Investigations
1st investigations to order
serum quantitative immunoglobulins
Test
Measures level of each immunoglobulin type in the serum but does not differentiate between polyclonal (normal) and monoclonal (abnormal) immunoglobulin (M-protein).
Can also be used to check response to therapy.
Result
typically increased concentration of IgG, followed by IgA; IgM, IgD, and IgE are rare
serum/urine protein electrophoresis
Test
Used to diagnose MM (including oligosecretory MM).[3][4] Identifies the presence and level of M-protein in serum/urine.
Negative (i.e., absence of detectable M-protein) in 1% to 5% of patients with MM. These patients are defined as having non-secretory MM.[48]
Can also be used to check response to therapy.
Result
smouldering/active MM: serum M-protein (IgG or IgA) ≥30 g/L (≥3 g/dL), or urine M-protein ≥500 mg/day, and hypogammaglobulinaemia; oligosecretory MM: serum M-protein (IgG or IgA) <10 g/L (<1 g/dL), or urine M-protein <200 mg/day; non-secretory MM: negative serum M-protein and negative urine M-protein
serum/urine immunofixation
serum free light-chain assay
whole-body, low-dose CT (WBLD-CT)
Test
Imaging to assess bone disease is essential for diagnosis and guiding treatment, and should be performed in all patients with suspected MM.[45][46][47]
WBLD-CT is more sensitive than conventional skeletal survey (radiography) for the detection of osteolytic lesions.[47][53][54] Positive lesions in WBLD-CT are considered to be those ≥5 mm in diameter.[53]
Result
osteolytic lesions (≥5 mm in diameter), pathological fractures
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/CT (FDG-PET/CT)
Test
Imaging to assess bone disease is essential for diagnosis and guiding treatment, and should be performed in all patients with suspected MM.[45][46][47]
FDG-PET/CT is more sensitive than conventional skeletal survey (radiography) for the detection of osteolytic lesions.[57][58]
FDG-PET/CT is particularly useful during treatment follow-up as it can detect active residual focal lesions and inform prognosis.[57][58][59]
Result
bone disease and bone marrow infiltration
bone marrow evaluation
Test
Bone marrow biopsy and aspirate are required to verify the presence of monoclonal plasma cells in the bone marrow, and to confirm the diagnosis of MM.[3][4]
The proportion of clonal bone marrow plasma cells can help to differentiate MM from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). See Classification.
Solitary plasmacytoma, which may progress to MM, is confirmed by the presence of a solitary lesion of bone (or soft tissue) on biopsy, with evidence of clonal plasma cells.[3] Bone marrow is normal and there is no evidence of clonal bone marrow plasma cells. Imaging studies are normal (except for the solitary lesion); there is no end-organ damage.[3]
Immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry may be performed on bone marrow samples to confirm the presence of monoclonal plasma cells and to accurately quantify plasma cell involvement.[45]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bone marrow biopsyCourtesy of Dr Robert Hasserjian, Hematopathology, Massachusetts General Hospital; used with permission [Citation ends].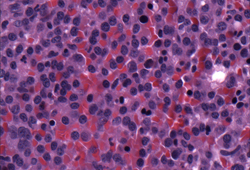 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bone marrow biopsy after histochemical analysis for kappa light chainCourtesy of Dr Robert Hasserjian, Hematopathology, Massachusetts General Hospital; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bone marrow biopsy after histochemical analysis for kappa light chainCourtesy of Dr Robert Hasserjian, Hematopathology, Massachusetts General Hospital; used with permission [Citation ends].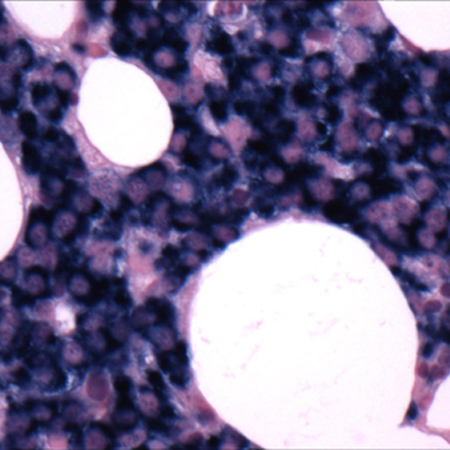
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Bone marrow biopsy after histochemical analysis for lambda light chainCourtesy of Dr Robert Hasserjian, Hematopathology, Massachusetts General Hospital; used with permission [Citation ends].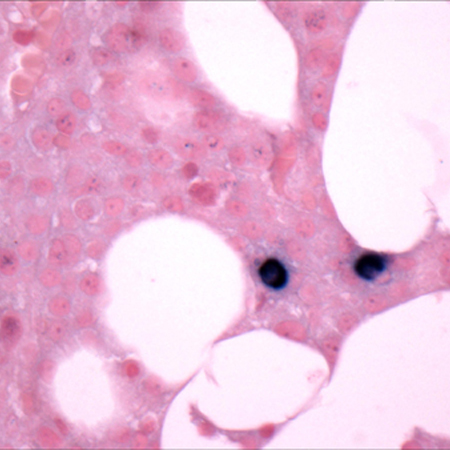 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Aspirate showing plasma cell infiltrateCourtesy of Dr Robert Hasserjian, Hematopathology, Massachusetts General Hospital; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Aspirate showing plasma cell infiltrateCourtesy of Dr Robert Hasserjian, Hematopathology, Massachusetts General Hospital; used with permission [Citation ends].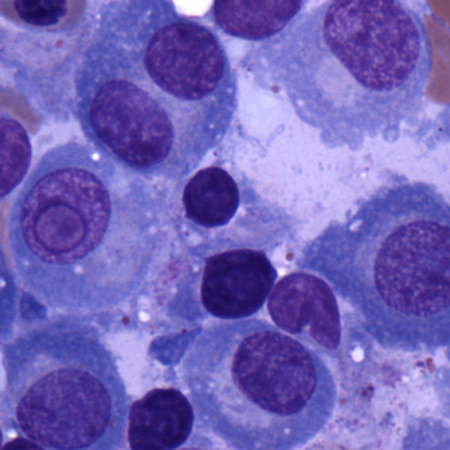
Result
monoclonal plasma cell infiltration in the bone marrow ≥10%; positive for monoclonal plasma cells on immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry staining
serum calcium
FBC with differential
peripheral blood smear
Test
May show stacked red blood cells (Rouleaux formation) due to elevated serum proteins.
Result
Rouleaux formation
serum creatinine, urea, electrolytes
serum uric acid
Test
May be elevated due to renal impairment and high tumour cell turnover.[72]
Result
may be elevated
liver function tests
Result
may be abnormal
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Test
Higher levels indicate more extensive disease and is associated with a worse prognosis.
Result
may be elevated
serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Test
Higher levels indicate more extensive disease.
LDH level has prognostic significance and is incorporated into revised versions of the International Staging System (ISS) classification system (RISS and R2-ISS) to improve risk stratification and prognostication.[63][64]
See Criteria.
Result
age ≤60: 100-190 units/L; age >60: 110-210 units/L
serum beta2-microglobulin
Test
Serum beta2-microglobulin correlates with clinical stages in the Durie Salmon staging system and is considered the single most important factor for predicting survival.[61]
Serum beta2-microglobulin levels combined with serum albumin levels have been shown to improve prognostic significance, and this forms the basis of the International Staging System (ISS) classification system (and subsequent revisions e.g., RISS and R2-ISS) used to risk-stratify patients with MM.[4][62][63]
Stage I MM is defined by serum beta2-microglobulin <3.5 mg/L (<0.35 mg/dL) in combination with serum albumin ≥35 g/L (≥3.5 g/dL).[62] Stage III is defined by serum beta2-microglobulin ≥5.5 mg/L (≥0.55 mg/dL).[62]
See Criteria.
Result
<3.5 mg/L (<0.35 mg/dL) and ≥5.5 mg/L (≥0.55 mg/dL)
serum albumin
Test
Serum albumin levels combined with serum beta2-microglobulin levels have been shown to improve prognostic significance, and this forms the basis of the International Staging System (ISS) classification system (and subsequent revisions e.g., RISS and R2-ISS) used to risk-stratify patients with MM.[4][62][63][64]
Stage I MM is defined by serum albumin ≥35 g/L (≥3.5 g/dL) in combination with serum beta2-microglobulin <3.5 mg/L (<0.35 mg/dL).[62]
See Criteria.
Result
≥35 g/L (≥3.5 g/dL)
N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) or BNP
Test
Higher levels of NT-proBNP or BNP indicate more extensive disease and is associated with a worse prognosis.[66]
BNP is used if NT-proBNP is unavailable.
Result
may be elevated
Investigations to consider
whole-body MRI
Test
Imaging is essential in all patients with suspected MM.[45][46][47]
Whole-body MRI should be considered if CT or FDG-PET/CT is negative or inconclusive, and suspicion remains high for MM.[45][46][47]
MRI is more sensitive than conventional skeletal survey (radiography) for the detection of osteolytic lesions.[47][55]
MRI can detect focal lesions and bone marrow infiltration. It has prognostic value in asymptomatic patients because the presence of small focal lesions (i.e., <5 mm) in these patients is a strong predictor of progression to symptomatic MM.[56]
MRI is particularly useful during treatment follow-up as it can detect residual focal lesions and inform prognosis.[57][58][59][60]
Result
>1 focal lesions on MRI study; bone marrow infiltration
skeletal survey
cytogenetic analysis
Test
Cytogenetic analysis (e.g., fluorescence in situ hybridisation [FISH]) should be performed on bone marrow samples to identify chromosomal abnormalities considered to increase risk for progression/relapse; for example, del(13q), del(17p), t(4;14), t(11;14), t(14;16), t(14:20), 1q21 gain/amplification, 1p deletion, and MYC translocation.[44][45]
Cytogenetics are incorporated into revised versions of the International Staging System (ISS) classification system (RISS and R2-ISS) to improve risk stratification and prognostication.[63][64]
See Criteria.
Result
del(13q), del(17p), t(4;14), t(11;14), t(14;16), t(14:20), 1q21 gain/amplification, 1p deletion, MYC translocation
mass spectrometry
Test
Mass spectrometry may be used as an alternative to immunofixation for the detection of M-proteins.[51]
Mass spectrometry is more sensitive than immunofixation, and can also assist in distinguishing between therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (administered to a patient) and endogenous M-proteins.[52]
Result
detects the presence of an M-protein
genetic testing
Test
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and/or next-generation sequencing (NGS) testing on bone marrow specimens provides further detail about clonal plasma cell genetics that may inform prognostication and aid minimal residual disease (MRD) testing/monitoring during treatment.[45][67]
Result
genetic mutations associated with MM (e.g., KRAS mutation)
serum viscosity
Test
Ordered if hyperviscosity is suspected (particularly those with high levels of M-protein).[45]
Result
may be elevated
viral infection screening
Test
Screening for hepatitis B and C, HIV, herpes simplex virus (HSV), and varicella zoster virus (VZV) should be considered, as clinically indicated
Result
positive or negative for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, HSV, VZV
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer