Investigations
1st investigations to order
echocardiogram
Test
The atrial mass is most commonly seen in the left atrium.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Large left atrial myxomaFrom the collection of Dr Syed Wamique Yusuf, Department of Cardiology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center; used with permission [Citation ends].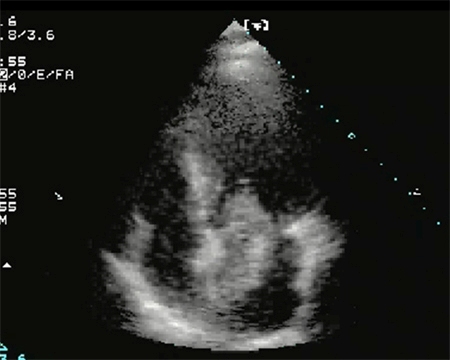 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Two-dimensional echocardiogram showing a right atrial mass suggestive of a myxomaFrom the collection of Dr Syed Wamique Yusuf, Department of Cardiology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Two-dimensional echocardiogram showing a right atrial mass suggestive of a myxomaFrom the collection of Dr Syed Wamique Yusuf, Department of Cardiology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center; used with permission [Citation ends].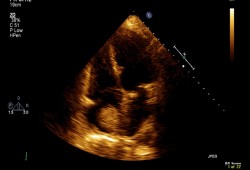
Result
atrial mass seen
ECG
Test
ECG abnormalities are present in about 60% of patients.[4] Left atrial hypertrophy is the commonest abnormality and is found in approximately 35% of patients.
Result
non-specific findings: for example, left atrial hypertrophy, rhythm disorder, conduction abnormalities
FBC
CXR
Test
Result
cardiomegaly, pulmonary oedema, occasionally calcification in the cardiac myxoma
Investigations to consider
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Test
Found in 55% of patients.[8]
Result
increased
C-reactive protein
Test
Found in 75% of patients.[8]
Result
increased
protein electrophoresis
Test
Found in 45% of patients.[8]
Result
increased gamma globulin levels
CT scan (chest)
Test
CT and MRI scans provide better delineation of the intracardiac mass, extent of tumour, and extracardiac structures.[10] They also provide anatomical definition for preoperative planning and may also help to identify whether the mass is solid, haemorrhagic, or fatty.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest CT demonstrating a mass in the right atrium (RA) subsequently confirmed to be an atrial myxoma. RV = right ventricle, LV = left ventricleA Yavari, H El-Mahy, ET McWilliams. BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.10.2008.1031 [Citation ends].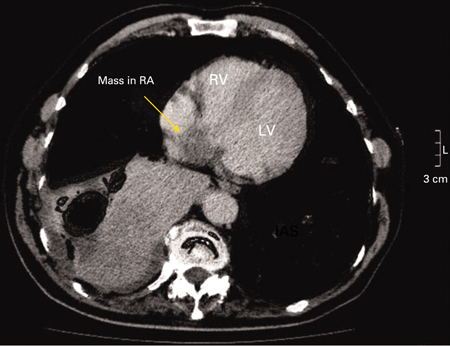
Result
differentiation between mass/tumour/myxoma and thrombus
MRI scan (chest)
Test
CT and MRI scans provide better delineation of the intracardiac mass, extent of tumour, and extracardiac structures.[10] They also provide anatomical definition for preoperative planning and may also help to identify whether the mass is solid, haemorrhagic, or fatty.
Result
differentiation between mass/tumour/myxoma and thrombus
biopsy
Test
The approach to biopsy of cardiac tumour is individualised. The specimen for histology can be obtained via a transvenous or transcutaneous approach or thoracotomy.
Result
differentiation between tumour mass/myxoma and thrombus; provides histological diagnosis
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer