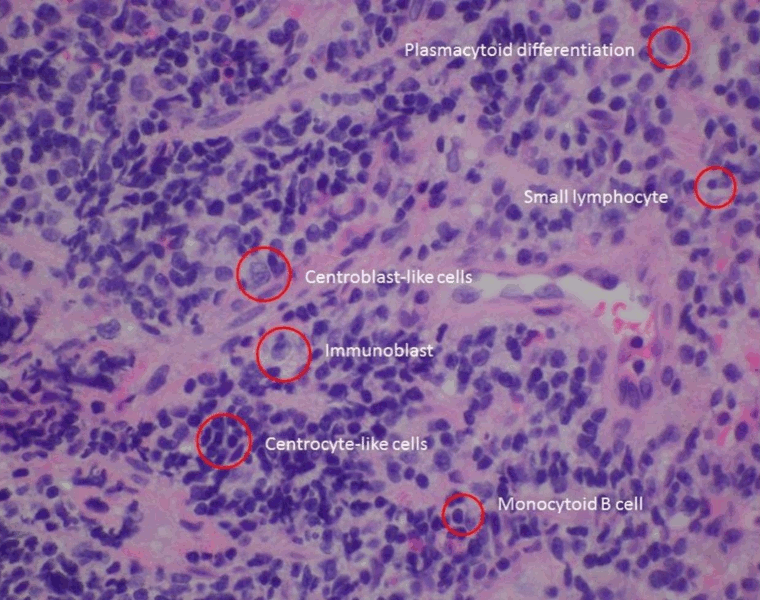
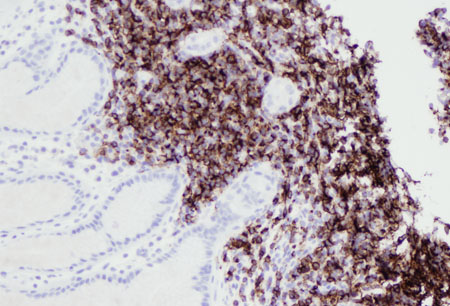
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- history of Helicobacter pylori gastritis
- history of autoimmune disorder
- age >60 years
- dyspepsia
- epigastric discomfort
- skin lesions
- red eye ± photophobia
- conjunctival fornix mass
- painless proptosis, motility disturbances of the eye, diplopia, ptosis, decreased vision
Other diagnostic factors
- abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, malabsorption, vomiting
- GI bleeding, perforation, and obstruction
- fever
- night sweats
- weight loss
- shortness of breath, hemoptysis, cough
- salivary gland swelling
- thyroid swelling
- esophageal/tracheal obstruction (shortness of breath, dysphagia, tracheal deviation)
- breast lump
- focal neurologic deficits
- lymphadenopathy
Risk factors
- Helicobacter pylori infection
- age >60 years
- autoimmune disease
- Chlamydia psittaci infection
- Campylobacter jejuni infection
- Borrelia burgdorferi infection
- hepatitis C virus infection
- hepatitis B virus infection
- HIV infection
- achromobacter xylosoxidans infection
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC with differential
- blood smear
- comprehensive metabolic panel (including LFTs)
- serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- serum beta-2 microglobulin
- upper GI endoscopy
- biopsy of affected site
- immunophenotyping
- H pylori (histologic testing)
- CT scan
Tests to consider
- H pylori (stool antigen test)
- H pylori (urea breath test)
- H pylori (serology test)
- PCR testing for infectious agents
- bone marrow biopsy with aspirate
- genetic studies
- immunoglobulin gene rearrangement studies
- MYD88 mutation testing
- serum protein electrophoresis
- 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT scan
- endoscopic ultrasound of the stomach
- lower GI endoscopy
- MRI orbit, brain
- mammography
- breast ultrasound
- MRI breast
- thyroid ultrasound
- bronchoscopy
- hepatitis C serology
- hepatitis B serology
- HIV serology
- multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan
- echocardiography
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Christopher McNamara, MBBS (Hons), FRACP, FRCPA, FRCPath
Consultant Haematologist
Royal Free Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
CM declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Christopher McNamara wishes to gratefully acknowledge Dr Rahul Joshi, a previous contributor to this topic. RJ declared that he had no competing interests. Unfortunately, we have since been made aware that Dr Rahul Joshi is deceased.
Peer reviewers
Markus Raderer, MD
Professor of Medicine
Department of Internal Medicine I
Division of Oncology
Medical University Vienna
Austria
Disclosures
MR is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Alan Lichtin, MD
Staff Hematologist
Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center
Cleveland
OH
Disclosures
AL declares that he has no competing interests.
Ian Chau, MD
Consultant Medical Oncologist
Royal Marsden Hospital
Sutton
UK
Disclosures
IC has been reimbursed by Roche Products, the manufacturer of rituximab, for attending several conferences. IC has also served on advisory boards and received honorarium for giving presentations for Roche Products. IC has received research funding from Novartis to conduct academic studies in the treatment of colorectal cancer.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer