Wrist fractures
- Overview
- Theory
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Follow up
- Resources
Treatment algorithm
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups: see disclaimer
Look out for this icon: for treatment options that are affected, or added, as a result of your patient's comorbidities.
closed
immobilization
Initial treatment of a closed fracture is immobilization.
Noncircumferential splints are often used acutely in the emergency department due to the risk of swelling. Typically, a short arm cast may be used for 3-4 weeks.
All fractures should have adequate follow-up care to ensure proper wrist function.
reduction
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Restoration of anatomy is essential in an effort to maximize functional outcome.
In the initial stages this may be achieved by a manipulative reduction, and thereafter formal treatment is planned.
For unstable fractures and those requiring fixation, immediate consultation with an orthopedic surgeon should be obtained (or with a specialist hand surgeon if available).
open
debridement and stabilization
Open fractures require urgent treatment with saline irrigation and debridement of the fracture and open wound, and removal of all devitalized tissue as well as foreign debris, prior to fixation.[53]Rupp M, Popp D, Alt V. Prevention of infection in open fractures: where are the pendulums now? Injury. 2020 May;51 Suppl 2:S57-63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31679836?tool=bestpractice.com
If any delay in definitive treatment is anticipated, the fracture may be provisionally stabilized via a splint or an external fixator.[16]British Orthopaedic Association and The British Society for Surgery of the Hand. Best practice for management of distal radius fracture. 2018 [internet publication]. https://www.bssh.ac.uk/professionals/management_of_distal_radial_fractures.aspx
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) recommends that patients with open fractures should be brought to the operating room for debridement and irrigation as soon as reasonable, and ideally within 24 hours post injury.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf
Preoperative antibiotics are recommended to prevent surgical site infections in operative treatment of open fractures.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf In patients with major extremity trauma undergoing surgery, the AAOS strongly recommends that antibiotic prophylaxis with systemic cefazolin or clindamycin be administered, except for Type III (an open segmental fracture, or an open fracture with extensive soft tissue damage, or a traumatic amputation) and possibly Type II (laceration greater than 1 cm long without extensive soft tissue damage, flaps, or avulsions), for which additional gram-negative coverage (e.g., piperacillin/tazobactam) is preferred.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf However, local sensitivities and protocols should be followed for antibiotic selection. In patients with major extremity trauma undergoing surgery, local antibiotic prophylactic strategies, such as vancomycin powder, tobramycin-impregnated beads, or gentamicin-covered nails, may be beneficial, when available.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf
One study suggests that open fractures should be debrided within 6 hours of injury.[56]Prodromidis AD, Charalambous CP. The 6-hour rule for surgical debridement of open tibial fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of infection and nonunion Rates. J Orthop Trauma. 2016 Jul;30(7):397-402. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26978135?tool=bestpractice.com Another prospective study concludes that time to irrigation and debridement does not affect the development of local infections, provided it is performed within 24 hours of arrival to the emergency department.[57]Srour M, Inaba K, Okoye O, et al. Prospective evaluation of treatment of open fractures: effect of time to irrigation and debridement. JAMA Surg. 2015 Apr;150(4):332-6. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamasurgery/fullarticle/2108746 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25692391?tool=bestpractice.com One systematic review reports that early debridement of open fractures by an experienced team within 24 hours is adequate.[53]Rupp M, Popp D, Alt V. Prevention of infection in open fractures: where are the pendulums now? Injury. 2020 May;51 Suppl 2:S57-63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31679836?tool=bestpractice.com
Should contamination be a concern, it is prudent to perform irrigation and debridement, and to provisionally stabilize the fracture via an external fixator.
ongoing antibiotic therapy
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Following preoperative antibiotics and initial debridement and stabilization, ongoing antibiotic therapy should be administered according to the type of open injury and severity of contamination at the time of diagnosis.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [53]Rupp M, Popp D, Alt V. Prevention of infection in open fractures: where are the pendulums now? Injury. 2020 May;51 Suppl 2:S57-63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31679836?tool=bestpractice.com [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf Local sensitivities and protocols should be followed for antibiotic selection.
Early delivery of antibiotics is suggested to lower the risk of deep infection in the setting of open fracture in major extremity trauma.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf
tetanus prophylaxis
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
May need to be considered, depending on the patient's tetanus vaccination history.[73]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical guidance for wound management to prevent tetanus. Aug 2024 [internet publication]. https://www.cdc.gov/tetanus/hcp/clinical-guidance
isolated fracture of distal radius
immobilization: short arm cast or splint
Short arm casts made of plaster of Paris or fiberglass are applied distal to the elbow and, in nondisplaced fractures, maintain the position of the wrist at neutral.[16]British Orthopaedic Association and The British Society for Surgery of the Hand. Best practice for management of distal radius fracture. 2018 [internet publication]. https://www.bssh.ac.uk/professionals/management_of_distal_radial_fractures.aspx
The thumb is free and the cast terminates at the level of the distal palmar flexion crease. This allows free motion of the metacarpophalangeal joints, thus maintaining digital mobility as the fracture heals, and minimizes post-traumatic stiffness.
Casts should be well fitting, and well padded to avoid any pressure effects, and the patient must be alerted to the possibility of needing a cast change. Cast changes may be necessary if the cast gets loose as the initial post-traumatic swelling reduces. Casts in this situation are maintained for a period of 3-4 weeks.[16]British Orthopaedic Association and The British Society for Surgery of the Hand. Best practice for management of distal radius fracture. 2018 [internet publication]. https://www.bssh.ac.uk/professionals/management_of_distal_radial_fractures.aspx [58]Bentohami A, van Delft EAK, Vermeulen J, et al. Non- or minimally displaced distal radial fractures in adult patients: three weeks versus five weeks of cast immobilization - a randomized controlled trial. J Wrist Surg. 2019 Feb;8(1):43-8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6358449 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30723601?tool=bestpractice.com [59]Delft EAKV, Gelder TGV, Vries R, et al. Duration of cast immobilization in distal radial fractures: a systematic review. J Wrist Surg. 2019 Oct;8(5):430-8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31579555?tool=bestpractice.com
In patients unable to tolerate casts or unwilling to wear a cast, or in patients who have an incomplete crack fracture of the distal radius, a forearm-based splint holding the wrist at neutral may be used.[60]Roth KM, Blazar PE, Earp BE, et al. Incidence of displacement after nondisplaced distal radial fractures in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Aug 7;95(15):1398-402. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23925744?tool=bestpractice.com
Splints are custom-made by occupational therapists, and can be custom-molded to the patient's anatomy. As swelling reduces, modification to fit the changing dimensions of the patient's limb may be necessary.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cast treatment of a distal radius fractureFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Whether the patient is being treated in a cast or a splint or is awaiting surgical fixation, it is critical to have them start rehabilitation of the hand at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (e.g., local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (e.g., ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid-sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
closed reduction and immobilization
Manipulative reduction in the acute setting is most often performed using a hematoma block (instillation of a local anesthetic within the fracture hematoma) and distraction of the fracture site aided by finger traps.[62]Myderrizi N, Mema B. The hematoma block an effective alternative for fracture reduction in distal radius fractures. Med Arh. 2011;65(4):239-42. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21950232?tool=bestpractice.com [63]Tseng PT, Leu TH, Chen YW, et al. Hematoma block or procedural sedation and analgesia, which is the most effective method of anesthesia in reduction of displaced distal radius fracture? J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 Mar 27;13(1):62. https://josr-online.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13018-018-0772-7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29580286?tool=bestpractice.com [64]Søsborg-Würtz H, Corap Gellert S, Ladeby Erichsen J, et al. Closed reduction of distal radius fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2018 Apr;3(4):114-20. https://eor.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/eor/3/4/2058-5241.3.170063.xml http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29780618?tool=bestpractice.com Diffusion of the anesthetic volarly around the median and ulnar nerves may occur, and patients should be reassured that digital numbness is to be expected. Conscious sedation may be used for reductions in the emergency department. Different fracture geometries require different reduction techniques; for example, a dorsally angulated fracture can be reduced by applying dorsal pressure to the distal fragment to "milk" it back into position.
Adequate reduction is verified by palpation for step-offs along the dorsal and radial surfaces. The fracture is then held in its reduced position in a well-molded splint. Postreduction radiographs should be obtained with the splint in place.
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Whether the patient is being treated in a cast or a splint or is awaiting surgical fixation, it is critical to have them start rehabilitation of the hand at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols.
carpal tunnel release
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Following manual or surgical fracture reduction, if median nerve dysfunction is found to worsen or persists, a carpal tunnel release procedure should be performed urgently.[48]Niver GE, Ilyas AM. Carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fracture. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012 Oct;43(4):521-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23026468?tool=bestpractice.com [49]Brüske J, Niedźwiedź Z, Bednarski M, et al. Acute carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fractures - long term results of surgical treatment with decompression and external fixator application [in Polish]. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2002;67(1):47-53. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12087674?tool=bestpractice.com [50]Mack GR, McPherson SA, Lutz RB. Acute median neuropathy after wrist trauma. The role of emergent carpal tunnel release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994 Mar;(300):141-6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8131326?tool=bestpractice.com
surgical reduction and fixation
The decision about whether a surgical intervention is warranted should be discussed between the patient and surgeon. Strong evidence suggests no significant difference in radiographic or patient-reported outcomes between fixation techniques for complete articular or unstable distal radius fractures, although volar locking plates lead to earlier recovery of function in the short term (3-6 months), and outcomes equalize within 1 year of injury.[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf [65]Selles CA, Mulders MAM, Winkelhagen J, et al; VIPAR Collaborators. Volar plate fixation versus cast immobilization in acceptably reduced intra-articular distal radial fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021 Nov 3;103(21):1963-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34314402?tool=bestpractice.com One randomized controlled trial involving 90 patients (46 in the nonoperative group and 44 in the operative group) found that 28% of nonoperatively managed patients had a subsequent surgical procedure.[65]Selles CA, Mulders MAM, Winkelhagen J, et al; VIPAR Collaborators. Volar plate fixation versus cast immobilization in acceptably reduced intra-articular distal radial fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021 Nov 3;103(21):1963-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34314402?tool=bestpractice.com Another randomized controlled trial reported that in patients with an acceptably reduced extra-articular distal radial fracture treated with open reduction and volar plate fixation, 42% of nonoperatively managed patients had a subsequent surgical procedure.[66]Mulders MAM, Walenkamp MMJ, van Dieren S, et al. Volar plate fixation versus plaster immobilization in acceptably reduced extra-articular distal radial fractures: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 May 1;101(9):787-96. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31045666?tool=bestpractice.com In older patients with low functional demands, the presence of deformity does not preclude good functional outcomes.[69]Gehrmann SV, Windolf J, Kaufmann RA, et al. Distal radius fracture management in elderly patients: a literature review. J Hand Surg Am. 2008 Mar;33(3):421-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18343302?tool=bestpractice.com Moderate evidence supports that for non-geriatric patients (most commonly defined in studies as under 65 years of age), operative treatment for fractures with post-reduction radial shortening >3 mm, dorsal tilt >10°, or intraarticular displacement or step off >2 mm leads to improved radiographic and patient-reported outcomes.[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf Strong evidence suggests that operative treatment for geriatric patients (most commonly defined in studies as 65 years of age and older) does not lead to improved long-term patient-reported outcomes compared with nonoperative treatment.[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
Following volar plate fixation, patients can be safely treated with a pressure bandage.[67]Poiset S, Abboudi J, Gallant G, et al. Splinting after distal radius fracture fixation: a prospective cohort analysis of postoperative plaster splint versus soft dressing. J Wrist Surg. 2019 Dec;8(6):452-5. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31815058?tool=bestpractice.com Some surgeons prefer a cast for pain management. However, this period should not be longer than 3 weeks.[68]Watson N, Haines T, Tran P, et al. A comparison of the effect of one, three, or six weeks of immobilization on function and pain after open reduction and internal fixation of distal radial fractures in adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018 Jul 5;100(13):1118-25. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29975268?tool=bestpractice.com
Monitoring for median nerve function should be maintained throughout the postoperative period. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Plate fixation after open reduction with a volarly placed plate and screwsFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].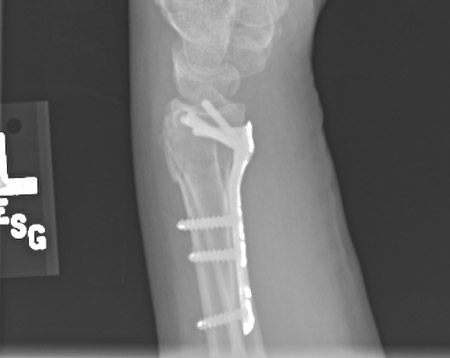 There is no apparent treatment benefit for the use of wrist arthroscopy at the time of distal radius fracture fixation.[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
[70]Yamazaki H, Uchiyama S, Komatsu M, et al. Arthroscopic assistance does not improve the functional or radiographic outcome of unstable intra-articular distal radial fractures treated with a volar locking plate: a randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2015 Jul;97-B(7):957-62.
https://online.boneandjoint.org.uk/doi/full/10.1302/0301-620X.97B7.35354
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26130352?tool=bestpractice.com
[71]Selles CA, Reerds STH, Roukema G, et al. Relationship between plate removal and Soong grading following surgery for fractured distal radius. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2018 Feb;43(2):137-41.
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1753193417726636
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28825371?tool=bestpractice.com
There is no apparent treatment benefit for the use of wrist arthroscopy at the time of distal radius fracture fixation.[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication].
https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
[70]Yamazaki H, Uchiyama S, Komatsu M, et al. Arthroscopic assistance does not improve the functional or radiographic outcome of unstable intra-articular distal radial fractures treated with a volar locking plate: a randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2015 Jul;97-B(7):957-62.
https://online.boneandjoint.org.uk/doi/full/10.1302/0301-620X.97B7.35354
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26130352?tool=bestpractice.com
[71]Selles CA, Reerds STH, Roukema G, et al. Relationship between plate removal and Soong grading following surgery for fractured distal radius. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2018 Feb;43(2):137-41.
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1753193417726636
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28825371?tool=bestpractice.com
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (e.g., local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (e.g., ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid-sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
carpal tunnel release
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Following manual or surgical fracture reduction, if median nerve dysfunction is found to worsen or persists, a carpal tunnel release procedure should be performed urgently.[48]Niver GE, Ilyas AM. Carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fracture. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012 Oct;43(4):521-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23026468?tool=bestpractice.com [49]Brüske J, Niedźwiedź Z, Bednarski M, et al. Acute carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fractures - long term results of surgical treatment with decompression and external fixator application [in Polish]. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2002;67(1):47-53. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12087674?tool=bestpractice.com [50]Mack GR, McPherson SA, Lutz RB. Acute median neuropathy after wrist trauma. The role of emergent carpal tunnel release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994 Mar;(300):141-6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8131326?tool=bestpractice.com
surgical reduction and fixation
In most situations, open fractures constitute a surgical emergency and operative treatment at the earliest possible opportunity is preferred.
Fractures are often provisionally reduced in the emergency department in anticipation of delay in getting the patient into the operating room. This helps to reduce deformity and soft-tissue swelling, and may relieve any symptoms of nerve compression.
Preoperative antibiotics are recommended to prevent surgical site infections in operative treatment of open fractures.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf In patients with major extremity trauma undergoing surgery, the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) strongly recommends that antibiotic prophylaxis with systemic cefazolin or clindamycin be administered, except for Type III (an open segmental fracture, or an open fracture with extensive soft tissue damage, or a traumatic amputation) and possibly Type II (laceration greater than 1 cm long without extensive soft tissue damage, flaps, or avulsions), for which additional gram-negative coverage (e.g., piperacillin/tazobactam) is preferred.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf However, local sensitivities and protocols should be followed for antibiotic selection. In patients with major extremity trauma undergoing surgery, local antibiotic prophylactic strategies, such as vancomycin powder, tobramycin-impregnated beads, or gentamicin-covered nails, may be beneficial, when available.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf
Thorough saline irrigation and debridement of the fracture and the open wound is required prior to fixation.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [53]Rupp M, Popp D, Alt V. Prevention of infection in open fractures: where are the pendulums now? Injury. 2020 May;51 Suppl 2:S57-63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31679836?tool=bestpractice.com [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf
One study suggests that open fractures should be debrided within 6 hours of injury.[56]Prodromidis AD, Charalambous CP. The 6-hour rule for surgical debridement of open tibial fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of infection and nonunion Rates. J Orthop Trauma. 2016 Jul;30(7):397-402. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26978135?tool=bestpractice.com Another prospective study concludes that time to irrigation and debridement does not affect the development of local infections, provided it is performed within 24 hours of arrival to the emergency department.[57]Srour M, Inaba K, Okoye O, et al. Prospective evaluation of treatment of open fractures: effect of time to irrigation and debridement. JAMA Surg. 2015 Apr;150(4):332-6. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamasurgery/fullarticle/2108746 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25692391?tool=bestpractice.com One systematic review reports that early debridement of open fractures by an experienced team within 24 hours is adequate.[53]Rupp M, Popp D, Alt V. Prevention of infection in open fractures: where are the pendulums now? Injury. 2020 May;51 Suppl 2:S57-63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31679836?tool=bestpractice.com
Should contamination be a concern, it is prudent to perform irrigation and debridement, and to provisionally stabilize the fracture via an external fixator.
After the infection is controlled, a formal open reduction and internal fixation may be performed at a later stage.
Monitoring for median nerve function should be maintained throughout the postoperative period.
ongoing antibiotic therapy
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Following preoperative antibiotics and surgery, ongoing antibiotic therapy should be administered according to the type of open injury and severity of contamination at the time of diagnosis.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [53]Rupp M, Popp D, Alt V. Prevention of infection in open fractures: where are the pendulums now? Injury. 2020 May;51 Suppl 2:S57-63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31679836?tool=bestpractice.com [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf Local sensitivities and protocols should be followed for antibiotic selection.
Early delivery of antibiotics is suggested to lower the risk of deep infection in the setting of open fracture in major extremity trauma.[44]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: appropriate use criteria. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumaauc.pdf [54]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/dod/ssitrauma/ssitraumacpg.pdf
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Whether the patient is being treated in a cast or a splint or is awaiting surgical fixation, it is critical to have them start rehabilitation of the hand at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
As the fracture unites, an occupational therapy program (graduated range of motion program) should be initiated.
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (e.g., local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (e.g., ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid-sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
carpal tunnel release
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Following manual or surgical fracture reduction, if median nerve dysfunction is found to worsen or persists, a carpal tunnel release procedure should be performed urgently.[48]Niver GE, Ilyas AM. Carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fracture. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012 Oct;43(4):521-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23026468?tool=bestpractice.com [49]Brüske J, Niedźwiedź Z, Bednarski M, et al. Acute carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fractures - long term results of surgical treatment with decompression and external fixator application [in Polish]. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2002;67(1):47-53. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12087674?tool=bestpractice.com [50]Mack GR, McPherson SA, Lutz RB. Acute median neuropathy after wrist trauma. The role of emergent carpal tunnel release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994 Mar;(300):141-6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8131326?tool=bestpractice.com Most open fractures are high-energy injuries and there is a low threshold to perform concomitant carpal tunnel release.[48]Niver GE, Ilyas AM. Carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fracture. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012 Oct;43(4):521-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23026468?tool=bestpractice.com [49]Brüske J, Niedźwiedź Z, Bednarski M, et al. Acute carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fractures - long term results of surgical treatment with decompression and external fixator application [in Polish]. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2002;67(1):47-53. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12087674?tool=bestpractice.com [50]Mack GR, McPherson SA, Lutz RB. Acute median neuropathy after wrist trauma. The role of emergent carpal tunnel release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994 Mar;(300):141-6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8131326?tool=bestpractice.com
forearm fasciotomy
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Most open fractures of the distal radius are high-energy injuries and may be accompanied by significant soft-tissue trauma.
In these patients it is mandatory to evaluate for forearm compartment syndrome. If there are obvious signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome, a clinical diagnosis is established and surgical fasciotomy is performed.[74]Duckworth AD, Mitchell SE, Molyneux SG, et al. Acute compartment syndrome of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 May 16;94(10):e63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22617929?tool=bestpractice.com
This is a surgical emergency and emergent fasciotomy, combined with open reduction and fixation of the fracture as well as a carpal tunnel release, is critical to minimize adverse long-term effects. See Compartment syndrome of extremities.
tetanus prophylaxis
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
May need to be considered, depending on the patient's tetanus vaccination history.[73]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical guidance for wound management to prevent tetanus. Aug 2024 [internet publication]. https://www.cdc.gov/tetanus/hcp/clinical-guidance
isolated scaphoid fracture
immobilization: forearm-based cast
Isolated nondisplaced scaphoid fractures can be treated nonoperatively in most patients, with high union rates and good clinical outcomes.[75]Clementson M, Jørgsholm P, Besjakov J, et al. Conservative treatment versus arthroscopic-assisted screw fixation of scaphoid waist fractures - a randomized trial with minimum 4-year follow-up. J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Jul;40(7):1341-8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25913660?tool=bestpractice.com [76]Fowler JR, Hughes TB. Scaphoid fractures. Clin Sports Med. 2015 Jan;34(1):37-50. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25455395?tool=bestpractice.com
Patients are placed in a forearm-based cast without incorporating the thumb. There is no universal consensus on the duration of casting, but usually the cast is maintained for a total of 8-12 weeks or until the fracture is healed.[77]Buijze GA, Goslings JC, Rhemrev SJ, et al; CAST Trial Collaboration. Cast immobilization with and without immobilization of the thumb for nondisplaced and minimally displaced scaphoid waist fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Hand Surg Am. 2014 Apr;39(4):621-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24582846?tool=bestpractice.com
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Whether the patient is being treated in a cast or a splint or is awaiting surgical fixation, it is critical to have them start rehabilitation of the hand at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
As the fracture unites, an occupational therapy program (graduated range of motion program) should be initiated.
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (e.g., local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (e.g., ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid-sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
surgical reduction and fixation
Patients with proximal pole fractures, those with fracture displacement, or those who are unwilling to accept the protracted duration of casting are considered candidates for percutaneous screw fixation or for open reduction and internal fixation of the scaphoid.[78]Shen L, Tang J, Luo C, et al. Comparison of operative and non-operative treatment of acute undisplaced or minimally-displaced scaphoid fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2015 May 5;10(5):e0125247. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0125247 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25942316?tool=bestpractice.com [79]Alnaeem H, Aldekhayel S, Kanevsky J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the differences between nonsurgical management and percutaneous fixation of minimally and nondisplaced scaphoid fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2016 Dec;41(12):1135-44;e1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27707564?tool=bestpractice.com
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Whether the patient is being treated in a cast or a splint or is awaiting surgical fixation, it is critical to have them start rehabilitation of the hand at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
As the fracture unites, an occupational therapy program (graduated range of motion program) should be initiated.
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (e.g., local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (e.g., ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid-sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
concomitant distal radius and scaphoid or ulnar styloid fractures
immobilization: short arm cast or splint
Stable nondisplaced fractures of the scaphoid and radius can in most instances be treated by nonoperative means.[75]Clementson M, Jørgsholm P, Besjakov J, et al. Conservative treatment versus arthroscopic-assisted screw fixation of scaphoid waist fractures - a randomized trial with minimum 4-year follow-up. J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Jul;40(7):1341-8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25913660?tool=bestpractice.com [76]Fowler JR, Hughes TB. Scaphoid fractures. Clin Sports Med. 2015 Jan;34(1):37-50. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25455395?tool=bestpractice.com
Patients are placed in a forearm-based cast without incorporating the thumb. There is no universal consensus on the duration of casting, but usually the cast is maintained for a total of 8-12 weeks or until the fracture is healed.[77]Buijze GA, Goslings JC, Rhemrev SJ, et al; CAST Trial Collaboration. Cast immobilization with and without immobilization of the thumb for nondisplaced and minimally displaced scaphoid waist fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Hand Surg Am. 2014 Apr;39(4):621-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24582846?tool=bestpractice.com
Ulnar styloid fractures often occur concurrently with distal radius fractures. They can usually be managed nonoperatively.[52]van Rossenberg LX, Beeres FJP, van Heijl M, et al. Operative versus non-operative treatment of ulnar styloid process base fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024 Sep 13 [Epub ahead of print]. https://www.doi.org/10.1007/s00068-024-02660-2 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39269646?tool=bestpractice.com
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Whether the patient is being treated in a cast or a splint or is awaiting surgical fixation, it is critical to have them start rehabilitation of the hand at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
As the fracture unites, an occupational therapy program (graduated range of motion program) should be initiated.
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (e.g., local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (e.g., ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid-sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
surgical reduction and fixation
Patients with proximal pole fractures, those with fracture displacement, or those who are unwilling to accept the protracted duration of casting are considered candidates for percutaneous screw fixation or for open reduction and internal fixation of the scaphoid.[78]Shen L, Tang J, Luo C, et al. Comparison of operative and non-operative treatment of acute undisplaced or minimally-displaced scaphoid fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2015 May 5;10(5):e0125247. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0125247 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25942316?tool=bestpractice.com [79]Alnaeem H, Aldekhayel S, Kanevsky J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the differences between nonsurgical management and percutaneous fixation of minimally and nondisplaced scaphoid fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2016 Dec;41(12):1135-44;e1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27707564?tool=bestpractice.com
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
Whether the patient is being treated in a cast or a splint or is awaiting surgical fixation, it is critical to have them start rehabilitation of the hand at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
As the fracture unites, an occupational therapy program (graduated range of motion program) should be initiated.
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
surgical reduction and fixation
It is essential to fix the scaphoid at the time of the radius fracture fixation.
The primary surgical option is open reduction and fixation.[78]Shen L, Tang J, Luo C, et al. Comparison of operative and non-operative treatment of acute undisplaced or minimally-displaced scaphoid fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2015 May 5;10(5):e0125247. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0125247 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25942316?tool=bestpractice.com However, displaced fractures may also be treated with plate fixation.[66]Mulders MAM, Walenkamp MMJ, van Dieren S, et al. Volar plate fixation versus plaster immobilization in acceptably reduced extra-articular distal radial fractures: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019 May 1;101(9):787-96. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31045666?tool=bestpractice.com [85]Gutierrez Olivera N, Ruchelli L, Iglesias S, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal radius fractures with metaphyseal extension: a series of 13 cases. Chir Main. 2015 Oct;34(5):227-33. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26359856?tool=bestpractice.com [86]Figl M, Weninger P, Liska M, et al. Volar fixed-angle plate osteosynthesis of unstable distal radius fractures: 12 months results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009 May;129(5):661-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19225792?tool=bestpractice.com
Monitoring for median nerve function should be maintained throughout the postoperative period. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Plate fixation after open reduction with a volarly placed plate and screwsFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].
rehabilitation + pain management
Treatment recommended for ALL patients in selected patient group
It is important for the patient to begin rehabilitation at the earliest opportunity.
The affected limb needs to be elevated. Active range of motion of the fingers and shoulder should begin during the first few days after injury. This is to help control edema in the hand, and to prevent stiffness in the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, and frozen shoulder.[46]Miller LK, Jerosch-Herold C, Shepstone L. Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017 Oct-Dec;30(4):432-46. https://www.jhandtherapy.org/article/S0894-1130(16)30228-9/fulltext http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28807598?tool=bestpractice.com [47]Itoi E, Arce G, Bain GI, et al. Shoulder stiffness: current concepts and concerns. Arthroscopy. 2016 Jul;32(7):1402-14. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27180923?tool=bestpractice.com
As the fracture unites, an occupational therapy program (graduated range of motion program) should be initiated.
Appropriate pain management is important, especially during rehabilitation; however, specific treatment varies widely depending on the patient, clinical presentation, method of treatment, and local treatment protocols. Opioid alternatives, both pharmacologic (local anesthetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, acetaminophen) and nonpharmacologic (ice, elevation, compression, cognitive therapies) should be considered alongside opioid sparing protocols when possible given the risks of opioid analgesics (adverse events, misuse, opioid use disorder, and diversion for nonmedical use).[35]American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication]. https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/distal-radius/drfcpg.pdf
carpal tunnel release
Treatment recommended for SOME patients in selected patient group
Following surgical fracture reduction, if median nerve dysfunction is found to worsen or persists, a carpal tunnel release procedure should be performed urgently.[48]Niver GE, Ilyas AM. Carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fracture. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012 Oct;43(4):521-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23026468?tool=bestpractice.com [49]Brüske J, Niedźwiedź Z, Bednarski M, et al. Acute carpal tunnel syndrome after distal radius fractures - long term results of surgical treatment with decompression and external fixator application [in Polish]. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2002;67(1):47-53. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12087674?tool=bestpractice.com [50]Mack GR, McPherson SA, Lutz RB. Acute median neuropathy after wrist trauma. The role of emergent carpal tunnel release. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994 Mar;(300):141-6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8131326?tool=bestpractice.com
confirmed wrist fracture
osteoporosis evaluation
Ordering a bone mineral density exam in patients over 50 years of age can improve osteoporosis evaluation and treatment rates following fragility fractures of the distal part of the radius.[16]British Orthopaedic Association and The British Society for Surgery of the Hand. Best practice for management of distal radius fracture. 2018 [internet publication]. https://www.bssh.ac.uk/professionals/management_of_distal_radial_fractures.aspx [51]Rozental TD, Makhni EC, Day CS, et al. Improving evaluation and treatment for osteoporosis following distal radial fractures: a prospective randomized intervention. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 May;90(5):953-61. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18451385?tool=bestpractice.com

Choose a patient group to see our recommendations
Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug formularies, or locations. Treatment recommendations are specific to patient groups. See disclaimer
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
