Tests
1st tests to order
ultrasound
Test
If the patient is clinically stable and perforation is not suspected, ultrasonography should be the initial diagnostic test for intussusception.
Sensitivity 98%; specificity 98%.[24]
The mass resulting from intussusception may be easily identified and the findings of intussusception by ultrasound closely mirror its pathophysiologic process.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ultrasound image showing invagination of a segment of bowel into the adjacent segmentBMJ Case Reports. 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1730; used with permission [Citation ends].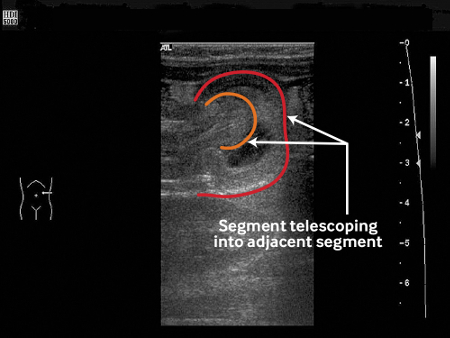
Mesenteric blood flow can also be assessed by ultrasound, the absence of which is predictive of bowel-wall necrosis and irreducibility.[26]
The target sign (variants according to appearance or imaging modality include bull’s eye sign, donut sign, crescent-in-donut sign, and multiple concentric ring sign) is a single hypoechoic ring with a hyperechoic center, indicating that one portion of the bowel has been drawn within the lumen of an adjacent portion.[1][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transverse sonogram of the abdomen showing the donut sign (concentric rings within the lumen of a distended loop of bowel)Adapted from the Student BMJ. 2008;16:76. Copyright 2010 by the BMJ Publishing Group; used with permission [Citation ends].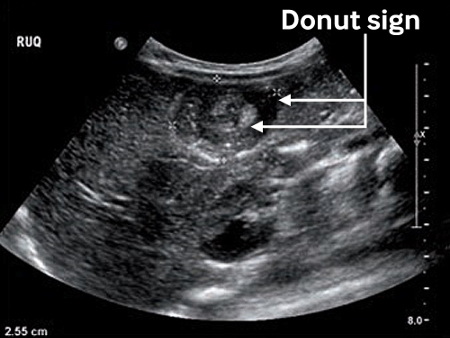
The pseudokidney sign appears as stacked hypoechoic and hyperechoic layers representing edematous bowel wall alternating with the layer of compressed mucosa.[22][27]
Sandwich sign is similar in appearance to pseudokidney sign.
Result
tissue mass; target sign (variants according to appearance or imaging modality include bull’s eye sign, donut sign, crescent-in-donut sign, and multiple concentric ring sign); donut sign; multiple concentric ring sign; crescent-in-donut sign; pseudokidney sign; sandwich sign; abnormal Doppler flow
abdominal plain-film x-ray
Test
Performed as initial investigation if perforation or obstruction is suspected. A test with very low specificity and sensitivity for the definitive diagnosis of intussusception.[1][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transverse sonogram of the abdomen showing the donut sign (concentric rings within the lumen of a distended loop of bowel)Adapted from the Student BMJ. 2008;16:76. Copyright 2010 by the BMJ Publishing Group; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
may appear normal; visible abdominal mass; abnormal wind pattern; air-fluid levels; dilated bowel loops; empty right lower quadrant; target sign (variants according to appearance or imaging modality include bull’s eye sign, donut sign, crescent-in-donut sign, and multiple concentric ring sign); pneumoperitoneum (may be indicative of intestinal perforation as a complication of intussusception)
diagnostic enema
Test
Contraindicated if peritonitis, shock, perforation, or an unstable clinical condition is present.[28]
Should perforation ensue, the use of barium would lead to barium peritonitis; therefore, it would be problematic.
Contrast enema (air or contrast reagent) is the long-standing most specific and sensitive diagnostic test.
The meniscus sign is the appearance of the rounded apex of the intussusceptum protruding into a column of contrast material.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Site of intussusception as revealed by abdominal x-ray, showing the meniscusFrom the collection of Dr David J. Hackam; used with permission [Citation ends].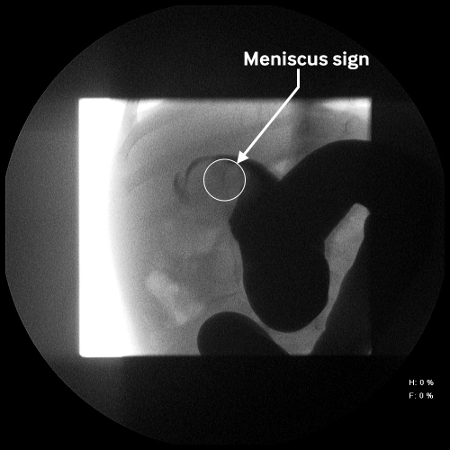
The coiled spring sign is the appearance of the edematous mucosal folds of the returning limb of the intussusceptum outlined by contrast material.
Result
meniscus sign; coiled spring sign
Tests to consider
CT abdomen
Test
Normally not indicated for the evaluation of intussusception.[19]
May be used to assess for the presence and identification of a pathologic lead point and identifying unsuspected intussusception in children with atypical abdominal signs and symptoms.[19][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Transverse sonogram of the abdomen showing the donut sign (concentric rings within the lumen of a distended loop of bowel)Adapted from the Student BMJ. 2008;16:76. Copyright 2010 by the BMJ Publishing Group; used with permission [Citation ends].
CT imaging for emergency evaluation of children with abdominal pain can be inconsistently used, including overused. When ordered appropriately, child-sized CT techniques should be used to avoid unnecessary exposure to ionizing radiation.[20]
Result
target sign (variants according to appearance or imaging modality include bull’s eye sign, donut sign, crescent-in-donut sign, and multiple concentric ring sign); dilated loops of bowel
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer