Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
White blood cell (WBC) count is elevated in up to 70% of cases of brain abscess.
This test should be ordered as part of the initial work-up of any patient with a suspected brain abscess. Additionally, platelet count and haemoglobin/haematocrit are critical preoperative tests.
Elevation in the WBC count favours abscess over tumour, especially if the patient has not yet received corticosteroids.
Result
leukocytosis
serum erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Test
This test is ordered as part of the initial work-up if abscess is suspected, or subsequent to the finding of a ring-enhancing lesion on neuro-imaging.
ESR is elevated in >90% of brain abscess patients. Rarely elevated in central nervous system neoplasm.[41]
Result
elevated
serum CRP
Test
Elevation favours abscess over tumour.
Result
elevated
serum PT, PTT, and INR
Test
Coagulation profile should be ordered for any patient who may need urgent surgical treatment.
Result
normal
blood culture
Test
The absence of positive blood cultures does not exclude the diagnosis of brain abscess. Blood cultures are less likely to be positive if the patient has received antibiotics. Not useful in cases of parasitic or fungal brain abscesses.
Result
may be positive
MRI with contrast
Test
MRI with contrast is the initial radiographic test ordered in a patient with suspected brain abscess, unless a head CT has already been obtained.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Contrast MRI of patient with brain abscessFrom the collection of Walter Hall, SUNY Upstate Medical University [Citation ends].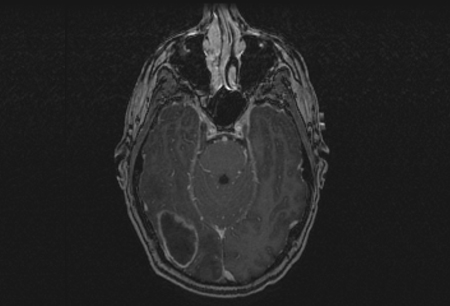 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Brain MRI before treatment (left image) and 18 months after antiretroviral therapy (ART) and antitoxoplasmosis therapy (right image)Aldeen T, Lunn M. Solitary ring enhancing brain lesion in a patient with AIDS. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Brain MRI before treatment (left image) and 18 months after antiretroviral therapy (ART) and antitoxoplasmosis therapy (right image)Aldeen T, Lunn M. Solitary ring enhancing brain lesion in a patient with AIDS. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136 [Citation ends].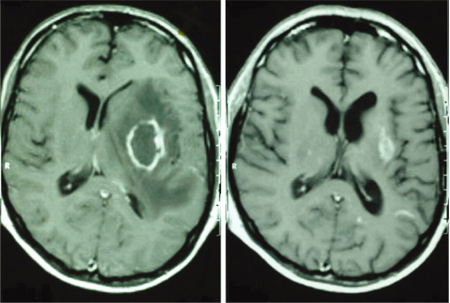
Result
one or more ring-enhancing lesions
CT head with and without contrast
Test
Often performed as the first radiographical study in patients with new neurological findings. If a good-quality MRI has been obtained, CT is not necessary. CT is less sensitive than MRI for detection of posterior fossa lesions as well as abscesses in the early stages.[39][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan, cerebral abscess within right temporal lobeRafiq MK. An interesting case of cerebral abscess. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136 [Citation ends].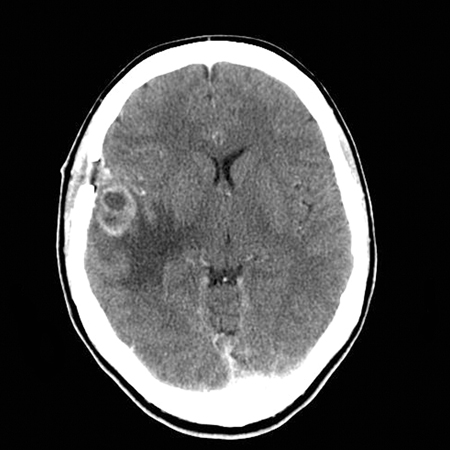
Result
one or more ring-enhancing lesions
ultrasound head (infants)
Test
Only useful in infants with open fontanelle. Sonography allows for more frequent neuro-imaging in infants, who are at a higher risk of sequelae from the radiation associated with CT scanning. This technique also screens for hydrocephalus in this high-risk age group.
Result
may show cavitary lesion
Investigations to consider
serum toxoplasma titre
Test
Appropriate if high index of suspicion for HIV or immunocompromise.
Negative antitoxoplasma IgM rules out acute infection, but false positives are possible.
Result
may be positive
magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS)
Test
Time-consuming. It has been suggested that the analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging sequences of traditional MRI may be more cost effective in most patients.[39] The use of MRS has been recommended by the American College of Radiology if there is the suspicion of a brain infection, especially a brain abscess.[40]
Result
increased succinate, acetate, amino acid, and lactic acid peaks
lumbar puncture (LP) with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
Test
Lumbar puncture is performed with extreme caution and only if a lesion is small and Toxoplasma gondii is likely. In cases of Toxoplasma gondii abscess, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is positive.
LP does not play a role when pyogenic abscess is suspected.
Result
increased CSF WBC count; decreased glucose; toxoplasmosis: positive PCR
CT chest, abdomen, and pelvis
Test
Ordered as part of a second round of tests, if the patient is not taken for surgery as an emergency. Part of the work-up for intracranial mass lesion, seeking malignancy.
Result
negative
bone scan
Test
Ordered as part of a second round of tests, if the patient is not taken for surgery as an emergency. Part of the work-up for intracranial mass lesion, seeking malignancy.
Typically negative, unless osteomyelitis is present.
Result
negative
mammogram
Test
Ordered only if there is a suspicion of breast cancer such as a family or personal history.
Result
negative
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer