History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
leukocoria (white pupillary reflex)
This is the most common clinical presentation and is usually seen in advanced disease.[8][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Leukocoria (white pupillary light reflex) in the left eye of a patient with unilateral retinoblastomaPersonal collection of Dr Timothy Murray [Citation ends].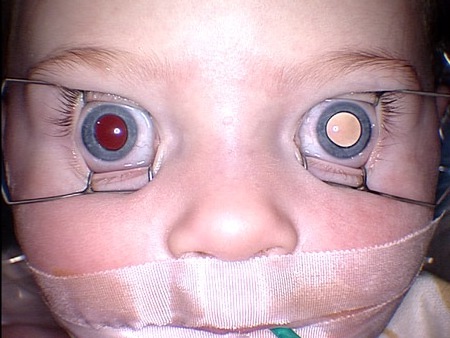
strabismus
The second most common clinical presentation.[9]
uncommon
positive family history
orbital pseudocellulitis
A relatively common clinical presentation.[12]
13q syndrome
Children who have a large deletion on the long arm of chromosome 13 present with retinoblastoma as well as other characteristic features that may include mental and growth retardation; craniofacial dysmorphisms; hand and foot anomalies; and defects of the brain, heart, and kidneys.[15]
Other diagnostic factors
Risk factors
strong
mutation in RB1 gene
A mutation in both alleles of the RB1 gene is widely believed to be a prerequisite for the presence of disease. Other mutations are likely necessary for progression to clinical retinoblastoma.[23]
Only 10% of patients have a previously established family history of the disease.[23][25]
The majority of cases occur as a result of spontaneous mutations either early in embryogenesis or de novo in one set of parental germline cells.[25]
weak
human papillomavirus (HPV) exposure
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer