Tests
1st tests to order
plain radiographs of the wrist
Test
An initial radiographic examination is required to make a conclusive diagnosis of a distal radius fracture.[31] Typically posteroanterior, lateral, and carpal views should be obtained.[31]
Fractures may be minimal cracks, extra-articular fractures, or intra-articular fractures.
Radiographs also suggest the degree of osteopenia and may offer some information about the degree of articular involvement or comminution.
Although uncommon, combined injuries of the distal radius and scaphoid are seen, and radiographs should also be examined for a scaphoid fracture.[2][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Type A extra-articular fracture of the distal radius: lateral viewFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Type B (simple) intra-articular fracture of the distal radius: lateral viewFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Type B (simple) intra-articular fracture of the distal radius: lateral viewFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].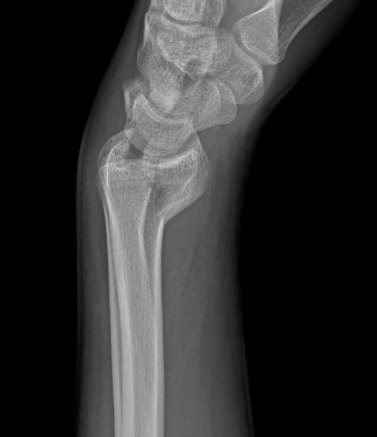 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Type C (complex) intra-articular fracture of the distal radius: lateral viewFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Type C (complex) intra-articular fracture of the distal radius: lateral viewFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].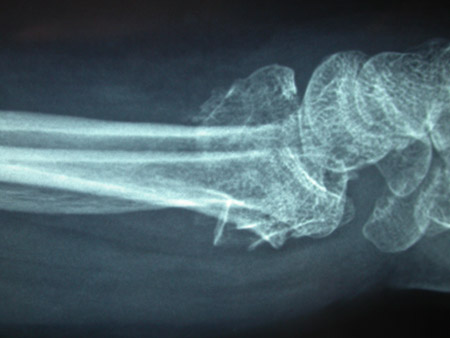
Result
fracture of the distal radius, distal ulna, or scaphoid
Tests to consider
CT wrist
Test
Do not order CT scans for children until physical exam has been completed and plain radiographs have been obtained. CT scans deliver a significant dose of radiation to a child, so their utility needs to be confirmed prior to ordering.[36] However, in patients where surgical fixation is considered, a CT scan of the distal radius is beneficial for the analysis of extra- and intra-articular fracture geometry and preoperative planning.[31]
A CT scan may also reveal any occult fractures around the carpus.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scans of the wrist provide excellent detail to assess fracture geometry and articular involvement, as well as degree of comminutionFrom the collection of Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal [Citation ends].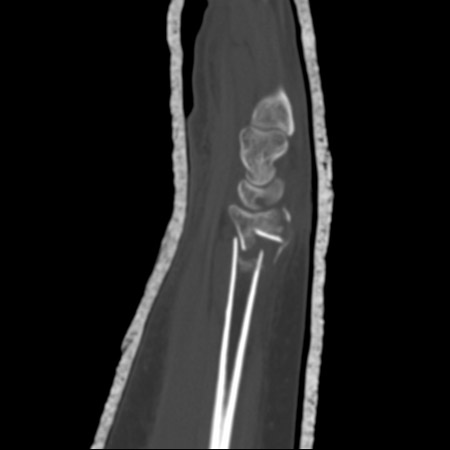
Result
fracture of the distal radius or ulna, with clarification of extent of comminution and/or articular involvement
MRI (without contrast) wrist
Test
Do not order MRI scans for children until physical exam has been completed and plain radiographs have been obtained. MRI scans may not be correctly interpreted without all of the necessary clinical information and frequently require sedation in a young child.[36] However, scaphoid fractures can be missed on x-ray; consider an MRI (without contrast) as first-line imaging if an occult fracture of the scaphoid is suspected.[37]
May also be used to define associated ligamentous injuries.[38][39]
Result
fracture of the scaphoid; defines associated ligamentous injuries
dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
Test
Order as part of follow-up in patients over 50 years of age with a fracture of the distal radius.[16]
DXA is considered the standard for measurement of bone density; the World Health Organization considers bone mineral density measurements diagnostic for osteoporosis.[40]
T-score between -1 and -2.5 or less indicates osteopenia; T-score -2.5 or less with fragility fracture(s) indicates osteoporosis.[40]
Result
T-score between -1 and -2.5 or less indicates osteopenia; T-score -2.5 or less with fragility fracture(s) indicates osteoporosis
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer