Tests
1st tests to order
CBC
Test
Should be requested in any patient with jaundice or splenomegaly or with a family history of HS.
The result can be very variable depending upon the severity of the HS. Mild cases may be missed without careful exam of the smear.
Anemia may be absent in HS when the marrow output increases sufficiently to keep the Hb normal, but there will be an increase in reticulocytes (known as compensated hemolysis).
Result
Hb: reduced or may be normal; MCHC: may be elevated; MCV: normal or reduced; platelet and WBC count: usually normal (with concurrent viral infection may be reduced)
reticulocyte count
Test
Unless the patient is experiencing a febrile suppression of erythropoiesis, the reticulocyte count will almost always be elevated, even if the patient is not anemic.
Result
elevated
blood smear
Test
The presence of spherocytes is not limited to HS. Other diagnoses must be ruled out by appropriate history, the clinical setting, and investigations.[16][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Blood smear of patient with HS (A) compared with normal blood smear (B); Pincer cell (mushroom-shaped cell) indicatedFrom the collection of Paula Bolton-Maggs, University of Manchester, UK; used with permission [Citation ends].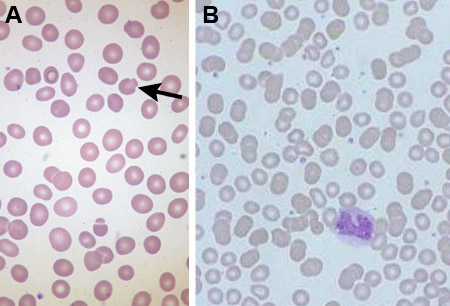 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Blood smear of a patient with HS; spherocyte indicatedFrom the collection of Shelley Crary, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, TX; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Blood smear of a patient with HS; spherocyte indicatedFrom the collection of Shelley Crary, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, TX; used with permission [Citation ends].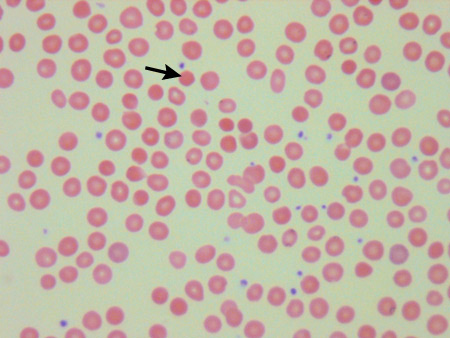
Pincer cells (mushroom-shaped cells) in addition to spherocytes, are due to band 3 protein mutations. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Blood smear of patient with HS (A) compared with normal blood smear (B); Pincer cell (mushroom-shaped cell) indicatedFrom the collection of Paula Bolton-Maggs, University of Manchester, UK; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
spherocytes present; may also demonstrate pincer cells
serum bilirubin
Test
There are several causes of jaundice in neonates, so other causes should be excluded.
Result
elevated unconjugated bilirubin
serum aminotransferases
Test
Performed in the presence of jaundice.
Usually normal in HS but may be deranged with intercurrent viral infection.
Result
usually normal
direct antiglobulin test (DAT)
Test
Usually performed by the blood transfusions section of the laboratory.
Antiglobulin reagent is added to a suspension of red cells that agglutinate if antibodies are present on the red cells. A negative test makes autoimmune hemolysis very unlikely.
Result
negative
Tests to consider
eosin-5-maleimide binding test
Test
Often not necessary to perform if typical features present on blood smear and positive family history present. Recommended when the features are not typical (e.g., the morphology on the blood smear is not quite typical or there is no family history).[15]
Only available in some laboratories. Fluorescence occurs when the reagent binds to band 3 protein in the membrane and is detected by flow cytometry. The intensity is reduced in HS.[26]
Result
reduced intensity of fluorescence with band 3 protein defect
acidified glycerol lysis test
Test
Another confirmatory test, rarely required and not widely available. May be used when the features are not typical (e.g., morphology on the blood smear is not quite typical, or no family history).[15]
Uses 20 microliters of whole blood and measures the time taken for the absorbance to fall to one half of its original value using a red-cell suspension before and after addition of glycerol. This test has a reported sensitivity of 98.3% for HS and a specificity of 91.1%,[22] but is also positive in autoimmune hemolytic anemia, pregnancy, myelodysplasia, and some other conditions.
Result
usually positive
Emerging tests
genetic analysis
Test
Next-generation sequencing may be performed in research settings to determine which protein is primarily affected in atypical families with unusual morphology.
If there are existing genetic test results, do not perform repeat testing unless there is uncertainty about the existing result, e.g., the result is inconsistent with the patient’s clinical presentation or the test methodology has changed.[24]
Result
genetic abnormality detected
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer