Tests
1st tests to order
serum creatinine
Test
To estimate GFR.[7]
Result
normal or elevated
serum potassium
Test
Hypokalemia or low-normal potassium may suggest RAS due to activation of the renin-angiotensin system.[7]
Result
low or normal
urinalysis and sediment evaluation
Test
Helpful in evaluating for glomerular source of kidney disease. In the absence of coexistent diabetic nephropathy or hypertensive glomerulosclerosis, RAS is not associated with proteinuria or abnormalities in the urinary sediment.[7]
Result
normal in the absence of diabetic nephropathy or hypertensive glomerulosclerosis
aldosterone-to-renin ratio
Test
Aldosterone-to-renin ratio <20 excludes primary aldosteronism as cause of hypertension and hypokalemia or low-normal potassium.[7]
Testing requires discontinuation of antihypertensive medication.
Result
<20
Tests to consider
duplex ultrasound
Test
Shows the renal arteries and measures flow velocity as a means of assessing the severity of stenosis.[1][31]
Compares peak systolic velocity in the renal artery to that in the adjacent aorta.
Sensitive only for lesions with >50% reduction in vessel diameter, and unable to provide further quantification of stenosis.
Ultrasound criteria for significant renal artery stenosis:
renal artery to aorta peak systolic velocity ratio (renal-aortic ratio) >3.5
peak systolic velocity >200 cm/sec with evidence of poststenotic turbulence
the presence of an end-diastolic velocity >150 cm/sec is suggestive of >80% renal artery stenosis.
Result
>50% reduction in vessel diameter
gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography (MRA)
Test
Visualizes the renal arteries and perirenal aorta.[1]
Use of gadolinium is recommended to be restricted in patients with stage 4 and 5 chronic kidney disease, due to nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy.
MRA is not available to patients with pacemakers, some aneurysm clips, and other metal implants.
Blooming artifact can cause overestimation of stenosis if calcification is present.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Magnetic resonance angiography (maximum-intensity projection) in a patient with fibromuscular dysplasia of the renal arteries. Arrow indicates the characteristic irregular contour in the right renal arteryCourtesy of Raul Galvez, MD, MPH and Hale Ersoy, MD; Department of Radiology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School [Citation ends].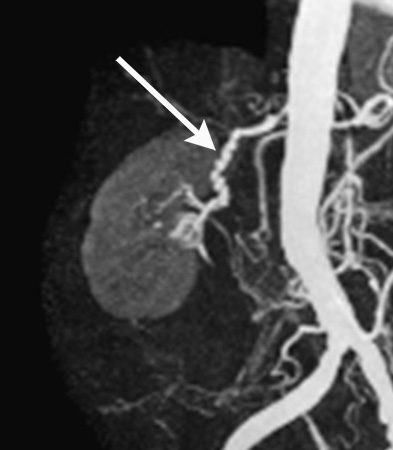 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Magnetic resonance angiography (3-dimensional volume rendered reconstruction) in a patient with significant bilateral atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Arrows indicate proximal bilateral stenosesCourtesy of David J. Sheehan, DO; Radiology Department, University of Massachusetts Medical Center and Medical School [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Magnetic resonance angiography (3-dimensional volume rendered reconstruction) in a patient with significant bilateral atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Arrows indicate proximal bilateral stenosesCourtesy of David J. Sheehan, DO; Radiology Department, University of Massachusetts Medical Center and Medical School [Citation ends].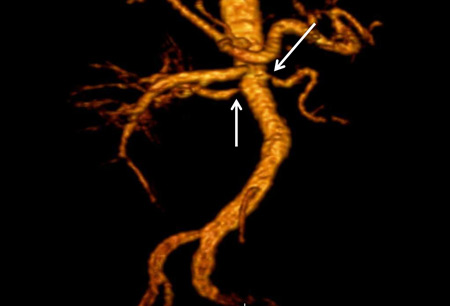
Result
>50% reduction in vessel diameter
CT angiography
Test
Visualizes the renal arteries and perirenal aorta.[1]
Use of intravenous contrast challenging in patients with stage 3, 4, and 5 chronic kidney disease, due to risk of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Blooming artifact can cause overestimation of stenosis if calcification is present.
Result
>50% reduction in vessel diameter
conventional angiography
Test
Angiography is the most sensitive and specific test in the evaluation of RAS.[1][2]
Possibility of performing intervention during the procedure.
Can measure pressure gradients across stenotic lesion to determine significance:
by measurement with a <5F catheter or with a pressure wire, a resting peak-to-peak gradient of ≥10 mmHg, or better a hyperemic peak-to-peak gradient of ≥20mmHg, or a hyperemic mean gradient of ≥7-10 mmHg is considered significant; hyperemia can be induced with either dopamine or papaverine intra-arterially[32][33]
a trans-stenotic-to-aortic pressure ratio of <0.9, as measured by a pressure wire across the stenotic lesion is considered significant, either at rest or with provocation with vasodilators.[34]
Angiography is an invasive procedure associated with known complications, including hematoma, pseudoaneurysm, renal artery dissection, atheroembolism, and acute kidney injury from intravenous contrast exposure.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Digital subtraction angiography in a patient with significant atherosclerotic left renal artery stenosis. Panel A, prior to stent placement. Panel B, after successful stent deployment. Arrows indicate the site of stenosis and stent placement in their respective panelsCourtesy of Alvaro Alonso, MD and Scott J. Gilbert, MD [Citation ends].
Result
>50% reduction in vessel diameter
carbon dioxide (CO2) angiography
Test
Alternative imaging modalities that experts might consider in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) include invasive angiography with carbon dioxide (CO2).[24][25][26]
CO2 angiography can be performed in specialized centers in patients with advanced CKD.
Result
>50% reduction in vessel diameter
noncontrast magnetic resonance angiography
captopril radionuclide renal scan
Test
Findings diagnostic of RAS include: a) delayed time to maximal radiotracer activity (TMax ≥11 minutes after captopril administration), b) significant asymmetry of peak activity of each kidney, c) marked cortical retention of the radionuclide after captopril administration, and d) marked reduction in calculated GFR of the ipsilateral kidney after ACE inhibition.[2]
To assess differential renal flow and kidney function between the two kidneys.
Useful in unilateral RAS, but limited in bilateral disease.[1][8]
Has a less relevant contemporary role owing to its complexity, poor sensitivity, and the availability of other easier and more accurate tests.[2][4][20] The American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association and the European Society of Cardiology/European Stroke Association/European Society of Vascular Surgery do not recommend captopril renal scan for diagnosing RAS.[16][17]
Result
delayed time to maximal radiotracer activity; significant asymmetry of peak activity of each kidney; marked cortical retention; marked reduction in calculated glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer