Tests
1st tests to order
plain abdominal x-ray
Test
In a newborn it is very difficult to differentiate between a dilated colon and small bowel; this is a nonspecific investigation. However, a dilated intestine with a paucity of rectal gas is suggestive of distal obstruction.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Abdominal x-ray image showing gaseous distension of the large bowel with air absent from the rectum (typical of Hirschsprung disease)BMJ Case Reports 2012; doi:10.1136/bmj.e5521 [Citation ends].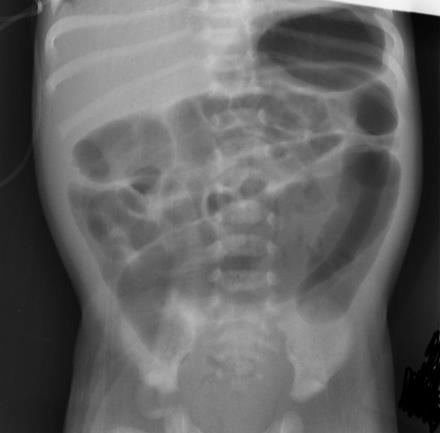
A normal film does not exclude the possibility of Hirschsprung disease.
Result
air-fluid levels present; dilated intestine
contrast enema
Test
Performed with water-soluble contrast material.
A contrast enema is the most valuable initial screening diagnostic test for Hirschsprung disease.
No bowel preparation required.
The infant is placed in a lateral position, and a rectal tube is introduced to barely above the anal canal.
The characteristic image of a dilated descending colon, followed distally by a nondistended rectosigmoid, may not be fully visible in a newborn. Weeks or months later the radiologic changes become more obvious.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Contrast enema demonstrates the typical proximal dilation, transition zone, and nondistended, aganglionic portionCorman ML. Colon and rectal surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2005:555-603; used with permission [Citation ends].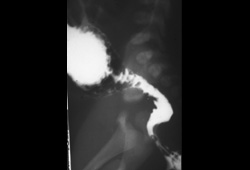 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Contrast enema showing an abnormal rectosigmoid ratio (sigmoid diameter larger than rectal diameter)From the personal collection of Lily Cheng, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Contrast enema showing an abnormal rectosigmoid ratio (sigmoid diameter larger than rectal diameter)From the personal collection of Lily Cheng, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].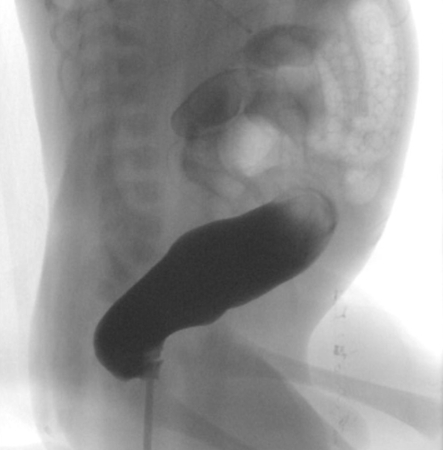 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Contrast enema may demonstrate mucosal irregularity in the aganglionic distal colon and may show a transition zone between smaller caliber aganglionic distal colon and dilated proximal ganglionic colonFrom the personal collection of Lily Cheng, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Contrast enema may demonstrate mucosal irregularity in the aganglionic distal colon and may show a transition zone between smaller caliber aganglionic distal colon and dilated proximal ganglionic colonFrom the personal collection of Lily Cheng, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].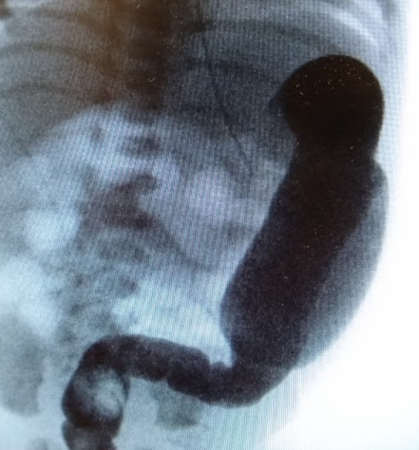
Result
contracted distal bowel and dilated proximal bowel with transition zone in between; rectosigmoid ratio of <1, mucosal irregularity, microcolon
Tests to consider
rectal biopsy
Test
Rectal biopsy is necessary for definitive diagnosis of Hirschsprung disease.[54] Biopsies can be performed using either suction or open surgical techniques, with a preference for the least invasive feasible method.[27]
Biopsies should be obtained at least 2 cm proximal to the dentate line and should be at least 3 mm in diameter, ensuring that at least one third of the sample includes submucosal tissue.[27][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histologic section including mucosa and submucosa of the rectum showing tortuous and hypertrophic nerve trunks of the submucosal plexus. There is no evidence of any ganglion cell present. This establishes the diagnosis of Hirschsprung diseaseCorman ML. Colon and rectal surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2005:555; used with permission [Citation ends].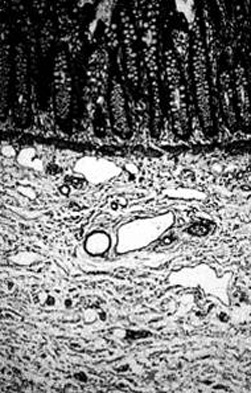
Result
absence of ganglion cells and presence of hypertrophic nerves (>40 micrometers in an infant <6 months); absent calretinin immunoreactivity, presence of acetylcholine esterase immunoreactivity, presence of choline transporter immunoreactivity
anorectal manometry
Test
Normally when the rectum is distended, the internal sphincter relaxes. This recto-anal inhibitory reflex (RAIR) is absent in patients with Hirschsprung disease and anal achalasia.[55]
An absent RAIR on manometry should be followed by a rectal biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of Hirschsprung disease.
Result
absent recto-anal inhibitor reflex (RAIR)
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer