Last reviewed: 16 Mar 2025
Last updated: 22 Jul 2022
Summary
Definition
History and exam
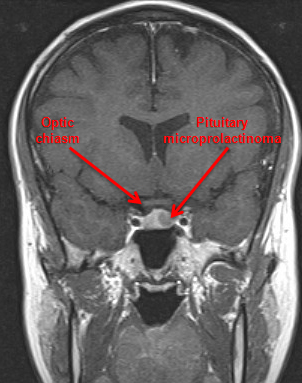
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- amenorrhoea or oligomenorrhoea
- infertility
- galactorrhoea
- loss of sexual desire (libido)
- erectile dysfunction
- visual deterioration (e.g., temporal hemianopia)
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition (e.g., presence of mutation resulting in multiple endocrine neoplasia-1 [MEN-1], familial isolated pituitary adenoma [FIPA])
- oestrogen therapy
- male sex, 30 to 60 years of age
- female sex, 20 to 50 years of age
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- serum prolactin
- pituitary MRI
- computerised visual-field examination
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Niamh Martin, MB ChB, PhD, FRCP
Reader in Endocrinology
Imperial Centre for Endocrinology
Department of Metabolism, Digestion and Reproduction
Imperial College London
London
UK
Disclosures
NM declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Niamh Martin would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Ilan Shimon, the previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
IS receives consultancy and lecturing fees from Pfizer, Israel, and is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Mark Molitch, MD
Professor
Division of Endocrinology
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
MM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer