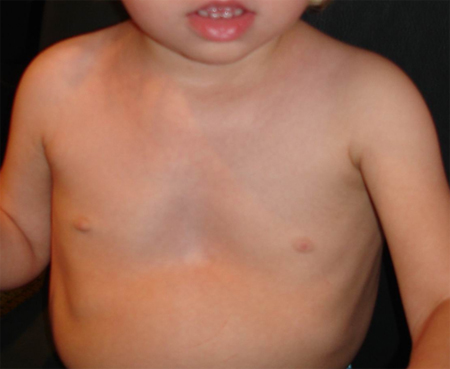
developmental delay/learning difficulty
Mild cognitive impairment is found in up to 33% of cases, and IQ ranges from 64 to 127.[29][34]
Specific visual-constructional problems, verbal-performance discrepancy, and language delay or impairment may be present even when IQ is normal.[29][35][36][37][60][39]
Children with NS have a specific impairment in the global processing of visuospatial information.[38]
Adults with NS may experience specific difficulties in information processing, but this rarely has an impact on cognition.[39]
skeletal anomalies
Cubitus valgus (an increased carrying angle of the forearm) is present in 50% of cases, and short fingers with blunt fingertips are seen in up to one third of cases.
Joint hyperextensibility occurs in 30% of cases.[29]
Less common skeletal anomalies include talipes equinovarus (clubfoot), joint contractures, scoliosis, and radioulnar synostosis (fusion of radius and ulna).
muscle weakness
Muscle weakness as measured by grip strength has been documented.[44]
uncommon
history of renal malformation
Present in up to 10% of cases. Renal malformations may include malformation such as duplex collecting system, distal ureteric stenosis, renal hypoplasia, unilateral renal agenesis, or unilateral renal ectopia.[50]
Risk factors
strong
weak
advanced paternal age
Advanced paternal age has been identified in a cohort of patients with sporadic NS (with no family history).[28]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer