Tests
1st tests to order
funduscopy and examination under anesthesia
Test
Dilated fundus examination with 360-degree scleral depression is important to enable identification of peripheral tumors. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Large retinoblastoma focus in the left eyePersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].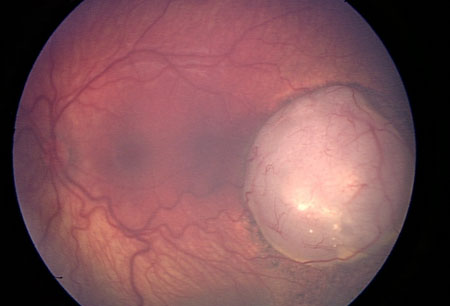 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Macular retinoblastoma in the right eyePersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Macular retinoblastoma in the right eyePersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].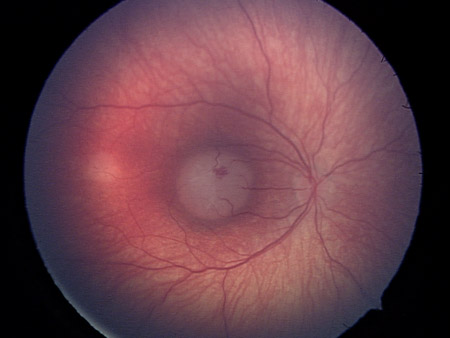 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Two large retinoblastoma foci in the left eye; note the associated subretinal seedingPersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Two large retinoblastoma foci in the left eye; note the associated subretinal seedingPersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].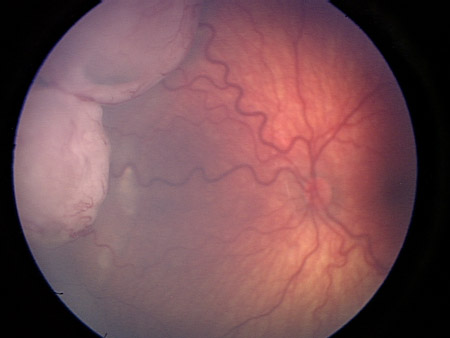 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Vitreous seeding associated with retinoblastomaPersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Vitreous seeding associated with retinoblastomaPersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].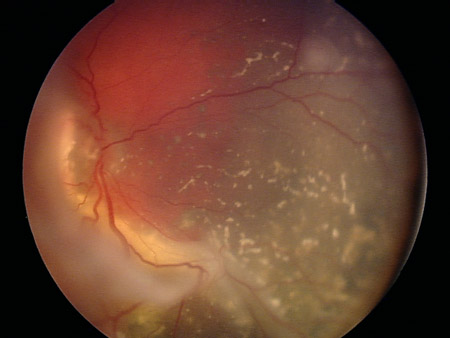
Result
chalky, white-gray retinal mass; may show retinal detachment with retinal vessels visible behind the lens; may show vitreous and/or subretinal seeding
wide-field fundus photography and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (sdOCT)
Test
Wide-field fundus photography allows for the acquisition of high-quality posterior and peripheral retinal images and for fluorescein angiography as needed to differentiate retinoblastoma from other disease entities.[44]
sdOCT establishes anatomic stability of the macula and fovea. Images document small areas of tumor growth, subtle vitreous seeding, and subretinal seeds, as well as frank and subtle subretinal fluid.[44] Can be used in an operative setting on anesthetized patients.
Result
retinal tumors noted and documented relative to optic nerve and fovea; presence of exudative retinal detachment, vitreous and subretinal seeding; sdOCT notes normal or abnormal foveal contour and may be exquisitely sensitive to document marginal tumor recurrence
ophthalmic A- and B-scan ultrasound
Test
Typically performed during the initial clinical examination.[45] If necessary, may be completed as part of the examination under anesthesia.
Result
A-scan reveals variable or high internal reflectivity; B-scan typically reveals a mass filling the globe with calcification and accompanying shadowing
Tests to consider
genetic testing
Test
Molecular testing for a mutation in the RB1 gene is most useful in patients for whom tumor tissue is available or if there are multiple affected family members.
Generally, results of molecular testing do not guide ocular therapy. However, the presence of a germinal mutation can be helpful for family planning and screening for secondary cancers.[14]
Result
may show mutation in the RB1 gene
MRI head/orbit
Test
In general, imaging studies of the head and orbit are not necessary for the diagnosis of retinoblastoma, but are routinely used to eliminate concerns for central nervous system (CNS)/orbital involvement.[46]
Patients diagnosed with bilateral retinoblastomas should have an MRI of the brain to exclude the possible presence of a concomitant primitive neuroectodermal tumor in the pineal gland. May also be used to detect metastases.
Result
may show presence of pinealoma in patients with bilateral retinoblastoma or metastases
bone marrow aspiration
Test
Recommended only if metastatic disease is suspected: for example, in patients with group E disease (International Classification of Retinoblastoma) or in patients who undergo enucleation and are found to have tumor present at the margin of the optic nerve.[48]
Result
presence of malignant cells
lumbar puncture
Test
Recommended only if metastatic disease is suspected: for example, in patients with group E disease (International Classification of Retinoblastoma) or in patients who undergo enucleation and are found to have tumor present at the margin of the optic nerve.[48]
Result
presence of malignant cells
Emerging tests
liquid biopsy
Test
Tissue biopsy is never performed because of the unacceptable risk of orbital seeding and metastasis.[49]
Sequencing cell-free DNA from aqueous humor for single nucleotide variant analysis of the RB1 gene, and detection of somatic copy number alterations (SCNAs), is currently being investigated as a companion diagnostic and prognostic for retinoblastoma.[51][52]
Result
may show pathogenic RB1 variants and focal RB1 deletions
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer