Complications
Median time to onset is 2 weeks after completion of therapy. Initial step in management consists of establishing the presence of persistent urethritis. Functional disorder, incomplete prior therapy, reinfection, herpes simplex virus, and Trichomonas vaginalis should be ruled out. There are no firm guidelines or studies showing any benefit of repeated courses of antibiotics.[55]
Preventable with treatment. May occur in prostate, Tyson's glands, or periurethrally.[55]
Preventable with treatment.[55]
May be associated with non-gonococcal urethritis in 1% to 2% of cases, primarily males.[54] Strongly associated with HLA-B27 (90% to 96%) and Chlamydia trachomatis in particular, but can also occur after bacterial enteritis. Arthritis typically starts 4 weeks after urethritis. Eye symptoms are usually acute, unilateral, and brief, lasting only a few days. The classic skin findings are keratoderma blenorrhagicum and circinate balanitis. Long-term antibiotic treatment is controversial. Standard antichlamydial therapy is recommended in addition to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.[2][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Circinate balanitis secondary to reactive arthritisAdapted from Public Health Image Library, CDC (Wiesner PJ, Kaufman RE, 1973) [Citation ends].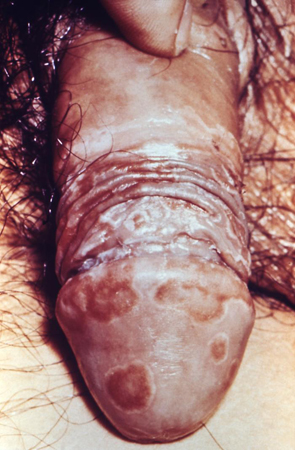
Occurs in <3% of gonorrhoea infections.[3] Features include fever, pustular or petechial rash, tenosynovitis, and arthritis. Hospitalisation and consultation with a specialist is recommended for patients who might not comply with treatment, have an uncertain diagnosis, or have purulent synovial effusions or other complications. Patients should also be examined for clinical signs of endocarditis and meningitis.[1]
Occurs in 1% to 2% of cases. Preventable with early treatment.[55]
Occurs in 1% to 2% of cases. Resolves with treatment.[2]
May occur by vertical transmission at birth.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: A case of gonorrhoeal conjunctivitis that resulted in partial blindness owing to the spread of N gonorrhoeae bacteriaCDC Image Library [Citation ends].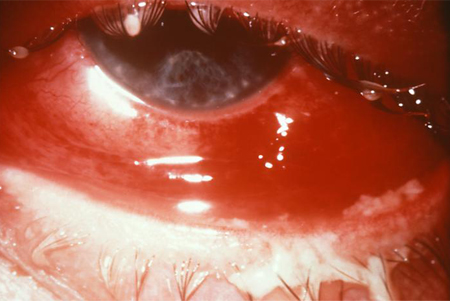
May occur as subacute, afebrile pneumonia with onset at ages 1 to 3 months following perinatal infection with Chlamydia trachomatis or as a complication of untreated urethritis in immunocompromised adults.[55]
Uncommon in treated patients.
Include salpingitis, orchitis, prostatitis, proctitis, cervicitis, seminal vesiculitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, infertility.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer