Primary prevention
Scurvy may be prevented with as little as 6.5 mg vitamin C daily. Recommended daily vitamin C doses attempt to take into account potential health benefits of vitamin C and thus differ according to age, sex, smoking status, pregnancy, and breastfeeding.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Recommended daily quantity of vitamin C to prevent deficiency. The appropriate RDA has been disputed in several large reviews. These guidelines are drawn from the most recent published large consensus of appropriate intake based on data from historical, biologic, epidemiologic, and intervention studiesFrom: Panel on Dietary Antioxidants and Related Compounds, Subcommittees on Upper Reference Levels of Nutrients and Interpretation and Uses of DRIs, Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Chapter 5: vitamin C. In: Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine's Dietary reference intakes for vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, and carotenoids. Washington DC: National Academy Press; 2000: 95-185 [Citation ends].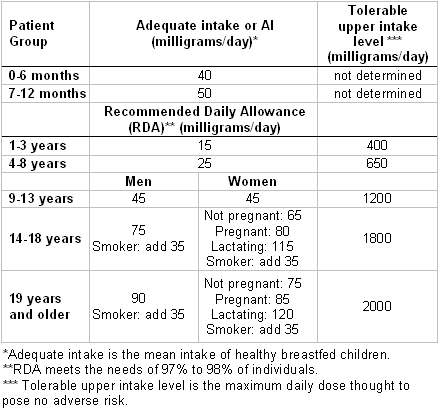
Secondary prevention
Concomitant deficiencies in calcium, vitamin B12, or iron are common; screening is suggested for vitamin B12, folate, iron, and zinc levels.[18]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer