Complications
A polymorphic ventricular tachyarrhythmias (VT) secondary to genetic mutations that lead to dysfunctional potassium channels and subsequent slowed repolarization and transmural dispersion of repolarization, which predisposes to VT.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Rhythm strips showing torsades de pointesChong DW, Ankolekar SJ, McDonald J. BMJ Case Reports. 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2009.1426 [Citation ends].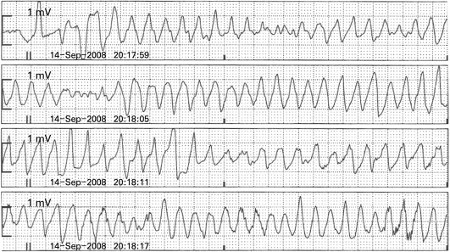
Treatment is with intravenous magnesium and electrical cardioversion.
Torsades de pointes with associated pause-dependent VT is additionally treated with temporary ventricular pacing or isoproterenol.
In addition, electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia) should be corrected, and drugs known to prolong the QT interval or cause depletion of potassium and/or magnesium should be discontinued.
Secondary to polymorphic ventricular tachyarrhythmias degenerating into ventricular fibrillation.
Emergency treatment is with CPR and defibrillation as per the adult advanced life support protocol.
In addition, electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia) should be corrected, and drugs known to prolong the QT interval or cause depletion of potassium and/or magnesium, such as quinidine, procainamide, sotalol, amiodarone, disopyramide, dofetilide, phenothiazines, and tricyclic antidepressants, should be discontinued. Credible Meds (Arizona CERT): drugs that prolong the QT interval Opens in new window
Secondary to cardiac arrest resulting from polymorphic ventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer