Tests
1st tests to order
breast ultrasound
Test
For an erythematous area, ultrasonography helps identify an underlying abscess.[5]
Abscesses usually form a hypoechoic lesion. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ultrasound image showing a well-circumscribed hypoechoic breast abscessFrom the collection of Holly S. Mason, MD, Tufts University School of Medicine, MA [Citation ends].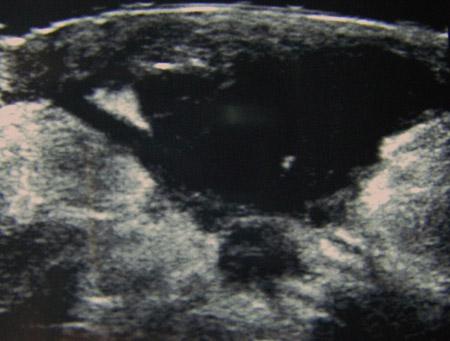
Result
hypoechoic lesion (abscess); may be well circumscribed, macrolobulated, irregular, or ill defined with possible septae
diagnostic needle aspiration drainage
Test
A breast abscess can be drained by needle aspiration for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Needle aspiration of a breast abscess under ultrasound guidance: note the needle piercing the abscess to the right of the imageFrom the collection of Holly S. Mason, MD, Tufts University School of Medicine, MA [Citation ends].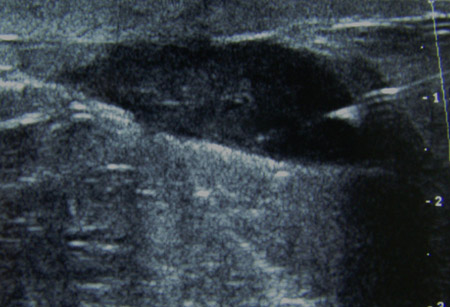
Can be directed by ultrasound guidance.
Result
purulent fluid indicates a breast abscess
cytology of nipple discharge or sample from fine-needle aspiration
Test
Nipple discharge and fine-needle aspirate should be sent for cytologic evaluation, looking for underlying malignancy in addition to infection.
Result
if present: infection and/or malignancy demonstrated
milk, aspirate, discharge, or biopsy tissue for culture and sensitivity
Test
Milk, aspirates, nipple, or sinus discharge, and biopsy tissue should be sent for bacterial (aerobic and anaerobic) culture and sensitivity.
Fungal and mycobacterial studies may be performed, but usually only if the condition is refractory to antibiotics.
Mycobacteria are usually demonstrable in only 12% to 33% of mammary tuberculosis.[37][38]
Result
positive culture indicates infection
Tests to consider
pregnancy test
Test
If mastitis develops unexpectedly, such as in an adolescent, a pregnancy test should be considered.
Result
may be positive
blood culture and sensitivity
Test
If systemic infection is suspected, blood cultures should be sent for bacterial (aerobic and anaerobic) culture and sensitivity.
Fungal and mycobacterial studies may be performed, but usually only if the condition is refractory to antibiotics.
Results guide appropriate therapy.
Result
positive culture indicates systemic infection
histopathologic examination of biopsy tissue
Test
Excised tissue should be sent for histopathologic evaluation, especially in refractory and recurrent cases.
Skin-punch biopsy can be undertaken to diagnose inflammatory breast carcinoma.
Result
if present: infection, granulomatous inflammation, or malignancy demonstrated
mammogram
Test
Useful to help identify underlying breast lesions.
Mammographic findings of breast infection and abscess are often nonspecific and may mimic cancer.[34][35][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tubercular mastitis: mammogram showing a mass lesion in the upper outer quadrantAdapted from the Internet J Surgery (2007); used with permission [Citation ends].
It is usually too painful to perform a mammogram if an abscess is present.
A mammogram should be ordered (following resolution of the acute phase) in women aged >40 years and whenever the presentation is complicated or atypical, or malignancy is suspected.[36]
Result
nonspecific findings in acute phase; may demonstrate underlying lesion if performed after the acute phase
milk for leukocyte counts and bacteria quantification
Test
Expressed milk or a midstream sample can be sent for leukocyte counts and bacteria quantification.[32]
Although the presence of pathogenic bacteria and/or high bacterial counts (>10³/mL of milk) indicates mastitis, the predictive value is low. Therefore, the presence of bacteria in milk does not necessarily indicate infection.[1]
Result
leukocytes >10⁶/mL milk and bacteria <10³/mL milk indicates noninfectious mastitis; leukocytes >10⁶/mL milk and bacteria >10³/mL milk indicates infectious mastitis
CBC
Test
Indicated for patients who appear toxic or have an abscess, recurrent infection, or treatment failure.
Result
normal; leukocytosis with infection; neutropenia with immunosuppression
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer