Last reviewed: 21 Mar 2025
Last updated: 05 Apr 2023
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Other diagnostic factors
- abdominal distension
- abdominal pain
- hypertension
- haematuria
- poor appetite or weight loss
- fever
- pallor
- shortness of breath
- hepatomegaly
- varicocele
- hypoglycaemia in infancy
- features of paraneoplastic syndrome
Risk factors
- age <5 years
- congenital urogenital anomalies
- congenital syndromes
- family history of Wilms' tumour
- antenatal exposure to harmful environmental factors
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- FBC
- renal function
- liver function tests
- urinalysis
- serum total protein/albumin
- coagulation studies
- serum calcium level
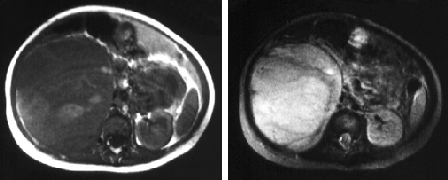
- abdominal ultrasound with Doppler
- CT or MRI abdomen and pelvis with and without contrast
- CT chest with and without contrast
- chest x-ray
Investigations to consider
- tumour histology
- genetic testing
- loss of heterozygosity (LOH) studies
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Sandeep Batra, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor
Riley Hospital for Children
Department of Pediatrics
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis
IN
Disclosures
SB declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Nadine Deannie Lee, MD
Pediatric Hematologist-Oncologist
Hematology/Oncology
Riley Children's Hospital
Indiana University Health
Indianapolis
IN
Disclosures
NDL declares that she has no competing interests.
Norbert Graf, MD
Direktor
Klinik für Pädiatrische Onkologie und Hämatologie
Universitätsklinikum des Saarlandes
Homburg
Germany
Disclosures
NG declares that he has no competing interests.
Zelig Tochner, MD
Associate Professor
Radiation Oncology
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
ZT declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer