Tests
1st tests to order
HIV test
CBC and comprehensive metabolic panel
Test
Bone marrow and organ function will need to be evaluated in patients requiring systemic chemotherapy.
Result
normal
skin/mucosal biopsy
Test
Skin punch biopsies are easy to perform and readily help exclude mimics. Histopathology shows characteristic atypical spindle-shaped cells.[36]
Immunohistochemistry techniques can be used to detect the following markers expressed by Kaposi sarcoma lesional cells: latency-associated nuclear antigen-1 (LANA-1, a surrogate marker for HHV-8); CD31/CD34 (vascular endothelial cell immunomarkers), and D2-40 (a lymphatic cell immunomarker).[37][38]
A positive LANA-1 stain can establish KS diagnosis; CD31 and CD34 may be useful if it is unclear whether the tumor is vascular in origin.[2][5][38]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrograph of the histopathology of Kaposi sarcoma showing fascicles of vasoformative spindle-shaped tumor cells (hematoxylin and eosin stain)From the collection of Dr Liron Pantanowitz; used with permission [Citation ends].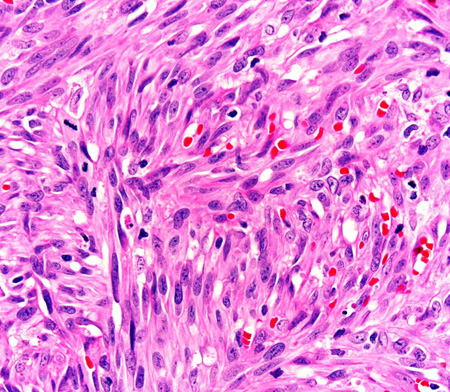
Result
characteristic vascular lesion
Tests to consider
chest x-ray
Test
Useful to screen for pulmonary KS in patients with advanced disease or respiratory symptoms.[2][5] Concomitant pulmonary infection should be excluded, because none of these findings are pathognomonic for KS.
Result
nodular, interstitial, and/or alveolar infiltrates; serosanguinous pleural effusion; hilar and/or mediastinal lymphadenopathy; solitary nodule
chest CT and bronchoscopy
Test
To establish a diagnosis of pulmonary KS. Indicated for patients with abnormal chest x-ray.[2][5]
Biopsy of respiratory tract lesions is relatively contraindicated because of the risk of bleeding.[39][40][41]
Result
characteristic purple or cherry-red, slightly raised vascular lesions in the tracheobronchial tree
CT abdomen/pelvis
Test
May be required to exclude other conditions, but not necessarily indicated as part of a routine evaluation.[2][5]
CT may be helpful for evaluating deep nodal and visceral KS, and bone lesions. Bone lesions are better detected by CT scan and MRI, as they frequently go undetected on plain x-ray or bone scans.[43][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the chest showing a reticular pattern due to pulmonary involvement by Kaposi sarcomaFrom the collection of Dr Bruce J. Dezube; used with permission [Citation ends].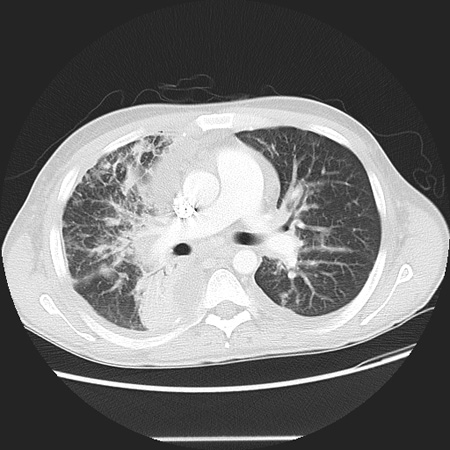
Result
helpful to evaluate deep nodal and visceral lesions
MRI
Test
May be required to exclude other conditions, but not necessarily indicated as part of a routine evaluation.[2] Findings are not specific to KS. MRI may be helpful for evaluating deep nodal and visceral KS, and bone lesions. Bone lesions are best detected by CT scan and MRI, as they frequently go undetected on plain x-ray or bone scans.[43]
Result
helpful for evaluating visceral disease and involvement of deep tissue planes
fecal occult blood
Test
Testing for fecal occult blood is useful to screen for gastrointestinal (GI) tract KS lesions.[2]
Result
a positive test may indicate GI tract bleeding that may be attributed to KS
gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy
Test
GI endoscopy in symptomatic individuals can be helpful, but is not recommended as part of routine evaluation in the absence of iron deficiency, GI blood loss, or GI symptoms.[2][4] A mucosal biopsy may not always be diagnostic as KS lesions are often submucosal.
Result
isolated or confluent hemorrhagic nodules
PET scan
lymph node biopsy
Test
In the presence of cutaneous disease, routine biopsy of small lymph nodes is not recommended for diagnosing nodal KS.
Lymphadenopathy should be examined histologically if a coexisting disorder (e.g., infection, lymphoma, multicentric Castleman disease) is suspected.[2][42]
Result
characteristic vascular lesion
renal function tests
Test
Patients requiring systemic chemotherapy will need their renal function evaluated.
Result
normal
liver function tests
Test
Patients requiring systemic chemotherapy will need their hepatic function evaluated.
Result
normal
Emerging tests
human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) viremia and serology
Test
May indicate patients at risk and/or correlate with KS disease burden.
Determination of HHV-8 (PCR) and assays for HHV-8 antibodies are not typically warranted in routine clinical practice, but may be considered an individual basis.[3][5]
Result
if available, presence of HHV-8 DNA (copies/mL) by PCR or HHV-8 antibodies by immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer